
Design Duo Creates A Home-Grown Biodegradable Mask From Bacteria
During the coronavirus pandemic, the shortage of personal protective equipment suddenly became very apparent, and various designers and scientists have offered their creative solutions. They have ranged from 3D printed shields to DIY face masks, but most of them have involved plastic. For this reason, Garrett Benisch and Elizabeth Bridges of Sum Studio have created a microbial cellulose face mask that you can actually… grow in your own kitchen.
More info: Vimeo
Image credits: Sum Studio
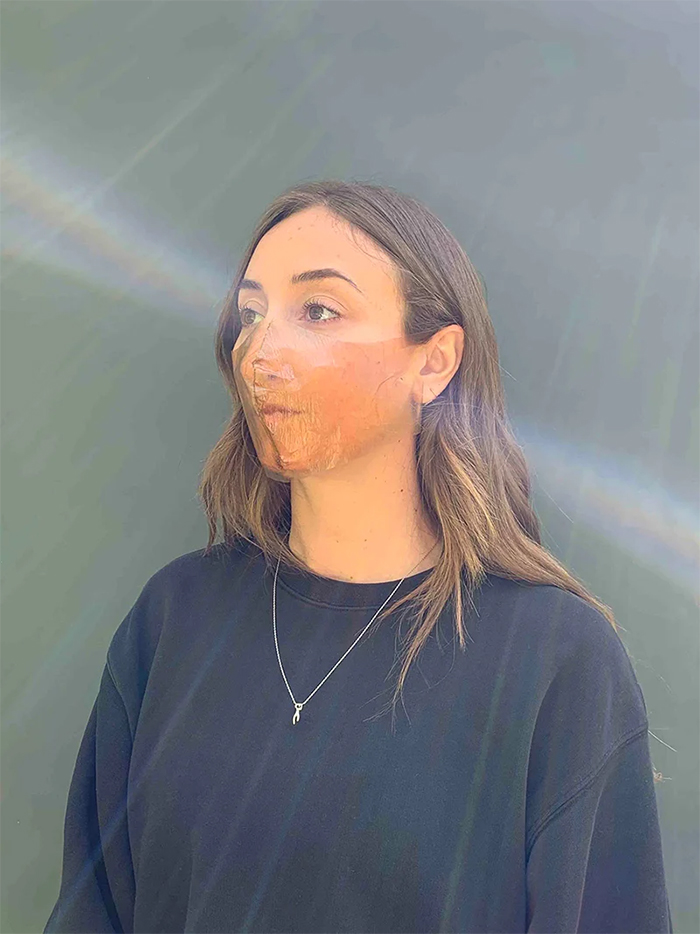
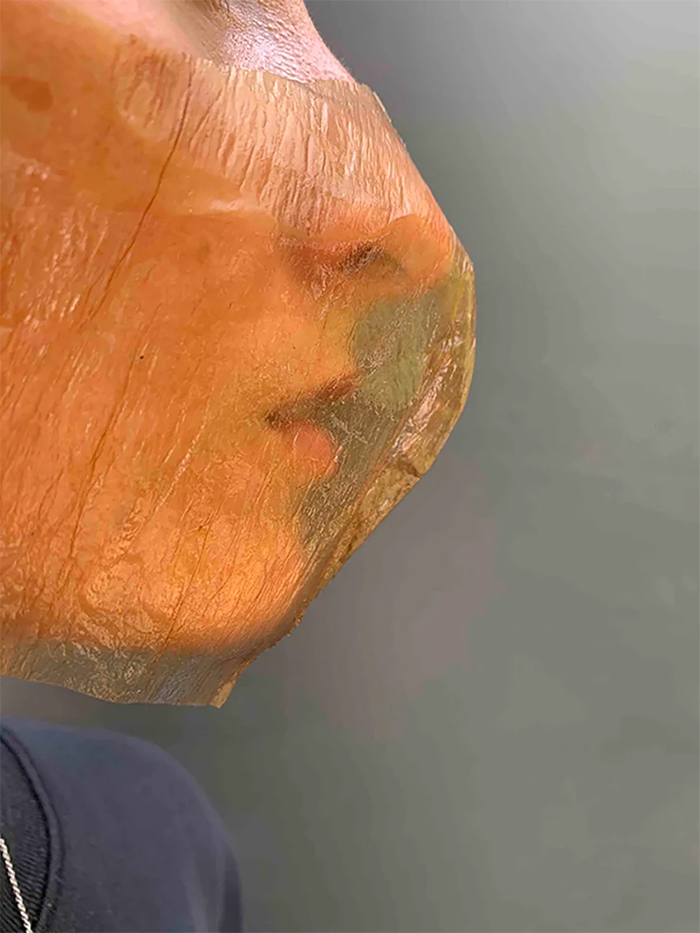
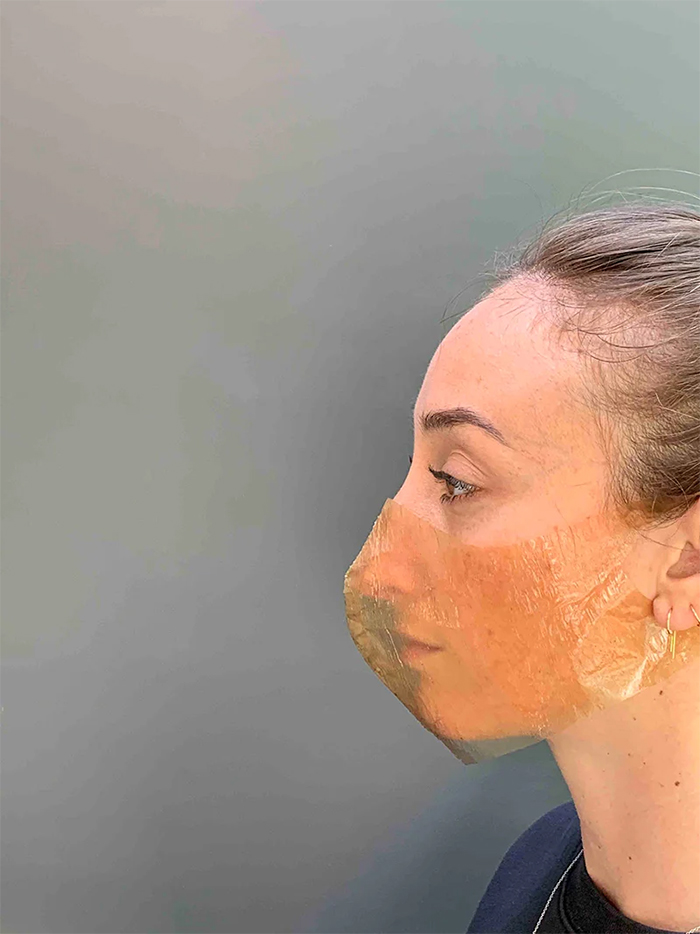
