In over 4.5 billion years of Earth’s existence and millions of years of human evolution, we’ve seen civilizations rise and fall, survived wars and famines, and made discoveries that have shaped the world we live in.
With so much behind us, it’s no surprise we want to know more about how we got here. To satisfy your (and our) curiosity, we’ve compiled a fascinating collection of photos and facts from the Facebook page ‘History’s Mysteries.’
Scroll down to explore them, and don’t forget to upvote your favorites!
More info: Instagram | YouTube | TikTok
This post may include affiliate links.
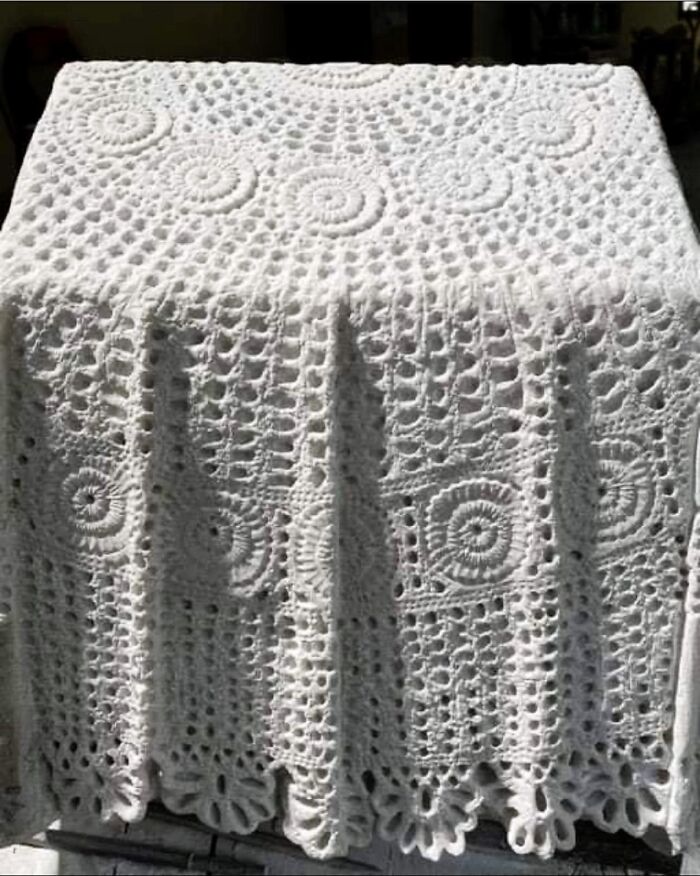
