
Scientists Discover “Very Weird” Truth About Starfish Heads, Solving Centuries-Old Mystery
After centuries of mystery, scientists have finally unraveled the puzzle of the location of a starfish’s head.
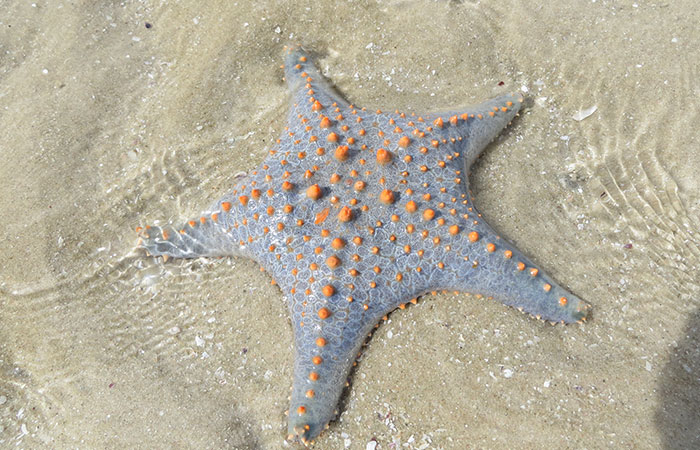
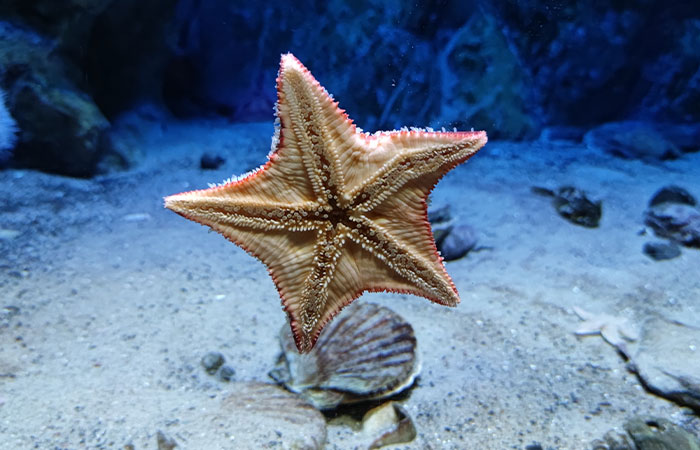
As it happens, starfish, also known as sea stars, don’t possess a single head positioned at the center of their bodies.
Scientists have found that the bodies of starfishes are in fact an extension of their heads, solving a centuries-old mystery
Image credits: Joffre Design/Unsplash
According to a paper published in Nature, these peculiar creatures actually have head-like regions in each of their limbs.
The revelation has been centuries in development, constituting a mystery that, as Laurent Formery, the lead author of the study, informed Insider: “dates back to the very origins of zoology.”
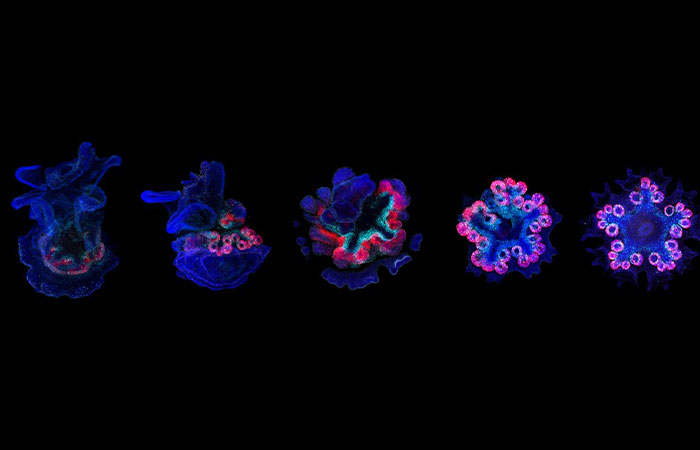
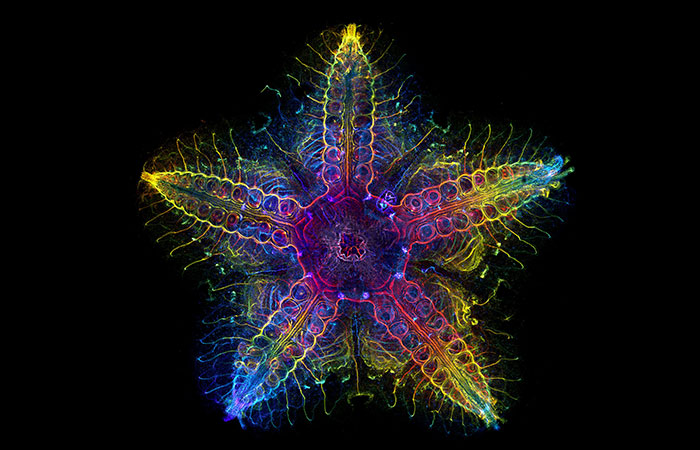
Genetic studies suggest that the fascinating creatures have a head in each limb
Image credits: FormeryLaurent
Laurent, a postdoctoral researcher at Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences, explained that the prolonged nature of solving this mystery stemmed from the distinctiveness of sea stars.
