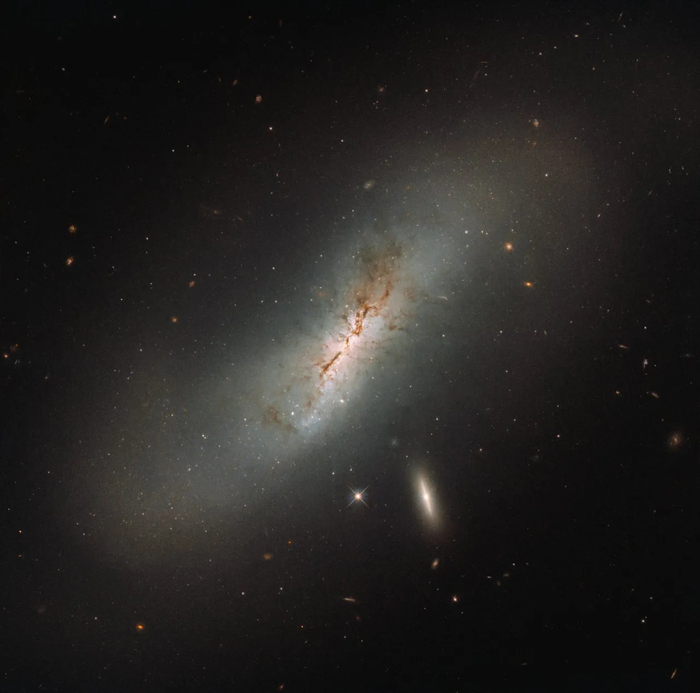
Oscar Wilde once said: "We are all in the gutter, but some of us are looking at the stars." I guess I would be that person who's always searching for the beauty in life no matter the circumstances. And what would be more fascinated and more magical than a night sky full of stars?
The Hubble Space Telescope launched into low Earth orbit in 1990s unveiled vast cosmic islands in the endless wild ocean of the universe, and here are some of the most beautiful ones.
This post may include affiliate links.
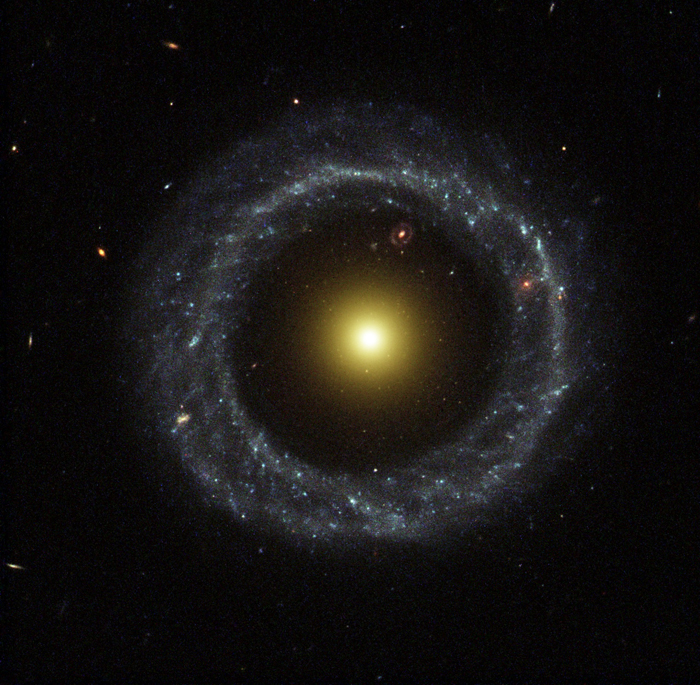
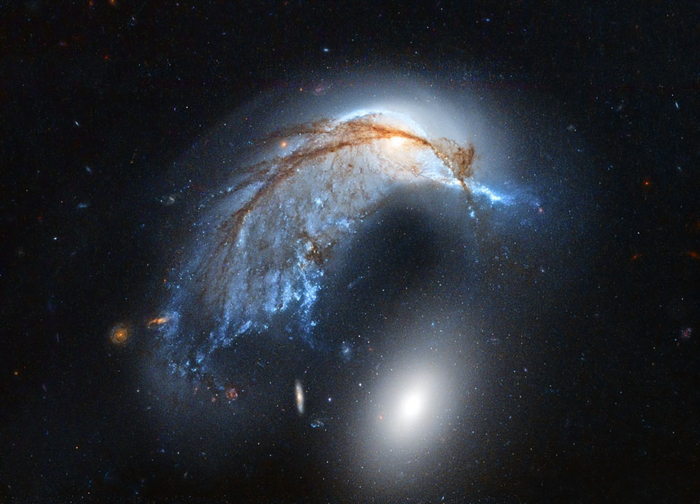
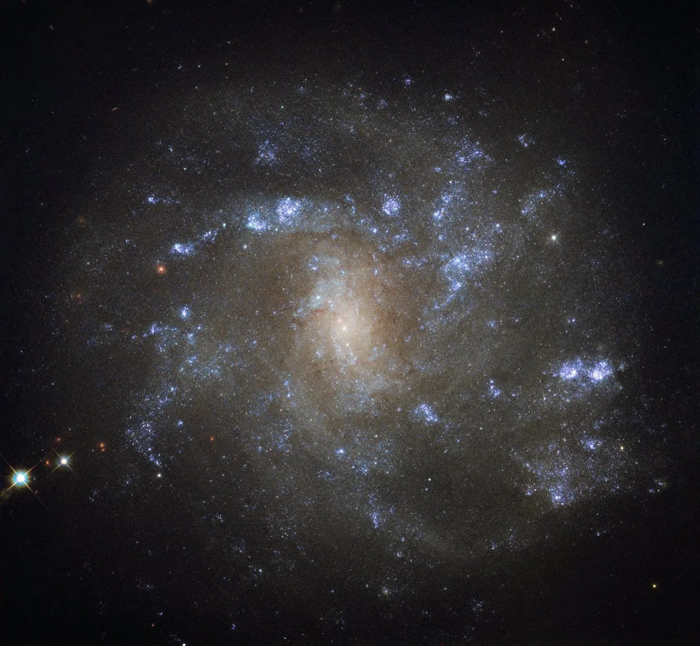
Hoag’s Object
Hoag's Object is an unusual ring galaxy in the constellation of Serpens Caput. It is identified as either a planetary nebula or a peculiar galaxy. The galaxy has approximately eight billion stars, and is roughly 120,000 light-years across.