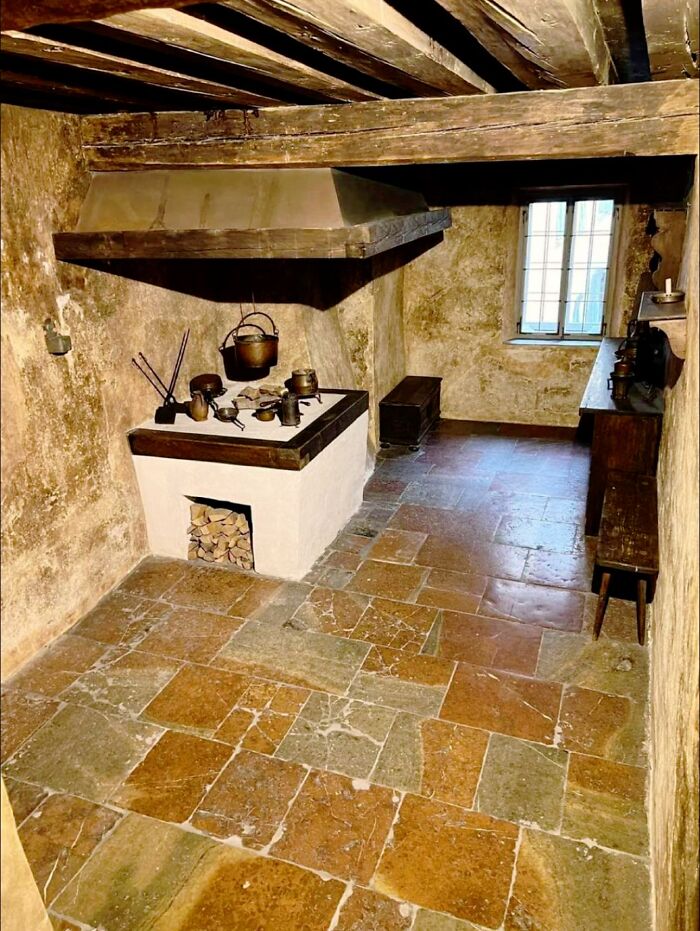
This Stunning Masterpiece, Though It Appears To Be Crafted From Crocheted Cotton, Is Actually Sculpted From Marble By The Greek Artist Argiris Rallias
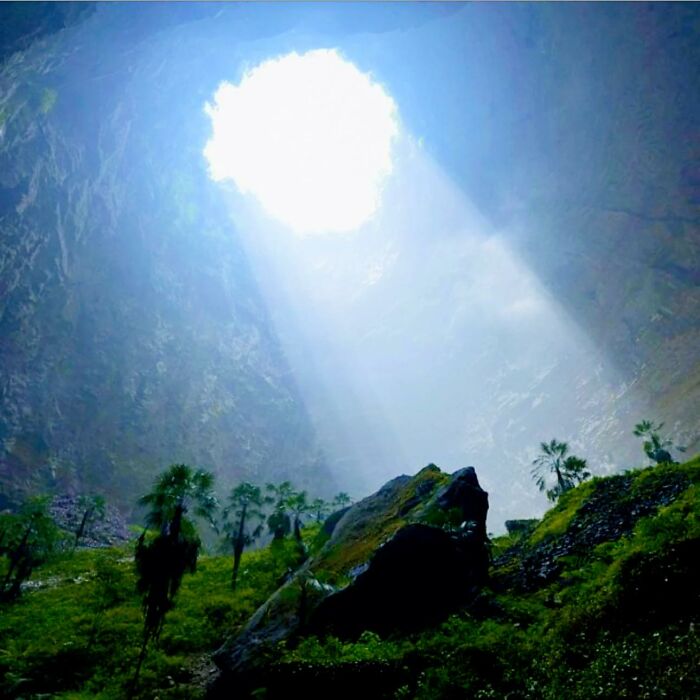
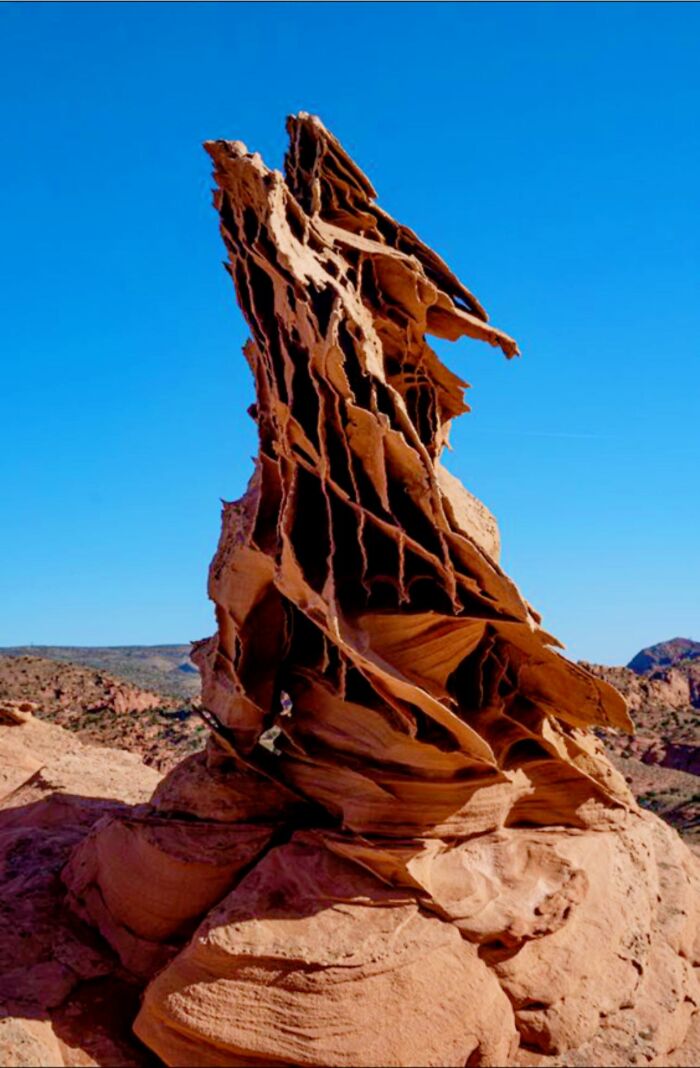
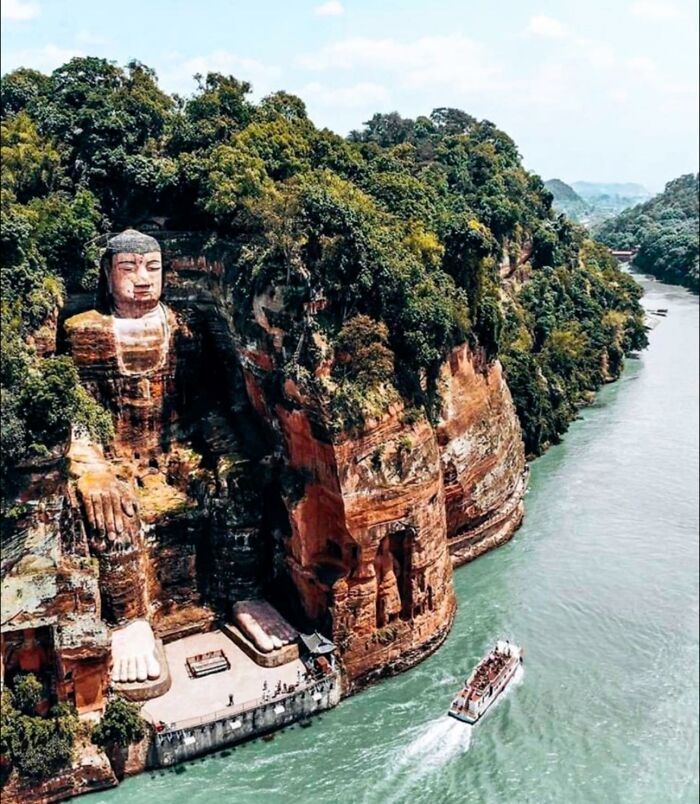
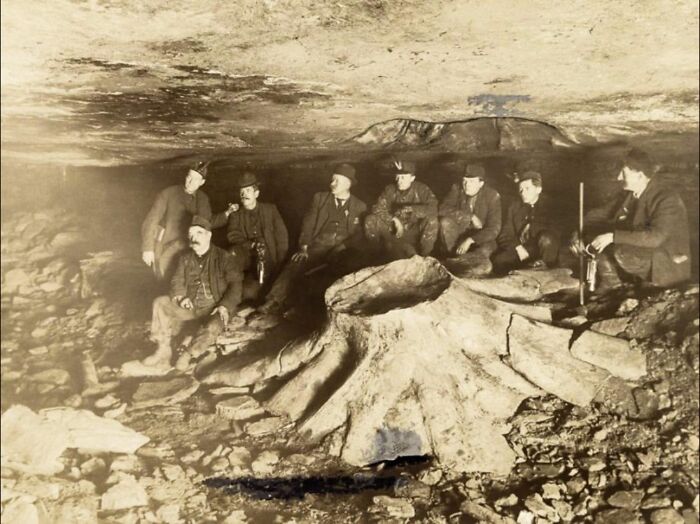
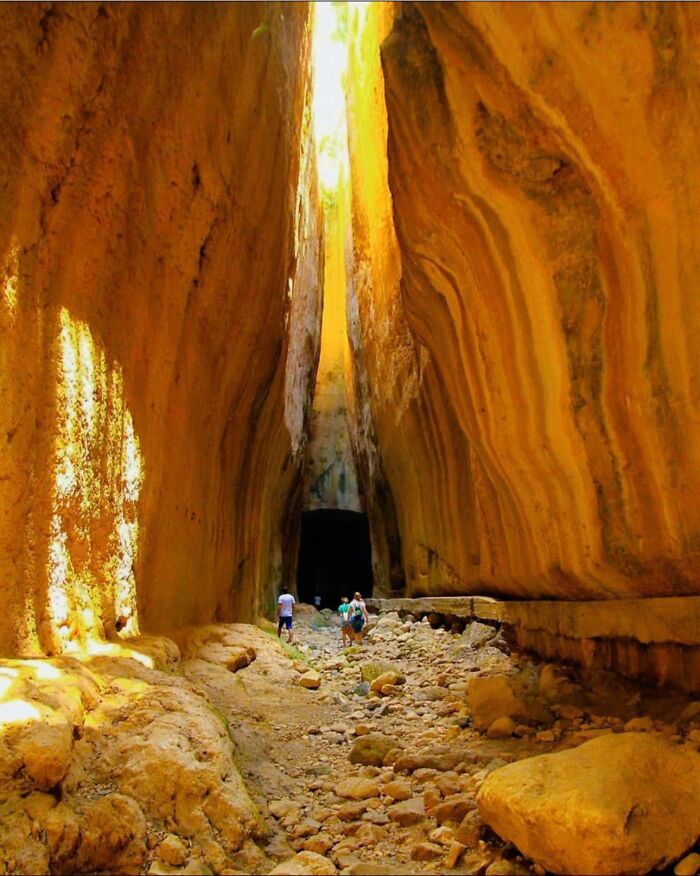
A Vast Sinkhole Over 290 Meters Deep In Xuanen County, Hubei, China, Housing A Unique Ecosystem Of Ancient Trees, Plants, And Animals
The humid climate and sunlight that reach the bottom create an extraordinary environment that remains largely inaccessible to humans.