“It’s as if the sea star is completely missing a trunk, and is best described as just a head crawling along the seafloor,” Laurent wrote in a statement.
“It’s not at all what scientists have assumed about these animals,” he added.
Unlike many animals, including insects, reptiles, birds, mammals, and humans, which exhibit bilateral symmetry along a midline, sea stars possess five-fold radial symmetry.
The expert highlighted how the presence of bilateral symmetry in other animals facilitated the identification of the head, trunk, limbs, and similar structures.
In contrast, sea stars’ unique five-fold radial symmetry posed a different challenge in locating corresponding features.
Observing a sea star, Laurent remarked: “There is nothing that looks like your head.
“You just have no idea.”
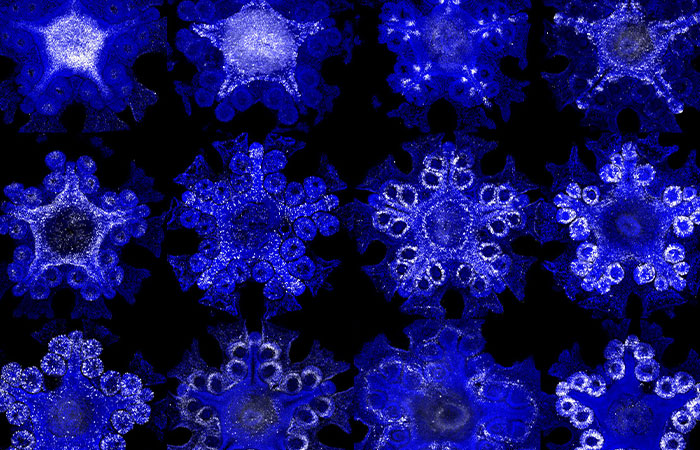
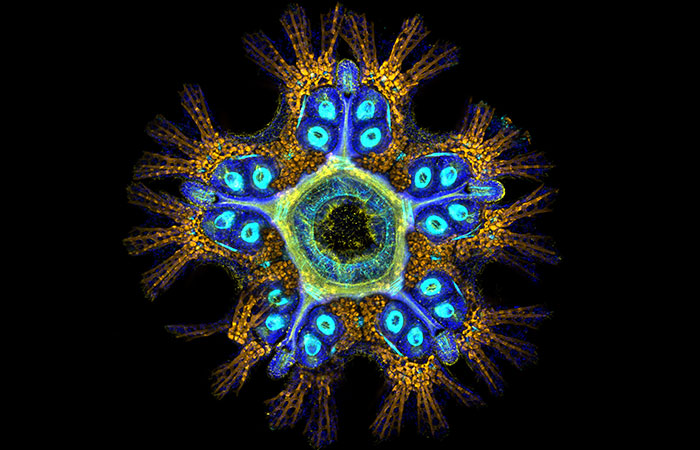
Contrary to their outward appearance, sea stars share more genetic similarities with animals like humans than one might assume
Image credits: FormeryLaurent
Stanford News reported that contrary to their outward appearance, sea stars share more genetic similarities with animals like humans than one might assume.
Animals follow a genetic code that unfolds and triggers various regions during development, determining the placement of limbs, heads, and other features.
Laurent and his colleagues delved into these genetic similarities.
However, as the researcher informed Insider, their exploration was made possible through the assistance of modern technology.
Image credits: FormeryLaurent
Laurent explained: “For a very long time, we just had access to anatomy and morphology.
“And they’re not very helpful when you look at a sea star.