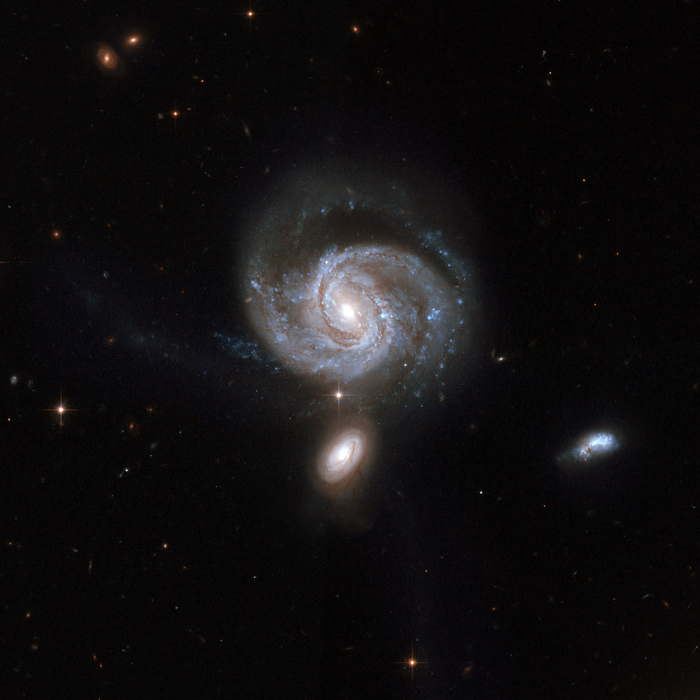
W2246-0526
W2246-0526 is the most luminous galaxy ever discovered that is cannibalizing not one, not two, but at least three smaller galaxies, which could explain its extreme brightness.
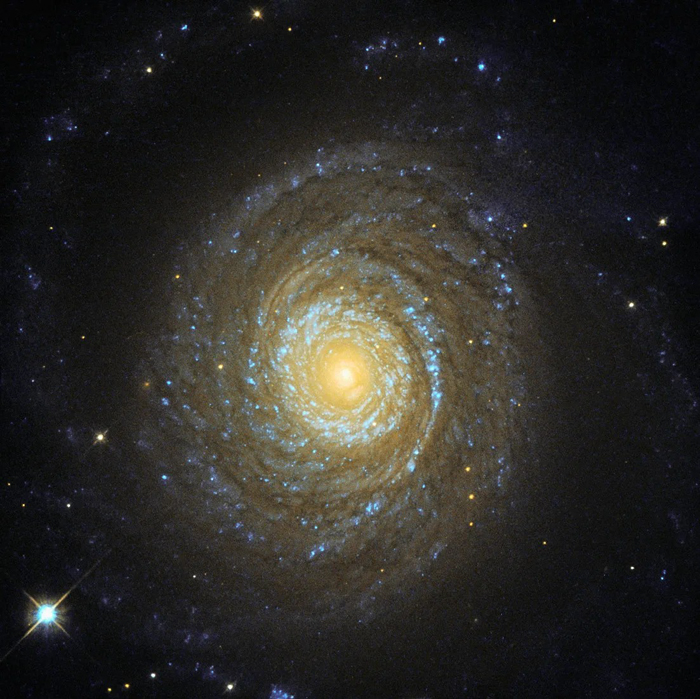
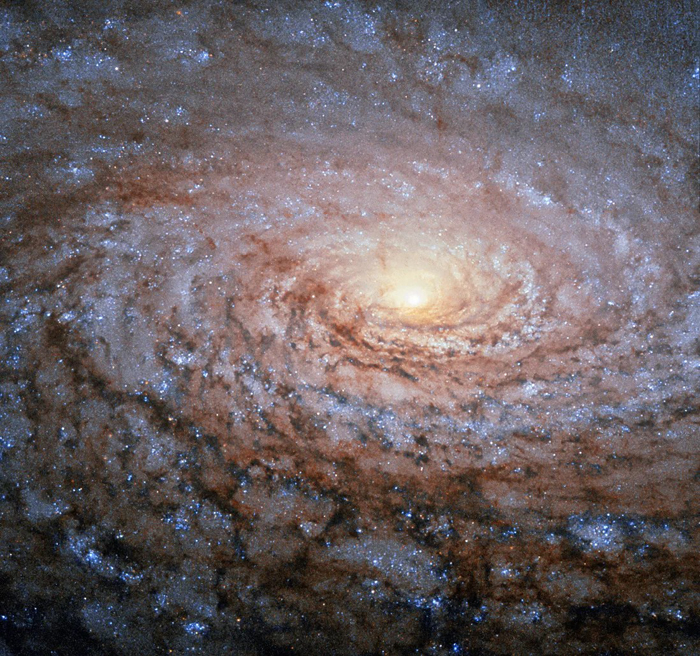
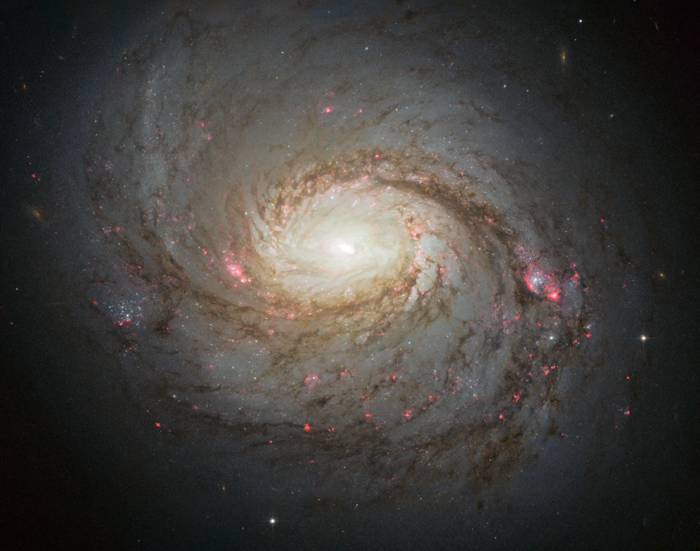
Sombrero Galaxy
The Sombrero galaxy is a peculiar galaxy of unclear classification in the constellation borders of Virgo and Corvus and located around 28 million light-years away from Earth.
See, like the Earth, it's flat. (Seriously, beautiful picture! We are extremely lucky to live and observe this amazing world!)
Most galaxies are between 10 billion and 13.6 billion years old and some are almost as old as the universe itself, which formed around 13.8 billion years ago. Some of the oldest galaxies observed formed when the universe was only about a billion years old. The scientists think those galaxies started to grow around pockets of space that were slightly denser than their surroundings, an effect created by cosmic inflation when the universe began.
Galaxies consist of stars, planets, and vast clouds of gas and dust, all held together by gravity. The largest one contain trillions of stars and could be more than a million light-years across. The smallest may contain a few thousand stars and span just a few hundred light-years. Most large galaxies have supermassive black holes at their centers, some with billions of times the Sun’s mass.