From centuries-old cave paintings to rare historical photos, these posts offer glimpses into the past that you don’t come across every day. Bored Panda reached out to Jonathan Ramsey, the creator behind ‘History’s Mysteries,’ to find out where he discovers all these captivating stories and images, and how he built such a large community.
“I was inspired to start this page out of a deep fascination with ancient history and the mysteries that surround it,” he told us. “I wanted to create a space where people could explore obscure and intriguing stories from the past in a captivating way. The journey so far has been incredibly rewarding, with each post uncovering new insights and building a community of curious minds who share my passion for history.”
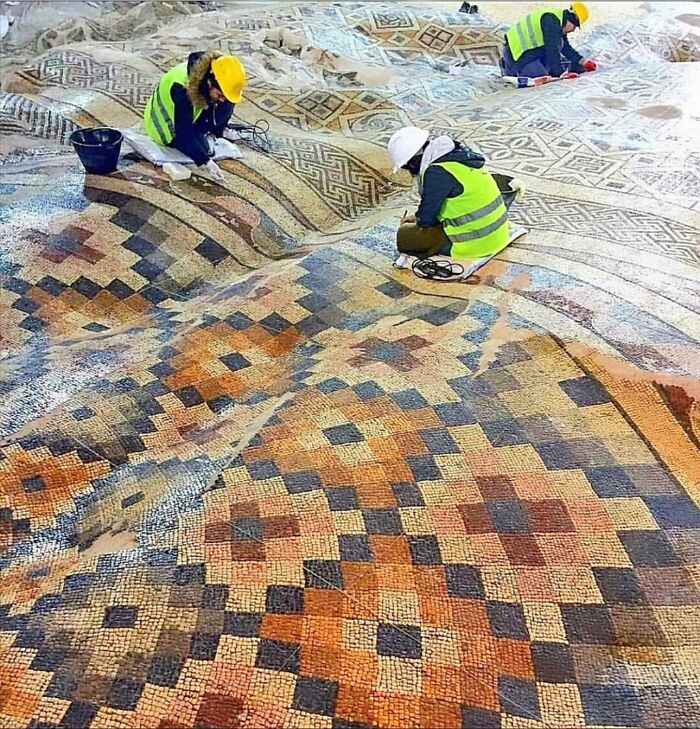
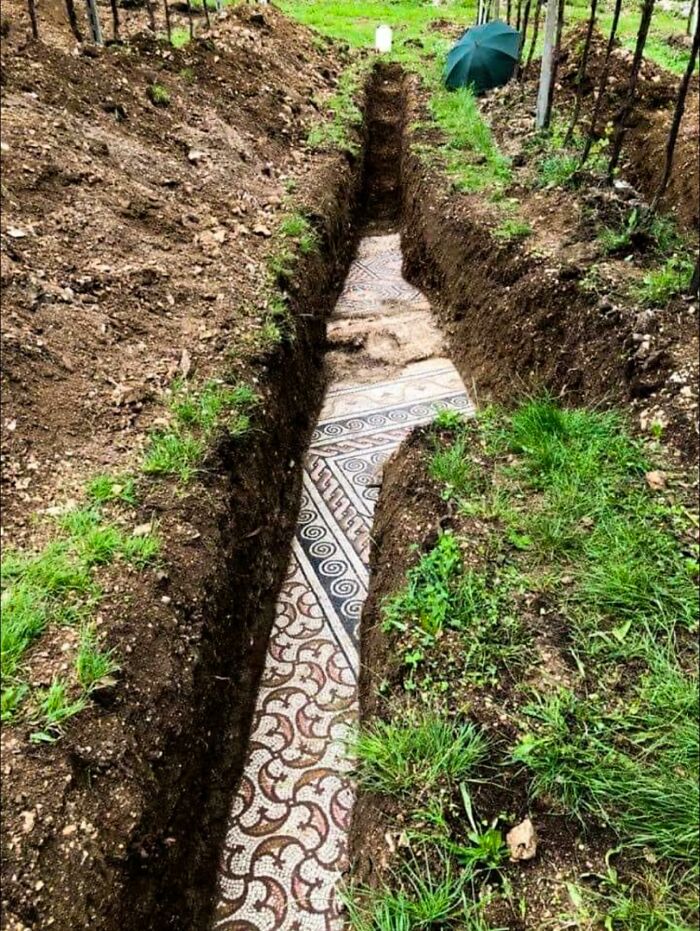
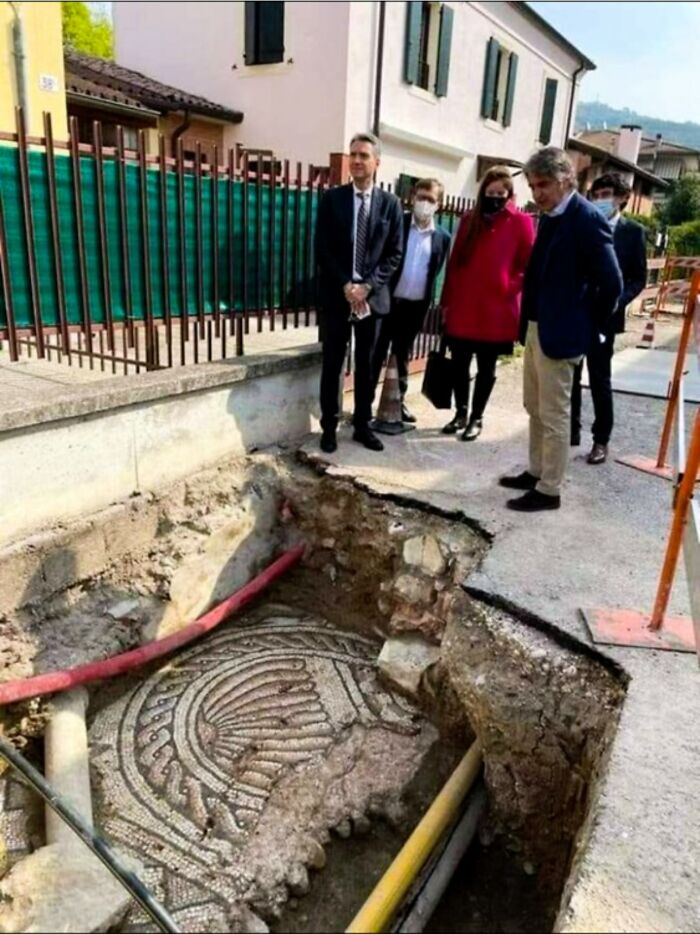
One Of The Largest Roman Mosaic Floors Ever Discovered Was Unearthed During The Construction Of A Hotel In Antakya, Turkey
This massive mosaic, dating back to the Roman period, features intricate designs and colorful patterns.