Garrett Benisch and Elizabeth Bridges have designed a prototype for an alternative to the N95 mask, which has a polymer-based filter made of artificial nonwoven plastic fibers—the key materials that are the main culprits of the shortage of PPE. The mask that Sum Studio has created offers a more sustainable approach to personal protective equipment.
Image credits: Sum Studio
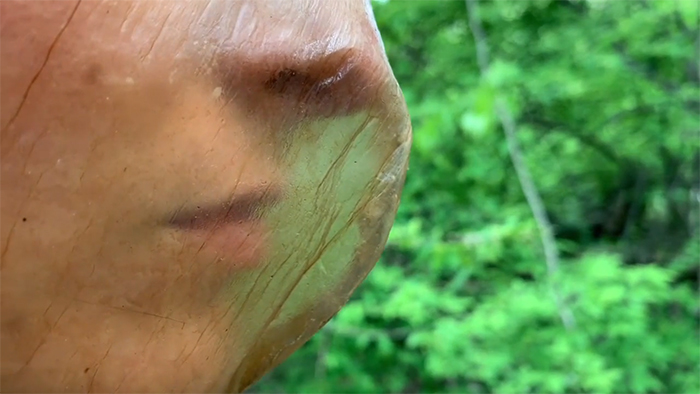
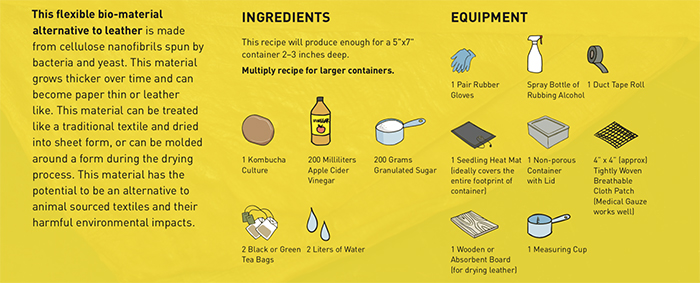
Called a “xylinum mask,” the newly-designed mask is made out of bacterial cellulose, a by-product of a common bacteria called xylinum acetobacter. Designers Garrett and Elizabeth say that you can actually grow the bacteria with a few simple ingredients at your own house. What you’ll need is water, tea, sugar, and a small bacterial sample of xylinum acetobacter, which can be found in unflavored kombucha.
