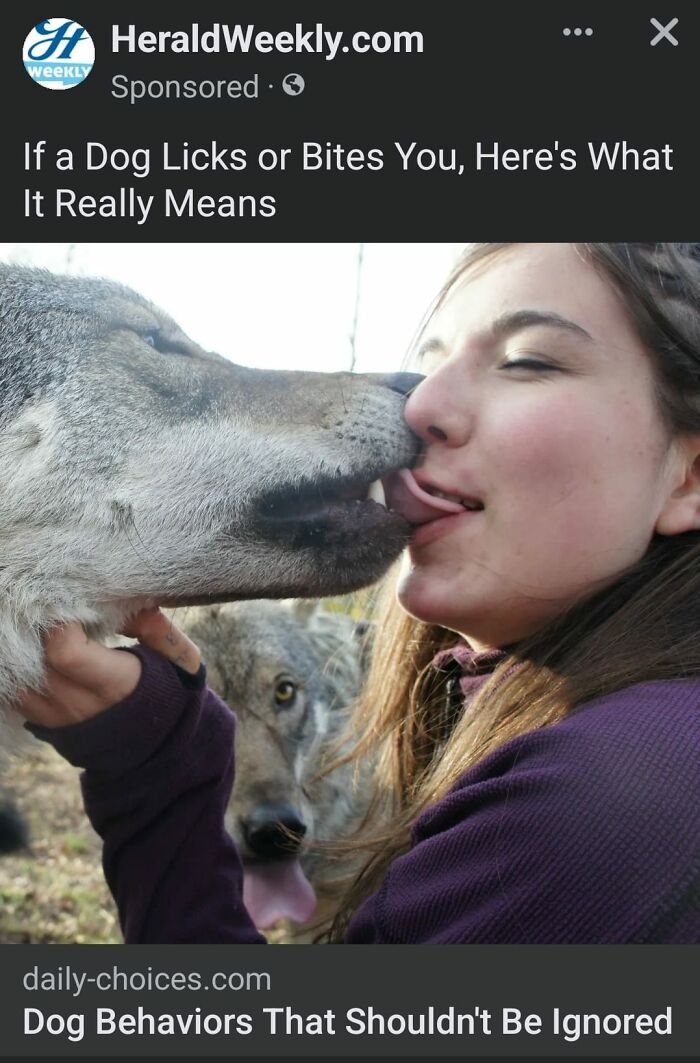
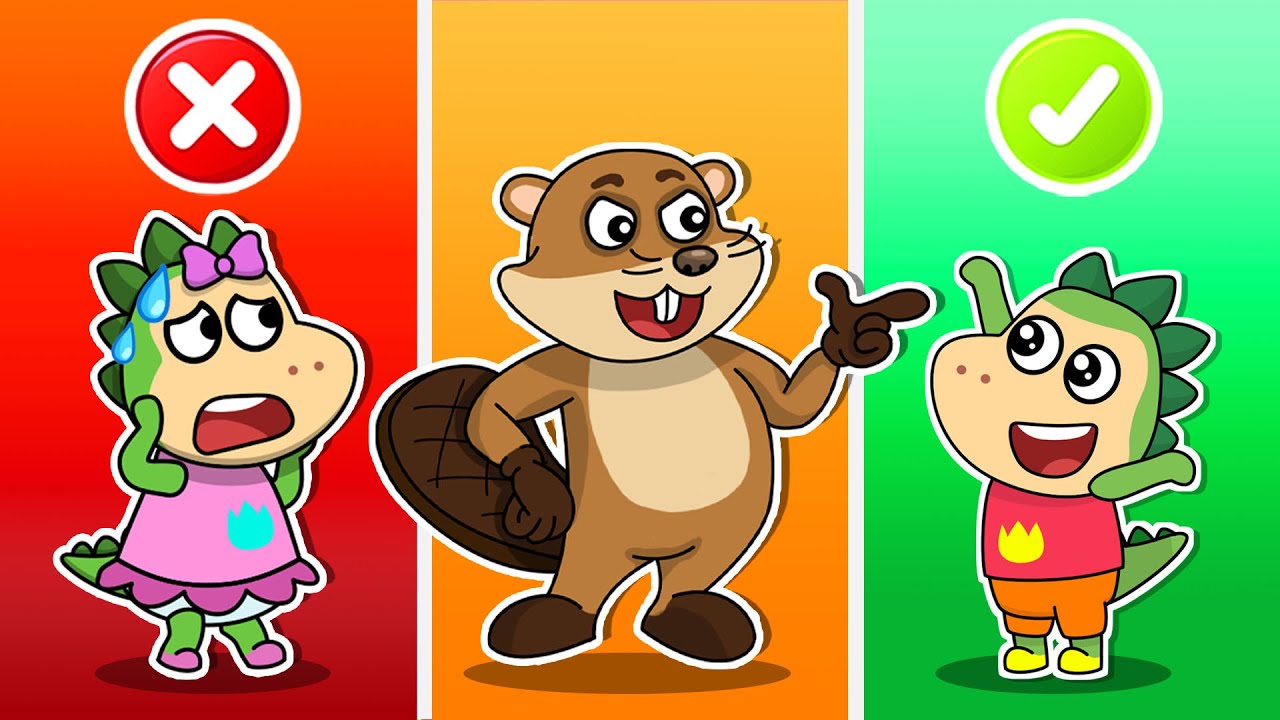
191Kviews
40 Times People Spotted Such Weird Ads, They Just Had To Share Them In The ‘Ads With Threatening Auras’ Facebook Group (New Pics)
Ads are downright creepy. They follow you around the internet after you looked at a specific product on Amazon and won't leave you alone even if you eventually make the purchase. But it's not just their behavior, ads can be freaky by design, too.
There's a Facebook group, called 'Ads with threatening auras,' which you may have already seen on Bored Panda here and here, and its content is a perfect example of that.
More info: Facebook
This post may include affiliate links.
Ads are trying to convince us that if we buy this or that, our lives will get better, however, we humans have a natural defense mechanism against consumerism.
The University of Warwick's Andrew Oswald and his team compared survey data on the life satisfaction of more than 900,000 citizens of 27 European countries from 1980 to 2011 with data on annual advertising spending in those nations over the same period. The researchers discovered an inverse connection between the two. The higher a country's ad spend was in one year, the less satisfied its citizens were a year or two later. Their conclusion was simple: advertising makes us unhappy.
"Colleagues and I have been studying human happiness for 30 years now, and recently my focus turned to national happiness," Oswald told Harvard Business Review about the origins of these findings. "What are the characteristics of a happy country? What are the forces that mold one? What explains the ups and downs? I'd never looked at advertising before, but I met a researcher who was collecting data on it for a different reason, and it seemed to me that we should combine forces."
"Like a lot of people in Western society, I can't help noticing the increasing amount of ads we’re bombarded with. For me, it was natural to wonder whether it might create dissatisfaction in our culture: How is your happiness and mine shaped by what we see, hear, and read? I think it's rather intuitive that lots of ads would make us less happy. In a sense, they're trying to generate dissatisfaction—stirring up your desires so that you spend more on goods and services to ease that feeling. I appreciate, of course, that the world’s corporate advertisers and marketing firms won’t like hearing me say that."