What’s most striking about the find is the unusual rippled effect across its surface, caused by centuries of earth shifting and earthquakes in the region. The result is an impressive, almost wave-like appearance, as if the mosaic were a giant, rippling blanket.
Despite this natural warping, the mosaic has remained remarkably intact, providing a glimpse into ancient Roman artistry and the impact of geological forces over time.
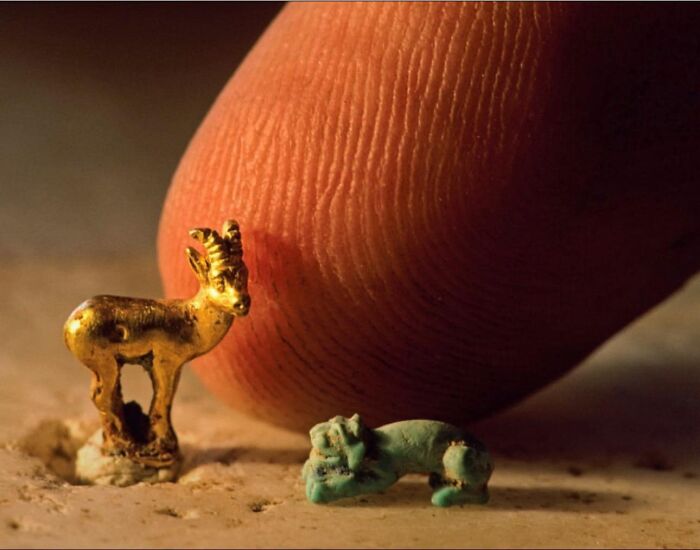
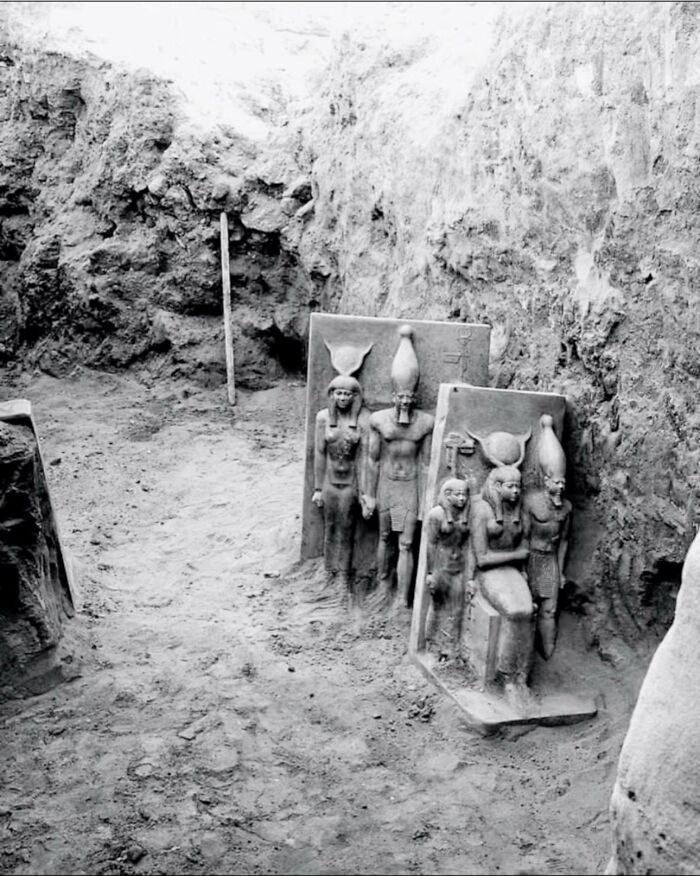
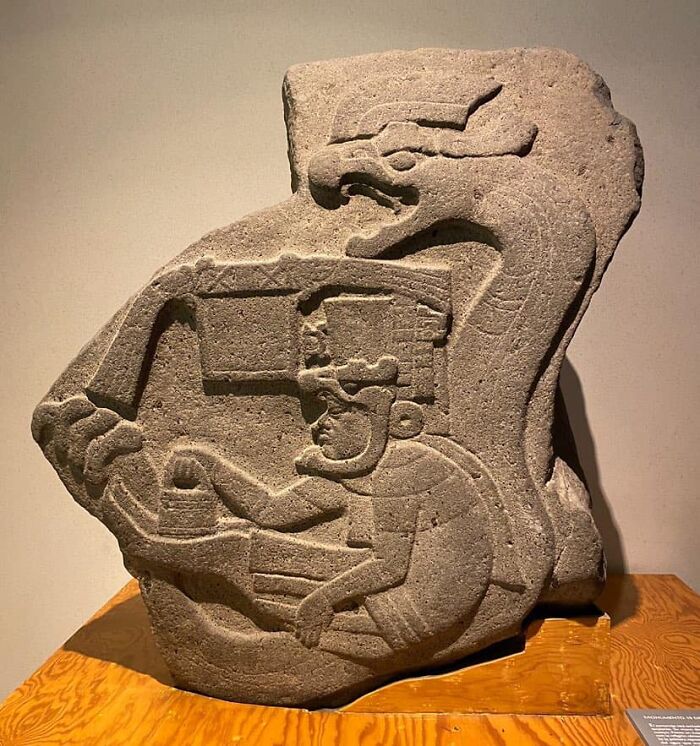
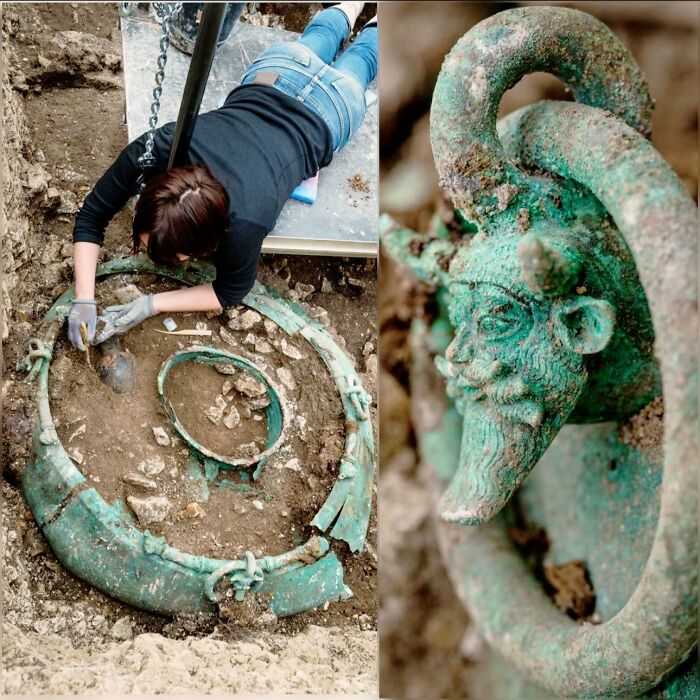
In Turkmenistan, At The Gonur Depe Archaeological Site, A Tomb Dating From 2,400 To 1,600 Bc Revealed Two Intriguing Artifacts
An extremely small golden ram and stone lion. These artifacts, indicative of the precision and craftsmanship of the Oxus civilization, offer a glimpse into the culture and artistic skill of this ancient society.