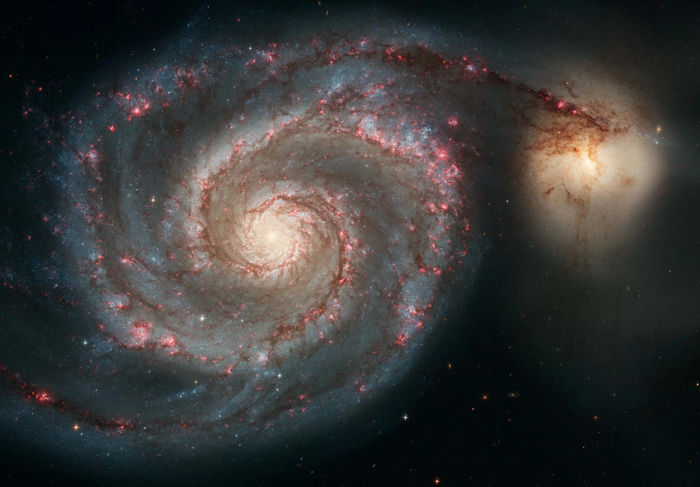
Whirlpool Galaxy
The Whirlpool Galaxy, also known as Messier 51a (M51a) or NGC 5194, is an interacting grand-design spiral galaxy with a Seyfert 2 active galactic nucleus. It lies in the constellation Canes Venatici and was the first galaxy to be classified as a spiral galaxy.
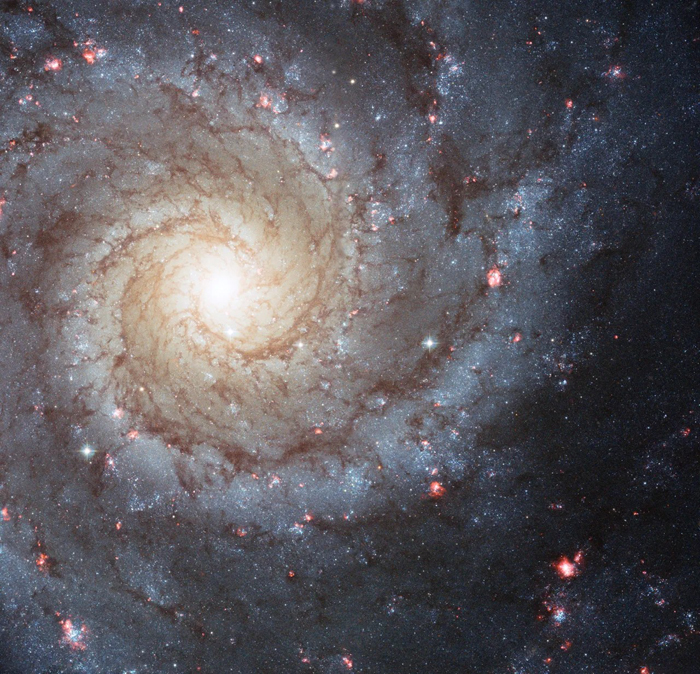
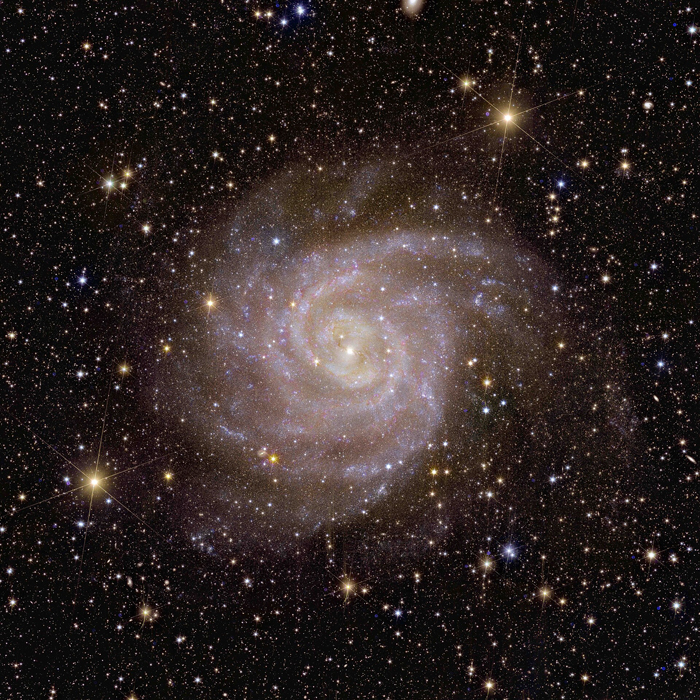
Phantom Galaxy or Messier 74
Phantom Galaxy or Messier 74 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation of Pisces and smaller than our own galaxy.
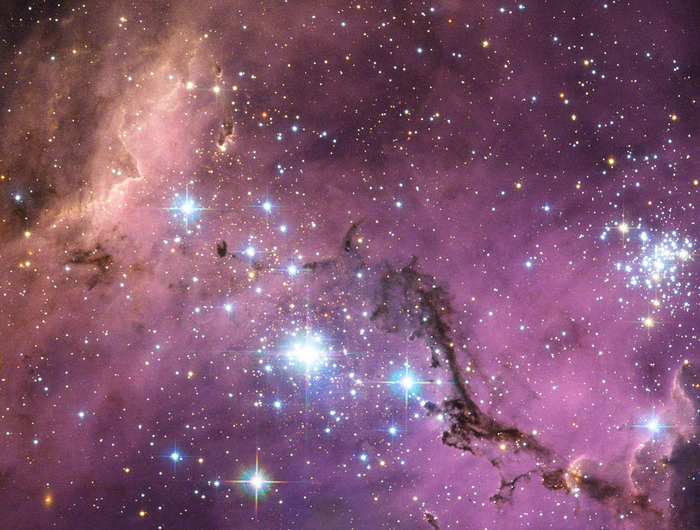
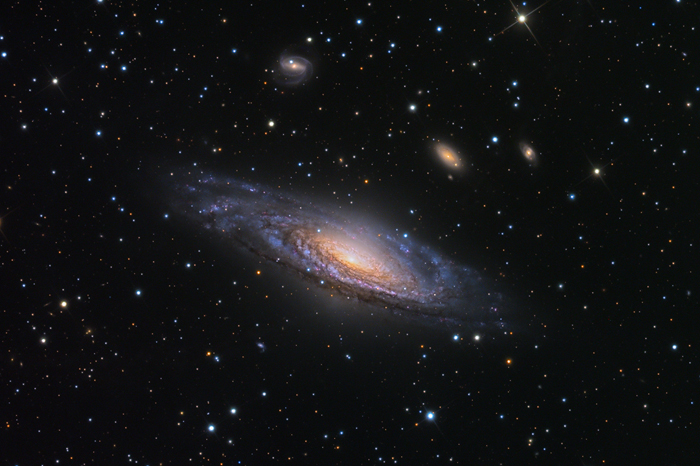
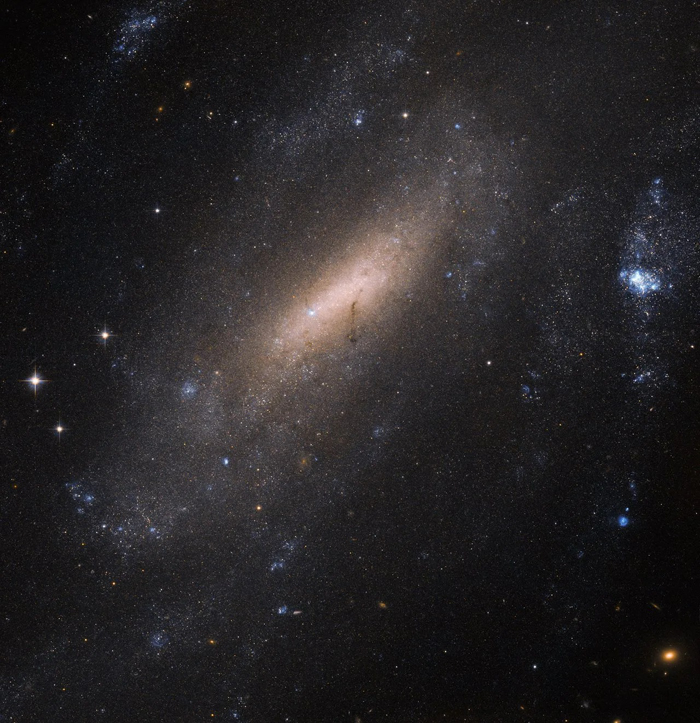
Large Magellanic Cloud
Large Magellanic Could is a spiral satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It is only 160,000 light-years from Earth therefore visible to the naked eye as a faint object in the Earth's southern hemisphere located between the constellations of Dorado and Mensa.