Oswald said the results are really significant. "When you look at changes in national happiness each year and changes in ad spending that year or a few years earlier—and you hold other factors like GDP and unemployment constant—there is a link," he explained. "This suggests that when advertisers pour money into a country, the result is diminished well-being for the people living there."
The official industry line is that advertising is trying to expose the public to new and exciting things to buy, and its task is to simply provide information. But the alternative argument, which goes back to Thorstein Veblen and others, is that exposing people to a lot of advertising raises their aspirations—and makes them feel that their own lives, achievements, belongings, and experiences are inadequate.
This study supports the negative view.
"The idea here is a very old one," Oswald said. "Before I can decide how happy I am, I have to look over my shoulder, consciously or subconsciously and see how other people are doing. Many of my feelings about my income, my car, and my house are molded by my next-door neighbor’s income, car, and house. That’s just part of being human: worrying about relative status. But we know from lots of research that making social comparisons can be harmful to us emotionally, and advertising prompts us to measure ourselves against others."
In other words, if I see an ad for a fancy new car, it makes me think about my ordinary one, which might make me feel bad. Or if I see this fancy $10,000 watch and then look at my own, which probably cost around $150, I might think, "Maybe there’s something wrong with me."
"In this paper, we don’t prove that the dissatisfaction is coming from relative comparisons, but we suspect that’s what happens," Oswald said.

 Dark Mode
Dark Mode  No fees, cancel anytime
No fees, cancel anytime