Running a page with nearly 500K followers isn’t easy, though. “Researching all these historical facts and photos definitely takes time and effort,” Jonathan shared. “I rely on a combination of academic sources, archaeological reports, historical texts, news outlets, and trusted online databases. I also follow new discoveries and studies in archaeology, which often lead to fascinating material. Social media and community input also play a part, as people share lesser-known stories that sometimes spark new ideas for content.”
Despite how much work goes into finding and researching historical facts, as well as staying up-to-date with relevant news, the result is definitely worth it, Jonathan admitted. “What I enjoy most about this page is seeing people engage with history in a meaningful way,” he said. “Watching the community grow and hearing how certain stories spark their curiosity or make them rethink what they know is really fulfilling. Ultimately, I hope to inspire a broader appreciation for history, shed light on some of the world’s hidden stories, and encourage critical thinking about the past and its impact on the present.”
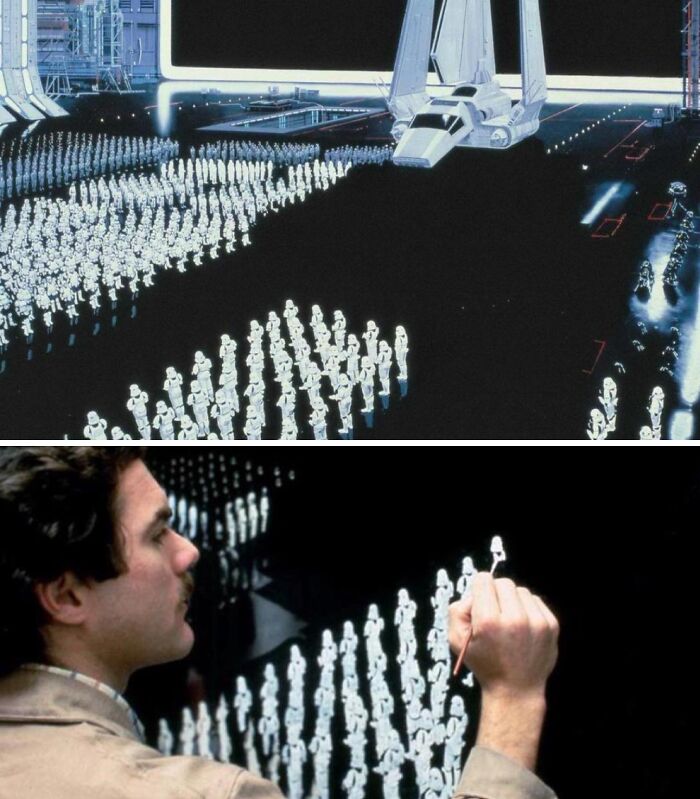
The Original Star Wars Trilogy Masterfully Used Matte Paintings To Seamlessly Create Vast, Detailed Worlds, Immersing Audiences In Realistic Environments Long Before Digital Effects
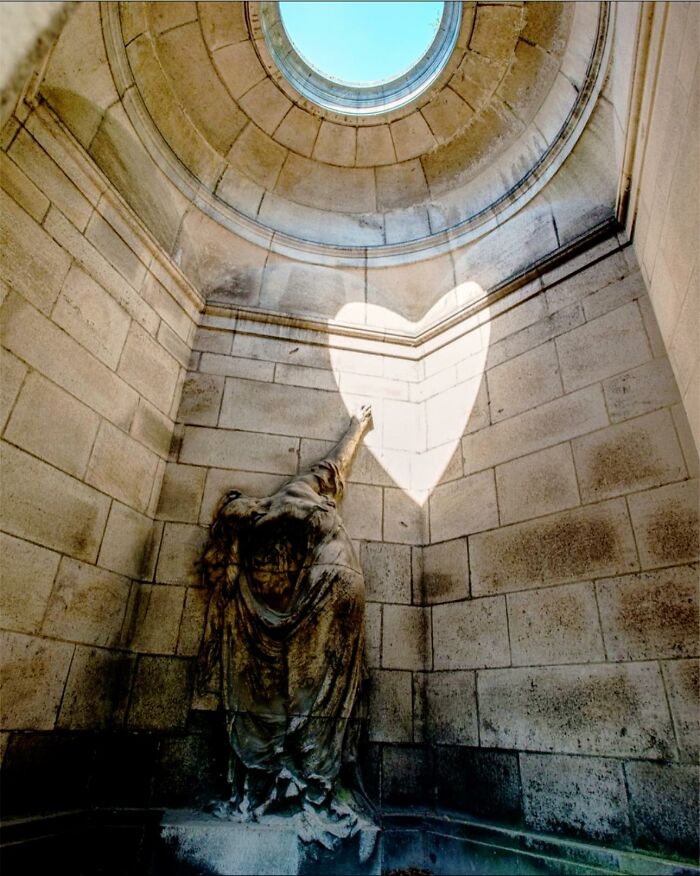
Tucked Away In The Historic Cimetière De Laeken In Brussels Lies A Mausoleum That Draws Attention Once A Year For A Truly Remarkable Display
Built in 1920 for Léonce Evrard and his wife, Louise Flignot, the tomb features a solemn sculpture of a mourner, arm outstretched toward a blank wall. However, it’s on the Summer Solstice, when the sun reaches its highest point in the sky, that the mausoleum’s true magic is revealed.
At precisely noon on June 21, sunlight pierces through an opening in the roof, creating a heart-shaped beam of light. This ethereal glow forms for just a few moments, hovering above the mourner’s hand—almost as if the figure is reaching out for this symbolic heart of light.
The phenomenon only lasts for about 15 minutes, but it has captivated visitors for decades, many of whom see it as a romantic testament to enduring love. The heart of light, cast during the longest day of the year, adds an emotional depth to the otherwise somber scene.