Before the 20th century, people didn't know other galaxies than the Milky Way; earlier astronomers had classified them as as “nebulae,” since they looked like fuzzy clouds.
It all changed in the 1920s when the astronomer Edwin Hubble showed that the Andromeda “nebula” was a galaxy in its own right. Despite the immense distance, Andromeda is the closest large galaxy to our Milky Way, and it's bright enough in the night sky that it's visible to the naked eye in the Northern Hemisphere.
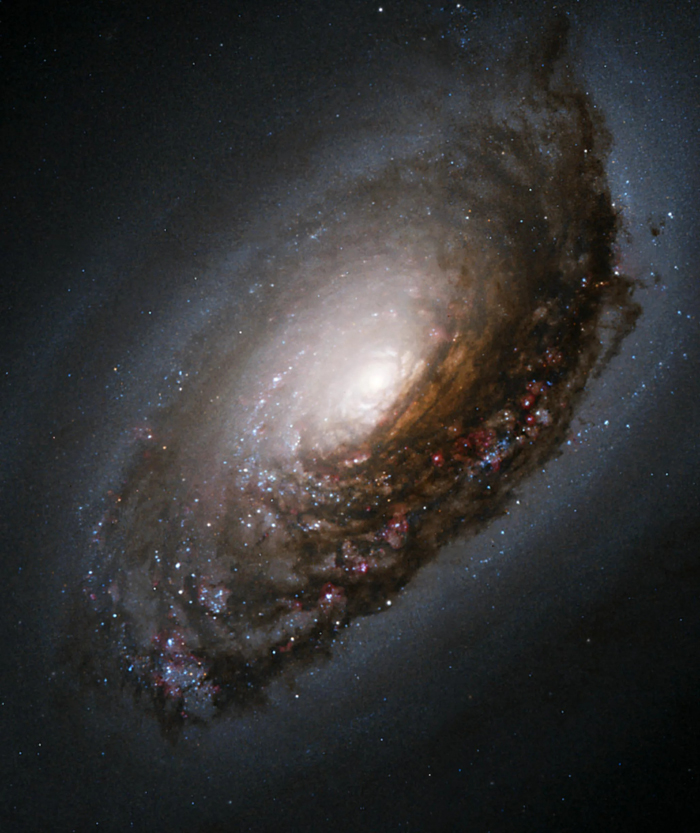
The Black Eye Galaxy
The Black Eye Galaxy is a relatively isolated spiral galaxy 17 million light-years away in the mildly northern constellation of Coma Berenices.
Maybe Hoag threw his object at it, and that's why it has a black eye.
Galaxy NGC 6753
This galaxy is 150 million light-years away from Earth. Astronomers mentioned, that it is one of only 2 known spiral galaxies, large enough and close enough to allow detailed observations of its crowns.
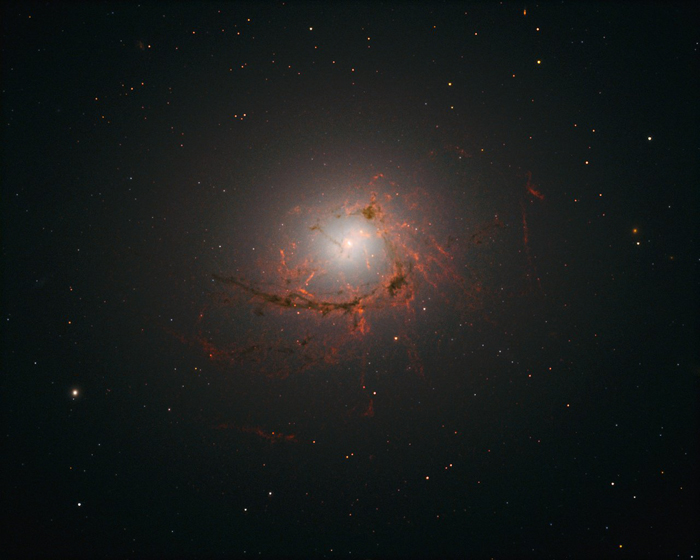
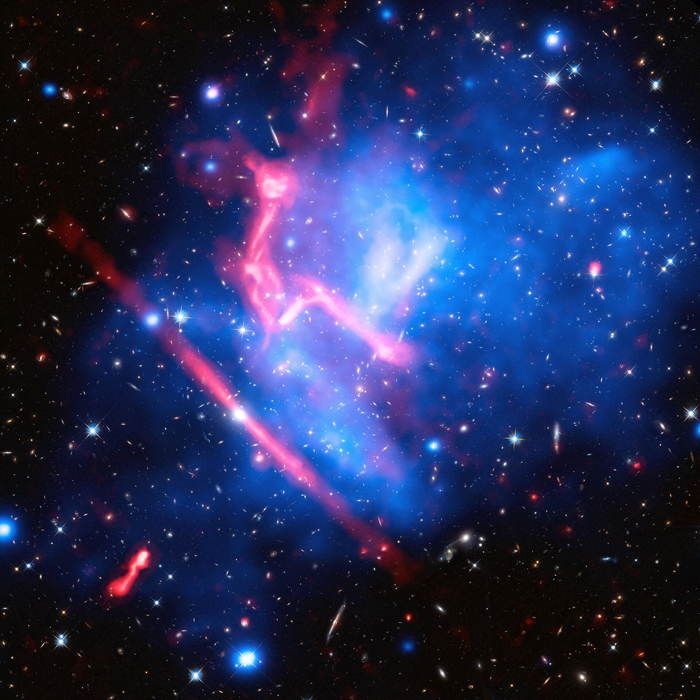
Galaxy NGC 4696
NGC 4696 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Centaurus. It has a supermassive black hole that beats like a heart every 5 to 10 million years.
The question is how do we know that it's black hole beats like a heart every 5-10M years? We've only been looking into deep space for <100 years.