Image credits: Sum Studio
“The prototype mask and the science referenced is coupled together to show that biodesign has real potential for rapid innovation and impact,” said Garrett, one of the designers. With that being said, while a mask made from biomaterials sounds exciting, at this point, it’s only speculative and hasn’t been tested yet.
Image credits: Sum Studio
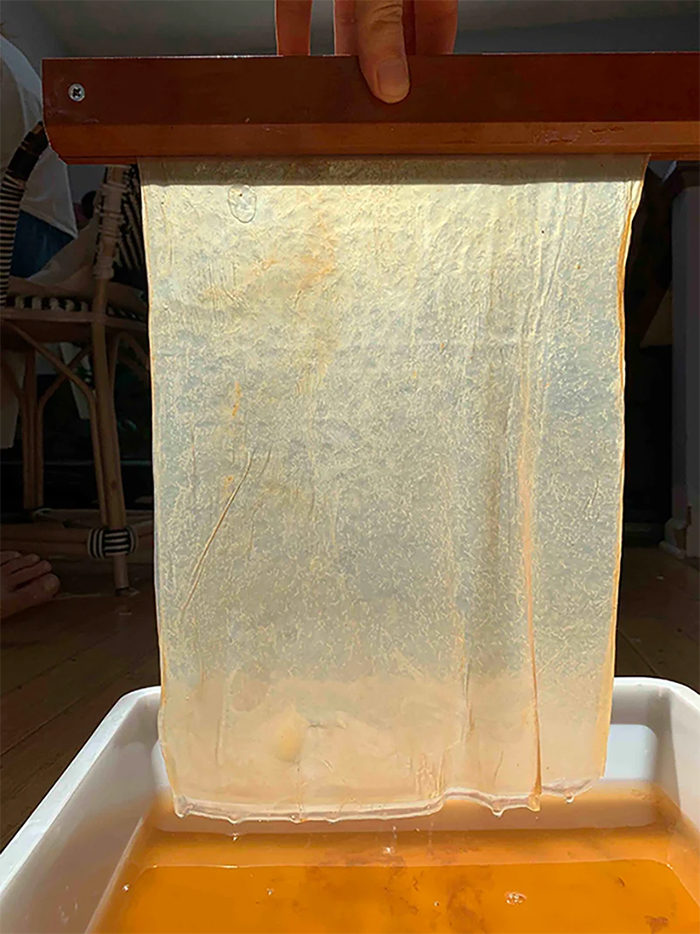
Bacterial cellulose is created by the bacteria called xylinum acetobacter on the surface of a liquid that they inhabit. As they multiply, these bacteria knit cellulose fibers into a single membrane that can be later harvested and dried to use as a material. While the cellulose is see-through to us, microscopic images show the tight web of cellulose fibers that make up this amazing knit.
Image credits: Sum Studio
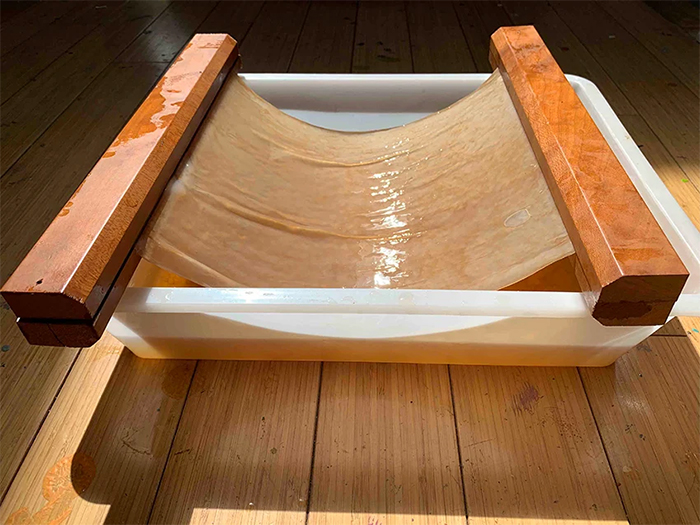
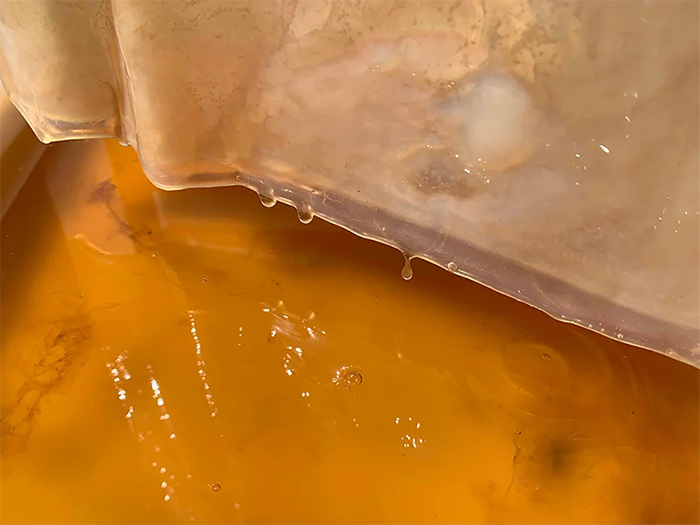
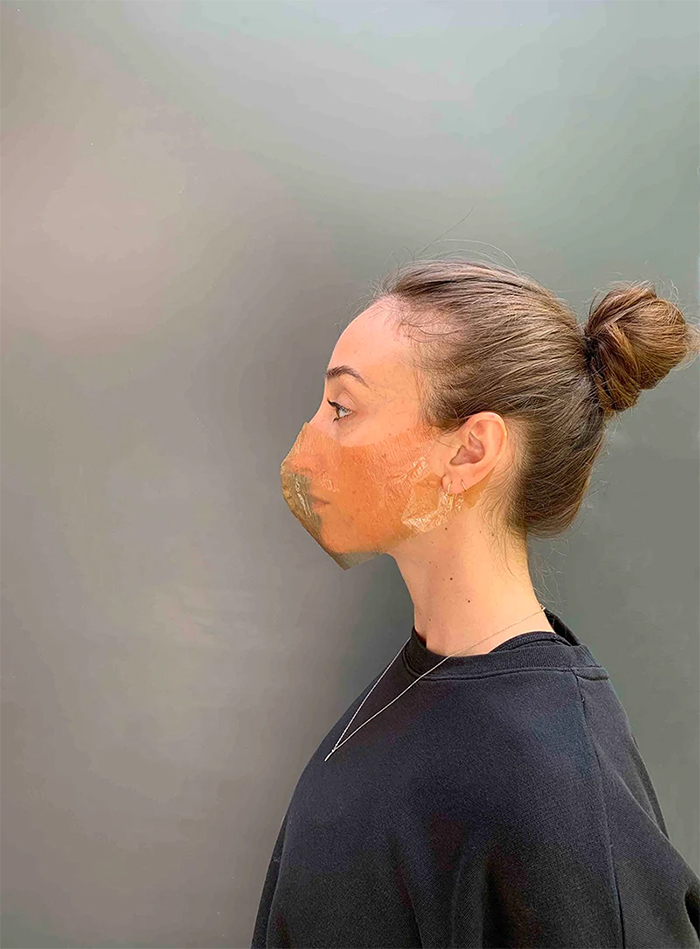
As soon as the material becomes thick enough, it can be removed to be hung and dried. The resulting sheet is as flexible as it is strong, while still easily degrading into the environment. It can be later waterproofed or oiled to provide the softness and strength of thin leather. The whole process takes up around two weeks.
Image credits: Sum Studio
What makes the idea of cellulose face masks so exciting is its availability. The material for it could be grown in people’s homes, local communities, or even in the hospitals themselves that need them.
Image credits: Sum Studio