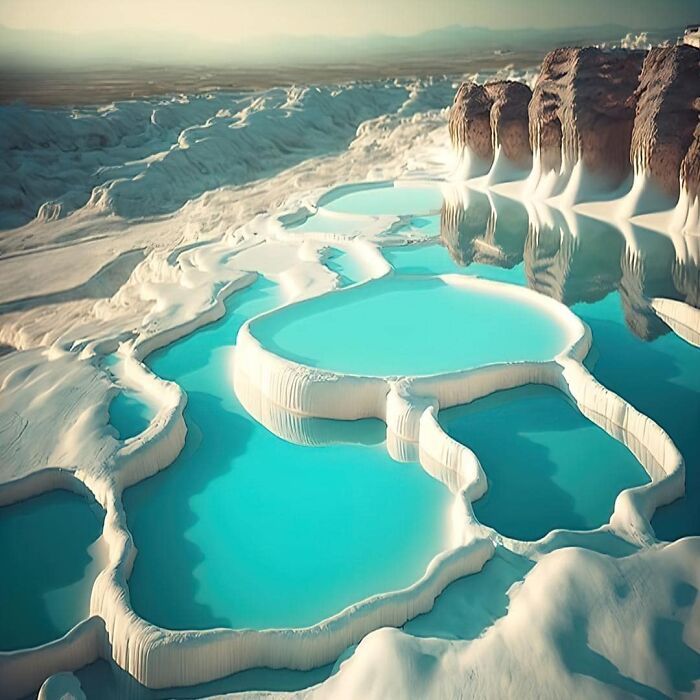
Pamukkale, Located In Southwestern Turkey, Is One Of The World’s Most Stunning Natural Wonders
Its name means “Cotton Castle” in Turkish, a fitting description for its surreal white terraces formed by the deposition of calcium carbonate from hot spring waters.
These terraces, filled with mineral-rich waters, cascade down the hillside, creating a visual spectacle of snow-white pools glistening in the sun. Pamukkale has been revered for its therapeutic qualities since antiquity.
The ancient city of Hierapolis was built adjacent to the site by the Greeks in the 2nd century BC, serving as both a healing center and a major cultural hub. People would travel from across the ancient world to bathe in the warm waters, believing them to have miraculous healing powers.
Today, Pamukkale is a UNESCO World Heritage site, combining natural beauty with historical significance. Visitors can still explore the ruins of Hierapolis and dip their feet into the same pools that were cherished thousands of years ago.
That these are such pure white is amazing. Here are some similar formations in (clockwise) Haung Long, China, Yellowstone National Park, and Carlsbad Caverns NP. Huang-Long...797e89.jpg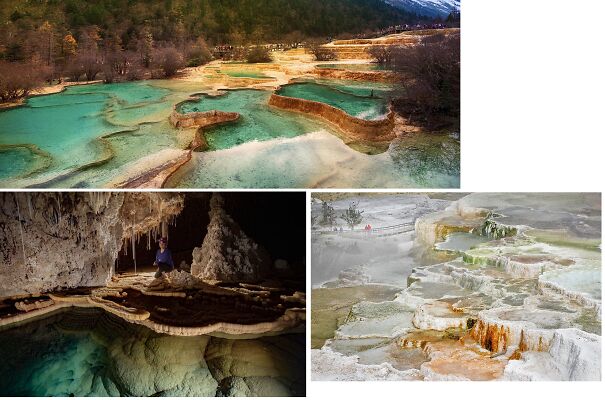 
Jonathan likely doesn’t have to worry about his followers losing interest in history anytime soon. According to a 2020 survey by Conner Prairie, 96 percent of people in the U.S. believe it’s important to look at history to inform the future. Additionally, 91 percent agree that learning about history helps build a strong foundation for what’s ahead. In fact, 42 percent of Americans report a higher level of curiosity about history compared to the previous year.
Clearly, enthusiasm for the past is on the rise. That’s why it’s great that Jonathan, along with his page and many other corners of the internet, is doing such a fantastic job of giving us exactly what we crave: fun, riveting nuggets of history that expand our knowledge and help us appreciate everything that came before us.
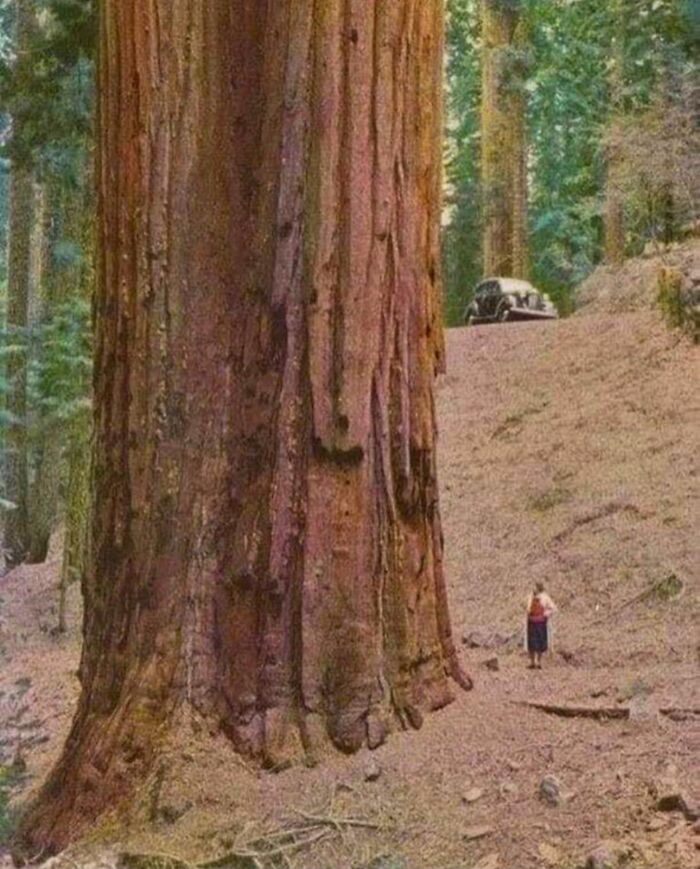
A Woman From The 1950s Stands Beside A Towering Redwood Tree
Redwood trees, among the tallest and oldest living organisms on Earth, dominate the coastal forests of Northern California. These majestic giants can reach heights of over 350 feet and live for more than 2,000 years, showcasing a resilience that has captivated nature lovers for centuries.
Their thick, reddish-brown bark is not only visually striking but also serves as a protective layer against pests and fire. The unique ecosystem they create supports diverse wildlife, from towering canopies filled with birds to the rich undergrowth teeming with life. As symbols of endurance and beauty, redwoods remind us of the importance of conservation and our connection to nature.