In 1936, because of Hubble, galaxies were grouped into four main types: spiral galaxies, lenticular galaxies, elliptical galaxies and irregular galaxies.
Interestingly enough, more than two-thirds of all observed galaxies are spiral galaxies that have a flat, spinning disk with a central bulge surrounded by spiral arms.
Elliptical galaxies contain many older stars, but little dust and other interstellar matter. Their stars orbit the galactic center but they do so in more random directions. The universe's largest known one may contain up to a trillion stars and span two million light-years across.
Lenticular galaxies, such as the funny Sombrero Galaxy, are between elliptical and spiral galaxies. They have a thin, rotating disk of stars and a central bulge, but they don't have spiral arms. Like elliptical galaxies, they have little dust and interstellar matter, and they seem to form more often in densely populated regions of space.
The rest of the galaxies are called Irregular - such as the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. They appear misshapen and lack a distinct form, very often because they are within the gravitational influence of other galaxies close by. They are full of gas and dust, which makes them great nurseries for forming new stars.
Galaxy NGC 4388
NGC 4388 is an active spiral galaxy in the equatorial constellation of Virgo and located at a distance of 57 million light-years from Earth.
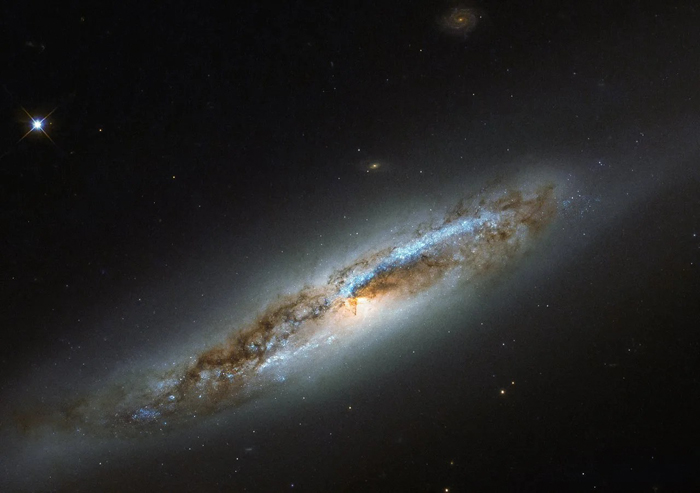
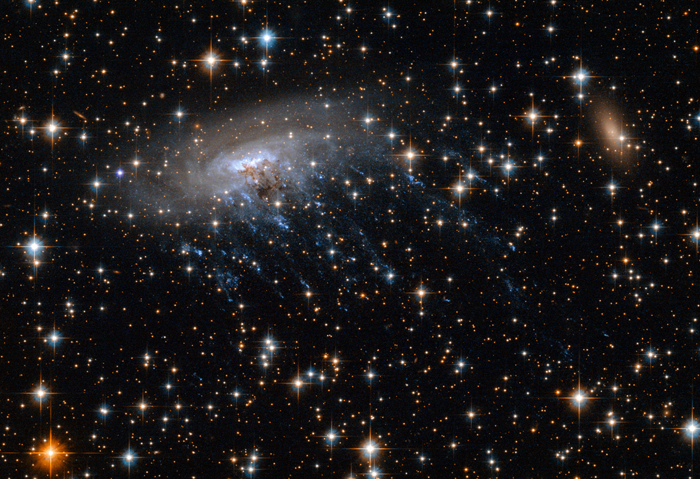
Porpoise Galaxy
Porpoise Galaxy or NGC 2936 is an interacting spiral galaxy located at a distance of 326 million light-years, in the constellation Hydra. NGC 2936 is interacting with elliptical galaxy NGC 2937 located just beneath it.
NGC 2207 and IC 2163
NGC 2207 and IC 2163 are a pair of colliding spiral galaxies about 80 million light-years away in the constellation Canis Major.
Some galaxies are quite often parts of larger associations known as groups, clusters, and superclusters. For example, the Milky Way is in the Local Group, a galaxy group about 10 million light-years across that also includes the Andromeda galaxy and its satellites.