“And recently, we can kind of ignore the morphology and just focus on the molecular aspects of development.”
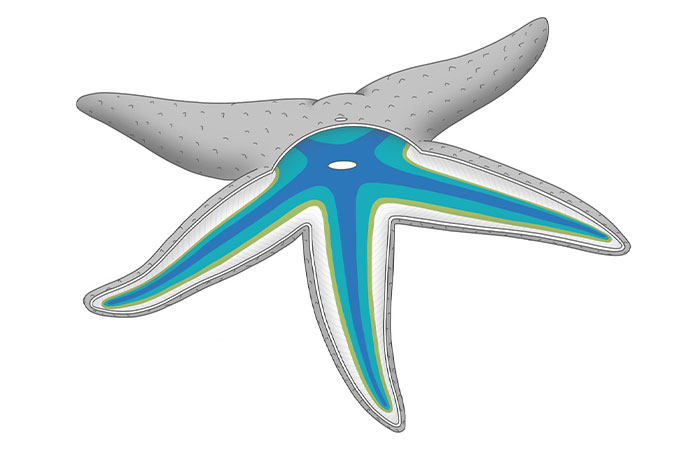
Scientists plan to further examine starfish to ascertain whether their multiple heads might also house multiple brains
Image credits: FormeryLaurent
The scientists scrutinized the distinct genes within individual starfish limbs.
Initially, they anticipated discovering genes resembling a head and others resembling a trunk, akin to most animals.
However, their findings primarily consisted of genes with head-like characteristics.
According to co-author Jeff Thompson, a lecturer at the University of Southampton, the genes commonly linked to the trunk of an animal were notably absent in starfish.
He stated that the entire body plan of a starfish is roughly equivalent to the head in other animal groups.
The revelation was “very weird” and took Laurent by surprise.
“Nobody really had [this] envisioned before we had access to this data,” Laurent admitted.
Moving forward, the scientist expressed his interest in further examining starfish to ascertain whether their multiple heads might also house multiple brains.
He recalled: “When you look at textbooks, they say sea stars have a very simple nervous system, and it’s like they don’t have a brain.”
Image credits: FormeryLaurent
The Stanford researcher explained that he and his colleague discovered that certain genes responsible for a sea star’s nervous system development were the same genes involved in our own developmental process for creating the brain.
As a result, Laurent explained that if starfish possessed genes akin to those involved in human brain development, it posed some intriguing inquiries: “Questions about what is the nervous system of a sea star. And is it a brain? Is it just a brain, basically?”
Belonging to a category known as echinoderms, sea stars are part of a group that also includes sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers
Image credits: Karo K./Unsplash
Belonging to a category known as echinoderms, sea stars are part of a group that also includes sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers.
Animal research predominantly focuses on species sharing similarities with humans; however, delving into groups like echinoderms has the potential to unravel some of the most intricate mysteries surrounding the evolution of life on Earth, CNN reported.
Watch Nature’s informative video on starfish below:
Image credits: nature video
Christopher Lowe, marine and developmental biologist at Stanford University, said: “Most animals don’t have spectacular nervous systems and are out chasing prey — they are modest animals that live in burrows in the ocean.
“People are generally not drawn to these animals, and yet they probably represent how much of life got started.”
Gaining an understanding of the developmental processes in animals like sea stars could also provide insights into the diverse mechanisms through which various species maintain their health.
Daniel Rokhsar, professor of genetics, genomics, evolution, and development at the University of California, Berkeley, and researcher at the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, wrote in a statement: “It’s certainly harder to work in organisms that are less frequently studied.
“But if we take the opportunity to explore unusual animals that are operating in unusual ways, that means we are broadening our perspective of biology, which is eventually going to help us solve both ecological and biomedical problems.”
Science fans were amazed at the recent discovery
thats actually rlly cool! the neons of the starfish are so satisfying to look at :DDD
I can't begin to tell you how many nights I've laid awake worrying about starfish.
thats actually rlly cool! the neons of the starfish are so satisfying to look at :DDD
I can't begin to tell you how many nights I've laid awake worrying about starfish.

 Dark Mode
Dark Mode 

 No fees, cancel anytime
No fees, cancel anytime 



















































78
18