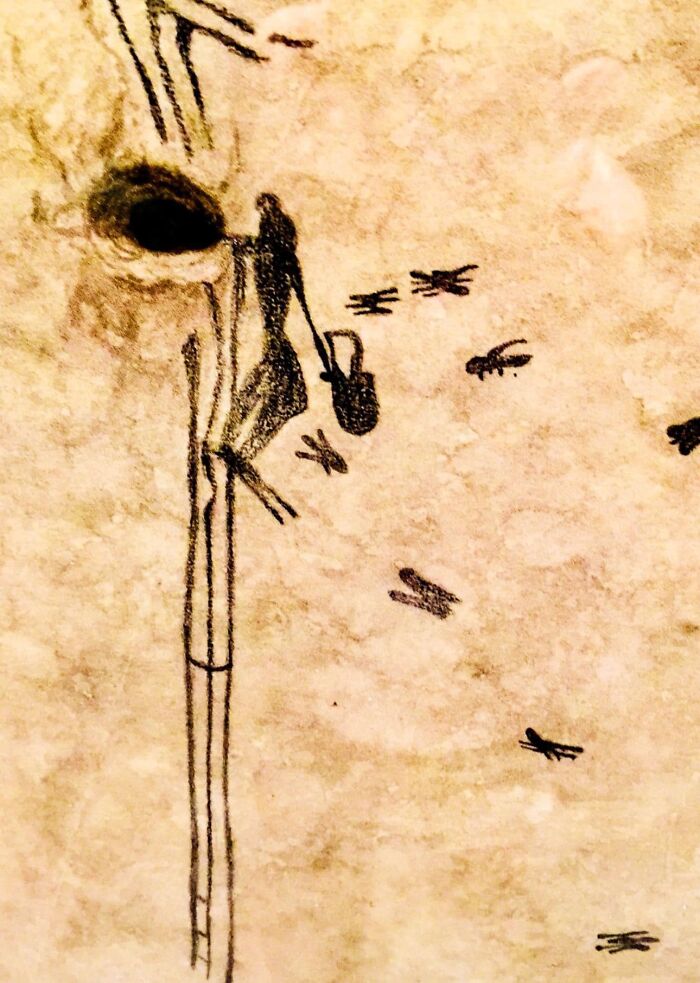
The Oldest Recorded Evidence Of Honey Collecting, Found In The Cuevas De La Araña Near Bicorp, Spain, Is Estimated To Be Between 8,000 To 10,000 Years Old
This Mesolithic cave painting depicts a person climbing to reach a wild bees' nest, with bees flying around and honeycombs visible, providing early documentation of human honey harvesting activities.
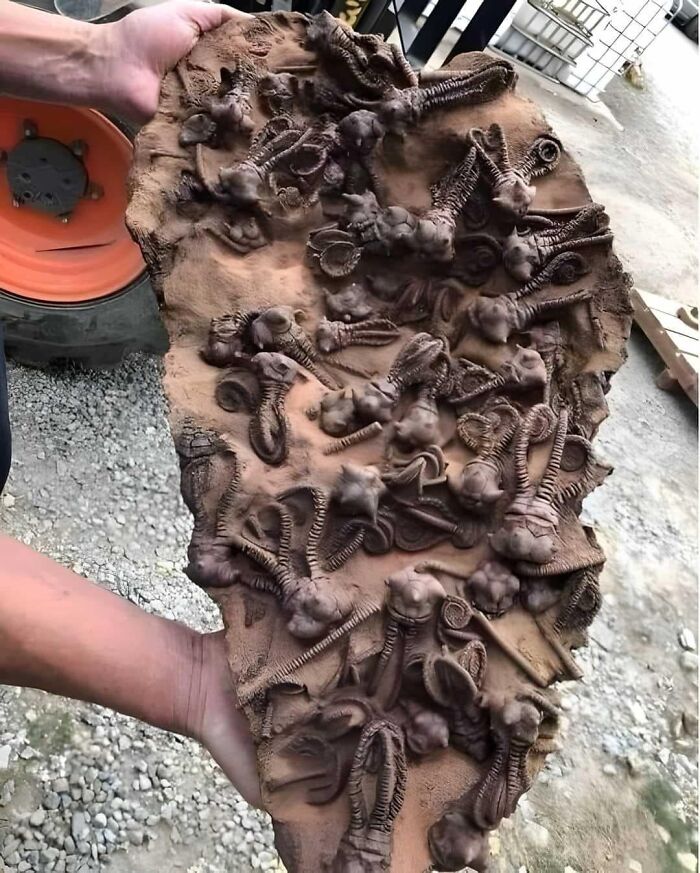
Jimbacrinus Crinoid Fossils From Gascoyne Junction, Western Australia, Offer A Rare Glimpse Into Life 250 Million Years Ago
These ancient sea creatures, with their stem-like bodies and feathery arms, once thrived in shallow waters.
Their stunning preservation reveals a rich marine ecosystem that existed before the devastating Permian extinction, when massive volcanic eruptions, global warming, and ocean acidification wiped out nearly 90% of marine species.
These fossils help unlock the mysteries of Earth’s deep history and the dramatic changes that followed this catastrophic event.
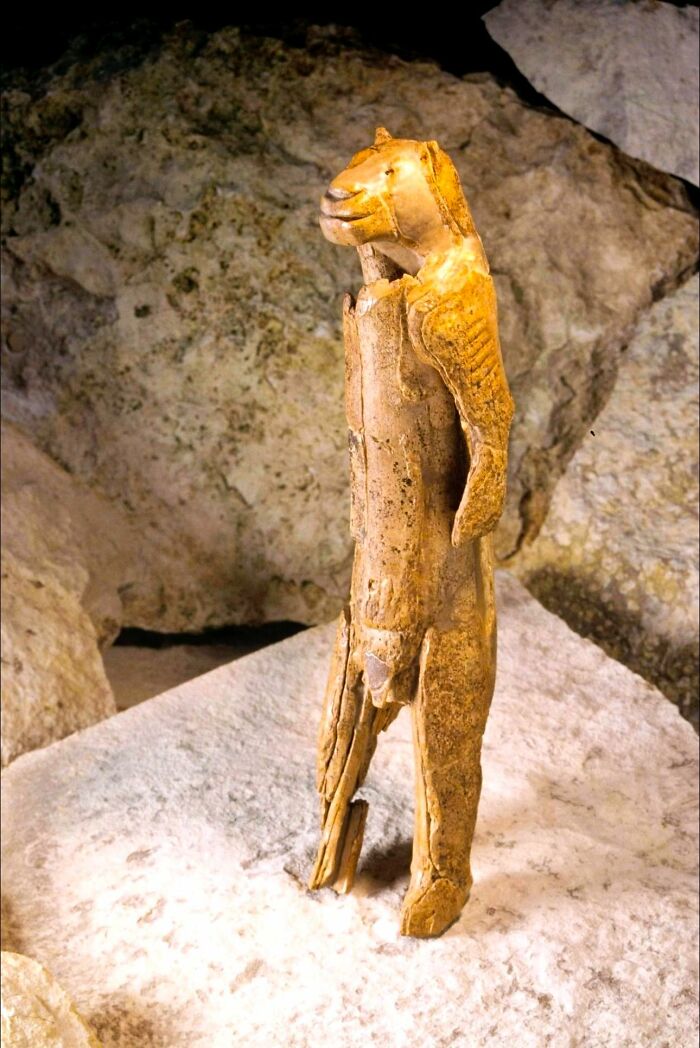
The Lion-Man, Carved From Mammoth Ivory Roughly 38,000 Years Ago, Stands As The Oldest Known Example Of Figurative Art
Discovered in a cave in Germany, this enigmatic sculpture merges human and animal features in a way that challenges understanding—both hauntingly familiar and strikingly otherworldly. It offers a profound glimpse into the creative genius of early humans, hinting at their capacity for imagination and symbolic thought.