Sometimes, galaxies collide. Astronomers think the Milky Way and its galactic neighbor Andromeda are set to collide in another 4.5 billion years.
If colliding galaxies don’t have enough momentum to move past each other, they can merge to form a single larger galaxy. Then it can look very different from the two that created it. For example, if a spiral and elliptical merge, the result could be an irregular galaxy.
Some larger galaxies can also eat up the smaller ones through proximity and gravitational interactions, pulling material away to fuel their own growth.
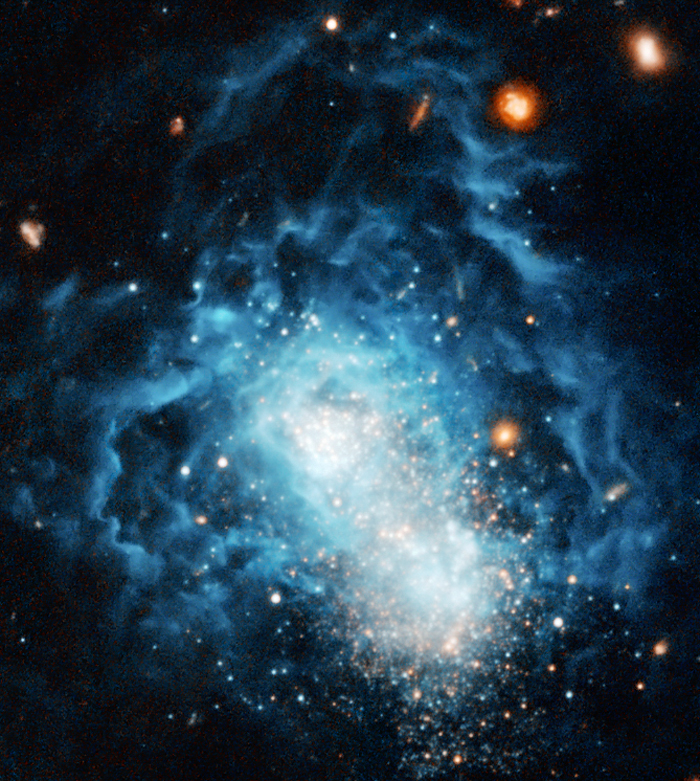
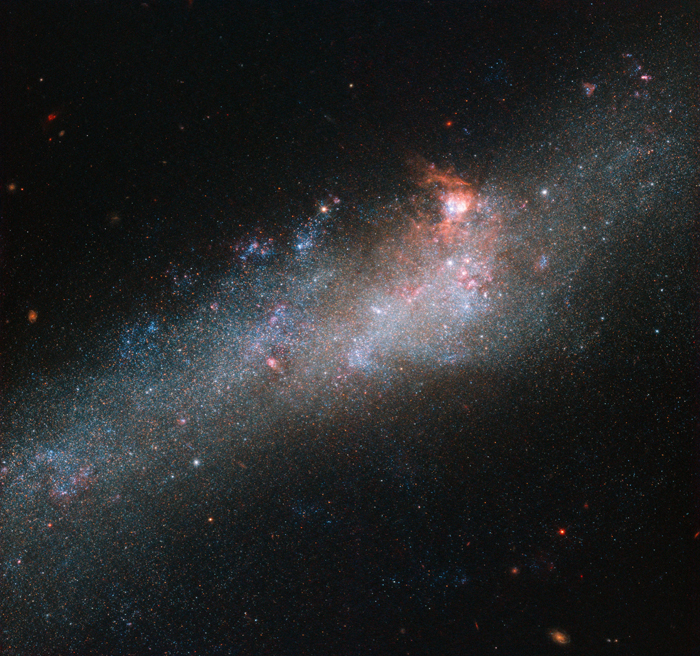
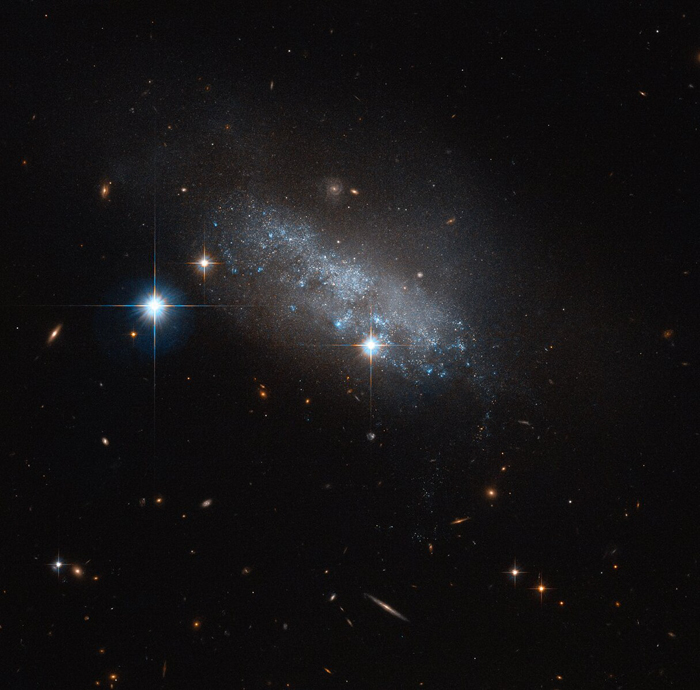
Galaxy I Zwicky 18
Galaxy I Zwicky 18 is a blue compact dwarf galaxy located about 59 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major.
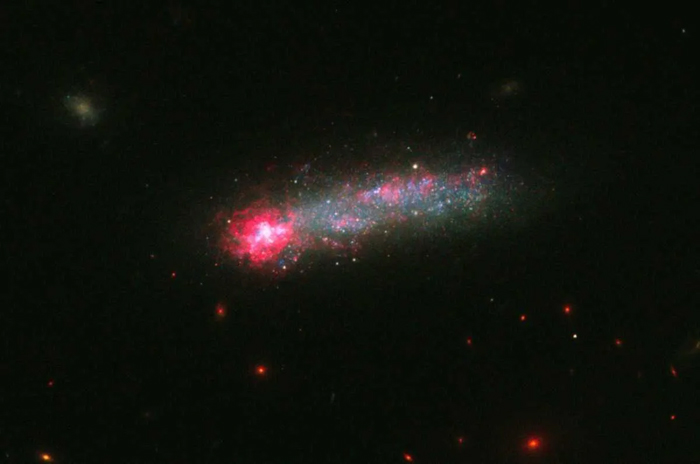
Kiso 5639
Kiso 5639 is a dwarf galaxy, member of a class of "tadpole" galaxies so named because of their bright heads and elongated tails.
Sunflower Galaxy
Sunflower Galaxy is a spiral galaxy in the northern constellation of Canes Venatici with approximately 400 billion stars.
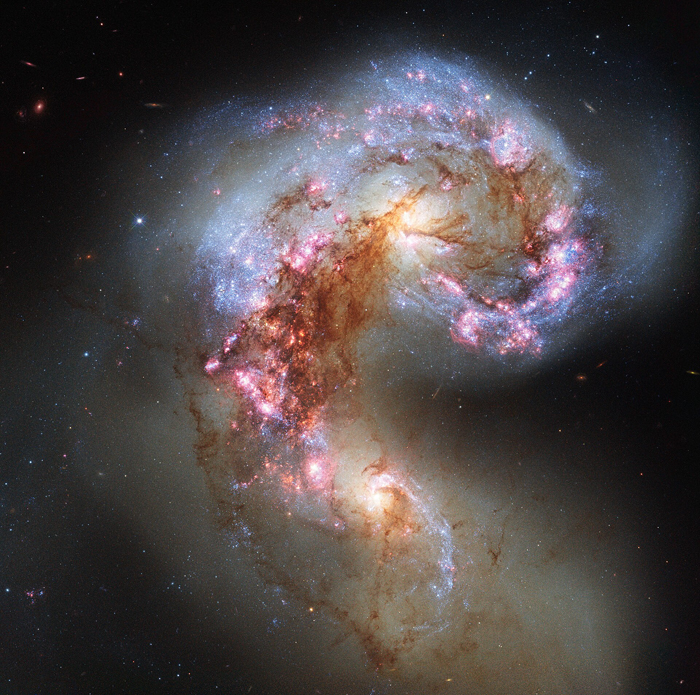
The Antennae Galaxies
The Antennae Galaxies are a pair of interacting galaxies in the constellation Corvus. They currently going through a starburst phase, in which the collision of clouds of gas and dust, with entangled magnetic fields, causes rapid star formation.
In 2004, NASA released the Hubble Ultra Deep Field: a tiny part of the constellation Fornax contained around 10,000 galaxies, some of which existed 13 billion years ago, less than 800 million years after the big bang. These types of snapshots are very important for scientists to be able to study galaxies at different evolutionary stages.
NGC 2336
NGC 2336 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Camelopardalis. It is located at a distance of circa 100 million light-years from Earth.
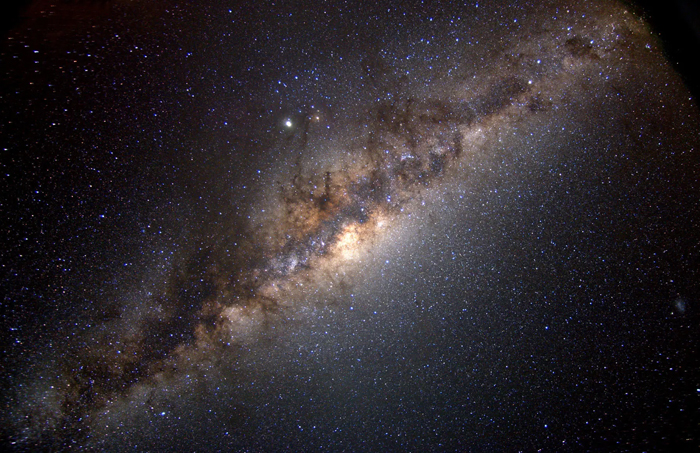
Milky Way
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy, around 13.6 billion years old and home to our own solar system.