Instead of petroleum plastic masks that don’t degrade in our environment for many years, these cellulose masks would decompose as easily as vegetables or fruit. By bringing this project forward, the designers Garrett and Elizabeth are hoping to bring attention to the possible use of biodesign, which can provide sustainable solutions to many modern problems.
Image credits: Sum Studio
For those interested in making “kombucha leather,” here’s an easy guide you can follow.
Xylinum Mask from Garrett Benisch on Vimeo.
18Kviews
Share on FacebookExplore more of these tags
Wrong. Bacterial cellulose (BC) is not a biodegradable polymer. In deed, due to its high crystalline structure, is more difficult to hydrolyze by fungi. On the other side, BC is an alternative to petroleum-based plolymers, and BC can be produced from alternative feedstock such as rotten fruits. In this way, BC is a greener alternative, but is not a biodegradable polymer.
I am wondering also to which degree it will be passable or non-passable for small particles, including viruses.
Load More Replies...Wrong. Bacterial cellulose (BC) is not a biodegradable polymer. In deed, due to its high crystalline structure, is more difficult to hydrolyze by fungi. On the other side, BC is an alternative to petroleum-based plolymers, and BC can be produced from alternative feedstock such as rotten fruits. In this way, BC is a greener alternative, but is not a biodegradable polymer.
I am wondering also to which degree it will be passable or non-passable for small particles, including viruses.
Load More Replies...
 Dark Mode
Dark Mode 

 No fees, cancel anytime
No fees, cancel anytime 



















































41
18