To see the actual Milky Way Galaxy, step outside and look up. For best results do this after dark.
Galaxy NGC 2500
NGC 2500 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Lynx.
Messier 77
Messier 77, also known as NGC 1068 or the Squid Galaxy. It is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Cetus and about 47 million light-years away from Earth.
Nearly 10,000 galaxies that were captured in the Hubble Ultra Deep Field may look like they’re randomly scattered across the sky yet they are often part of larger structures and superstructures in space.
Galaxies, galaxy groups and clusters, superclusters, and galactic walls are arranged in twisting, threadlike structures called the cosmic web. The web forms as the gravitational attraction of the universe’s matter draws larger and larger objects together leading to concentrations of galaxies with voids of space in between, as if the galaxies were resting on empty bubbles. In the places where those concentrations intersect, they form larger structures like clusters and walls. The cosmic web forms a sort of scaffolding that cradles everything that exists within the universe.
MACS 2129-1
MACS 2129-1 is an early universe so-called 'dead' disk galaxy that lies approximately 10 billion light-years away from Earth. MACS 2129-1 has been described as 'dead' as it has ceased making new stars.
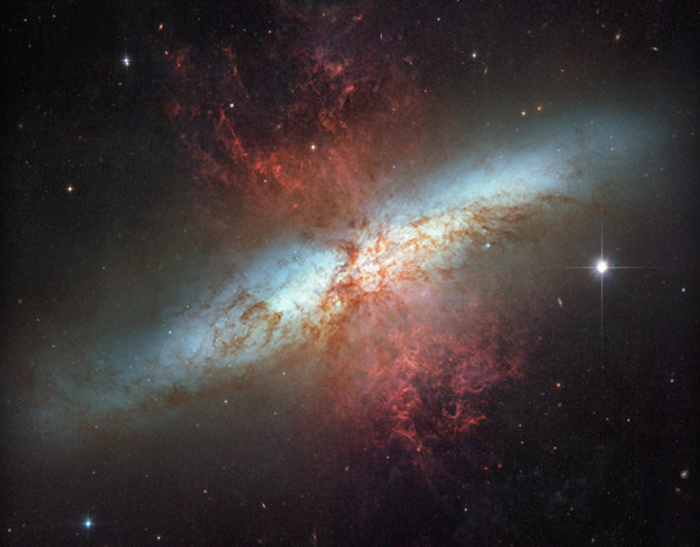
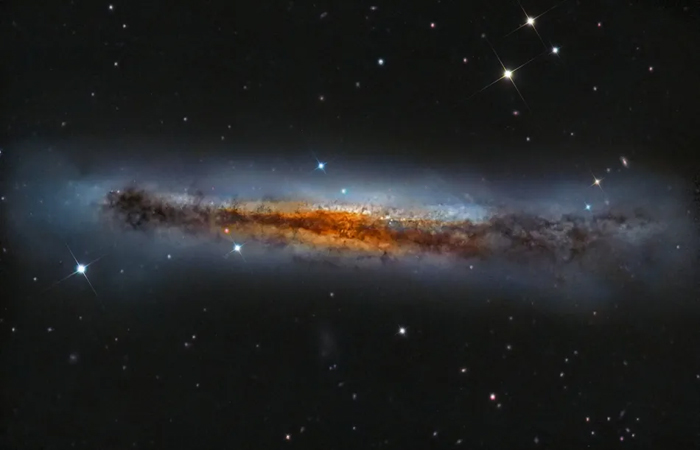
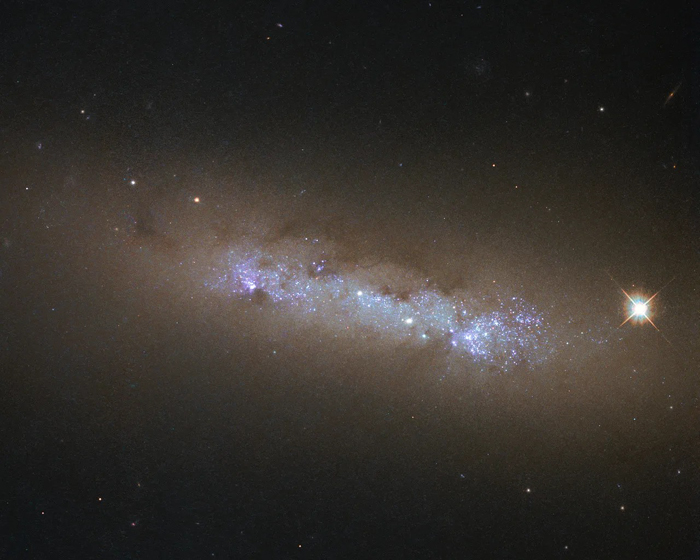
Cigar Galaxy Or Messier 82
Cigar Galaxy is a starburst galaxy approximately 12 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Ursa Major.
Galaxy RX J1140.1+0307
Galaxy RX J1140.1+0307 is a spiral galaxy that is centered on one of the lowest black hole masses known in any luminous galactic core.
NGC 7674
NGC 7674 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Pegasus. It is located at a distance of circa 350 million light-years from Earth.
Late March to mid-May is considered the best time of the year to find some amazing galaxies. Of course, a telescope or binoculars are required to see the distant ones, but you can also witness our nearest galaxy from your own backyard! Until then, I invite you to scroll up and down the images here and to get to know the most beautiful ones in our universe!
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy, the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way and the one of the few visible to the naked eye. It is located about 2,480,000 light-years from Earth.
It's also going to collide and merge with the Milky Way.
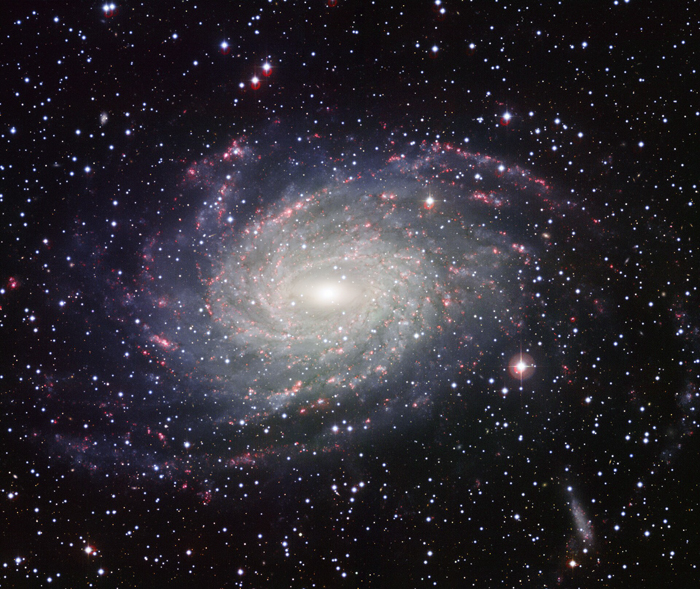
Galaxy IC 342
IC 342 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Camelopardalis, located relatively close to the Milky Way.
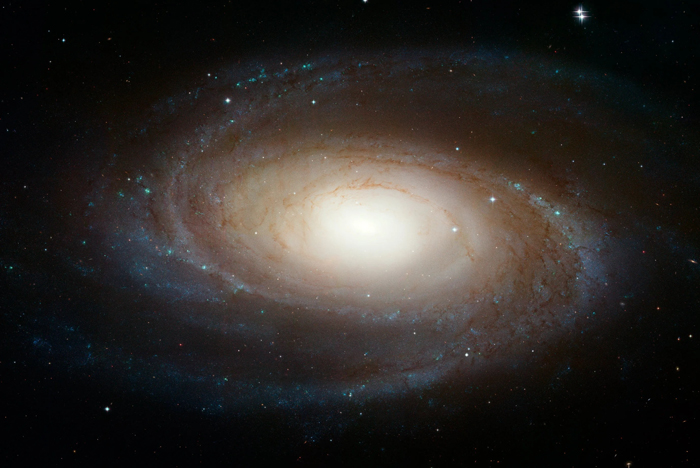
Messier 81
Messier 81 is a grand design spiral galaxy about 12 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major.
Hamburger Galaxy
NGC 3628, also known as the Hamburger Galaxy or Sarah's Galaxy, is an unbarred spiral galaxy about 35 million light-years away in the constellation Leo.
It should be Wimpy's galaxy. I'll gladly pay you Tuesday for a hamburger today.
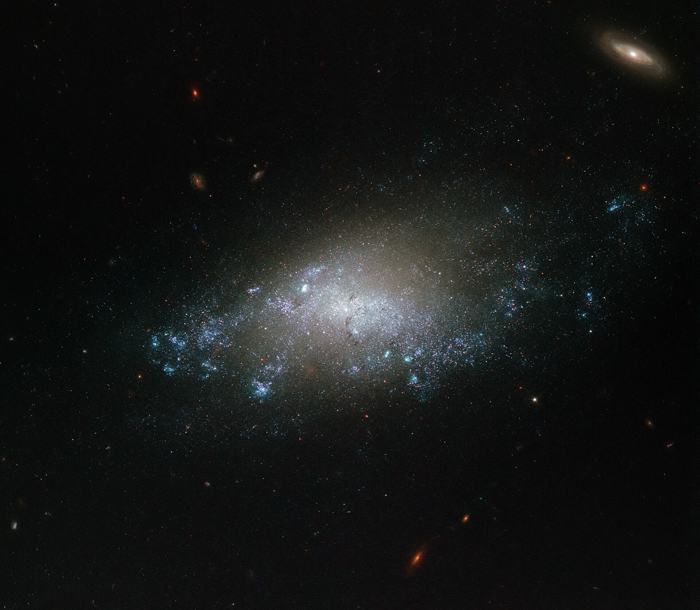
Galaxy NGC 3274
Galaxy NGC 3274 is a relatively faint spiral galaxy that is located over 20 million light-years away in the constellation of Leo.
Galaxy NGC 6744
NGC 6744 is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 30 million light-years away in the constellation Pavo.
Galaxy MACS J0717.5+3745
MACS J0717.5+3745 is a large galaxy cluster located 5,4 billion light-years away in the constellation Auriga, appearing in the Massive Cluster Survey.
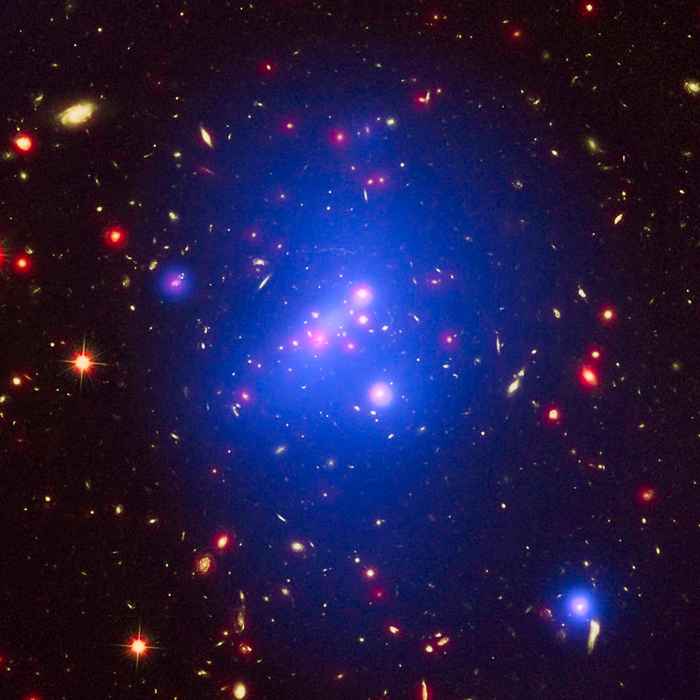
Galaxy Cluster IDCS 1426
This rare galaxy cluster, which is located 10 billion light years from Earth, weighs almost 500 trillion Suns.
NGC 7331
NGC 7331, also known as Caldwell 30, is an unbarred spiral galaxy about 40 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus.
Ahahaha I just realized they named Colonel Caldwell from Stargate Atlantis (set in the Pegasus galaxy) after this!
Galaxy Hockey Stick
The Hockey Stick is a highly warped edge-on barred spiral galaxy located in the local universe 30 million light years away from earth in the constellation Canes Venatici.
Galaxy NGC 4248
This beautiful clump of glowing gas, dark dust, and glittering stars is the spiral galaxy NGC 4248 is located about 24 million light-years away in the constellation of Canes Venatici.
Galaxia ESO 486-21
Galaxia ESO 486-21 is a spiral galaxy, with an irregular and ill-defined structure, located about 30 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Lynx.
Galaxy NGC 4424
NGC 4424 is a spiral galaxy located in the equatorial constellation of Virgo and 13,5 million light-years away from Earth.
Galaxy IC 5201
IC 5201 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Grus and about 35 million light-years from Earth.
Galaxy IC 3583
Galaxy IC 3583 is an irregular galaxy around 30 million light-years away in the constellation of Virgo.
ESO 137-001
ESO 137-001 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Triangulum Australe and in the cluster Abell 3627. As the galaxy moves to the center of the cluster at 1900 km/s, it is stripped by hot gas, thus creating a 260,000 light-year long tail.
Bear in mind that we are also looking back in time with these images. We see them, not as they are, but as they were, however millions or billions of years ago!
That is just what I was thinking. In other words, if a galaxy is described as x million light years away, that means we are seeing an image of the galaxy as it existed x million years ago.
Load More Replies...Bear in mind that we are also looking back in time with these images. We see them, not as they are, but as they were, however millions or billions of years ago!
That is just what I was thinking. In other words, if a galaxy is described as x million light years away, that means we are seeing an image of the galaxy as it existed x million years ago.
Load More Replies...
 Dark Mode
Dark Mode 

 No fees, cancel anytime
No fees, cancel anytime