Remarkably, the Lion-man predates the advent of known written language by more than 30,000 years. To put that in perspective, it is older than Stonehenge by tens of thousands of years. This ancient artifact showcases an extraordinary leap in artistic expression, marking one of the earliest examples of humans conveying complex ideas long before written records existed
Think about that. That person knew what a lion (or the local puma variant) looked like, then killed a mammoth, in germany, and carved that art out of the tooth of it. 38,000 years ago.
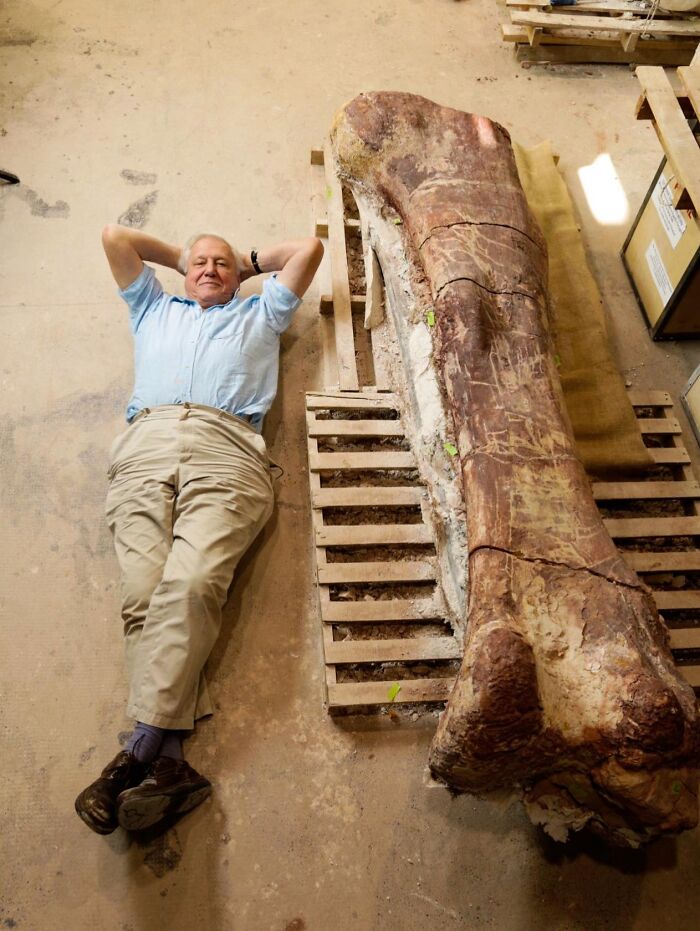
Sir David Attenborough Is Pictured With A Colossal Thigh Bone From A Titanosaur, One Of The Largest Dinosaurs Ever To Walk The Earth
In 2013, a shepherd in Argentina’s Chubut Province made a remarkable discovery on La Flecha farm, spotting the tip of a massive fossil bone protruding from the ground.
This led to an excavation by paleontologists, who uncovered the 2.4-meter (8-foot) femur, along with over 220 bones from at least seven titanosaur individuals. The dinosaur, estimated to be 37 meters long and weighing around 70 tonnes, is believed to have lived approximately 100 million years ago, making it the largest known species to have ever existed.
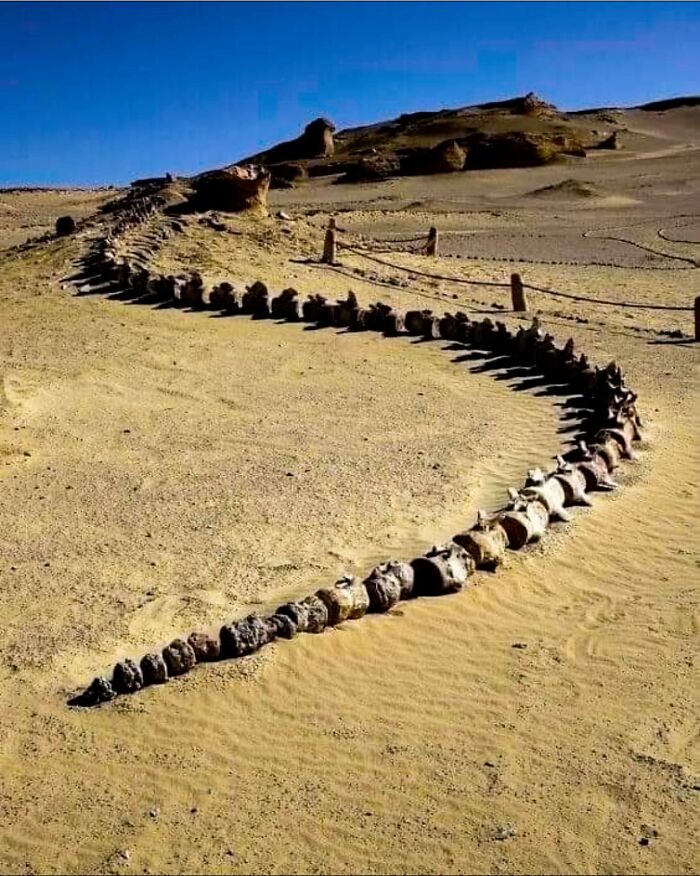
In The Arid Expanse Of Wadi Al Hitan, An Egyptian Desert Region, A 37-Million-Year-Old Whale Skeleton Has Been Uncovered
This site, known as the Valley of the Whales, has revealed dozens of rare fossilized whale skeletons, offering invaluable insights into prehistoric marine life.
To safeguard these remarkable discoveries and promote their study, a dedicated museum has been established at the site. This museum not only helps preserve the fossils but also serves as an educational hub, shedding light on the evolutionary history of whales and the ancient environments they inhabited
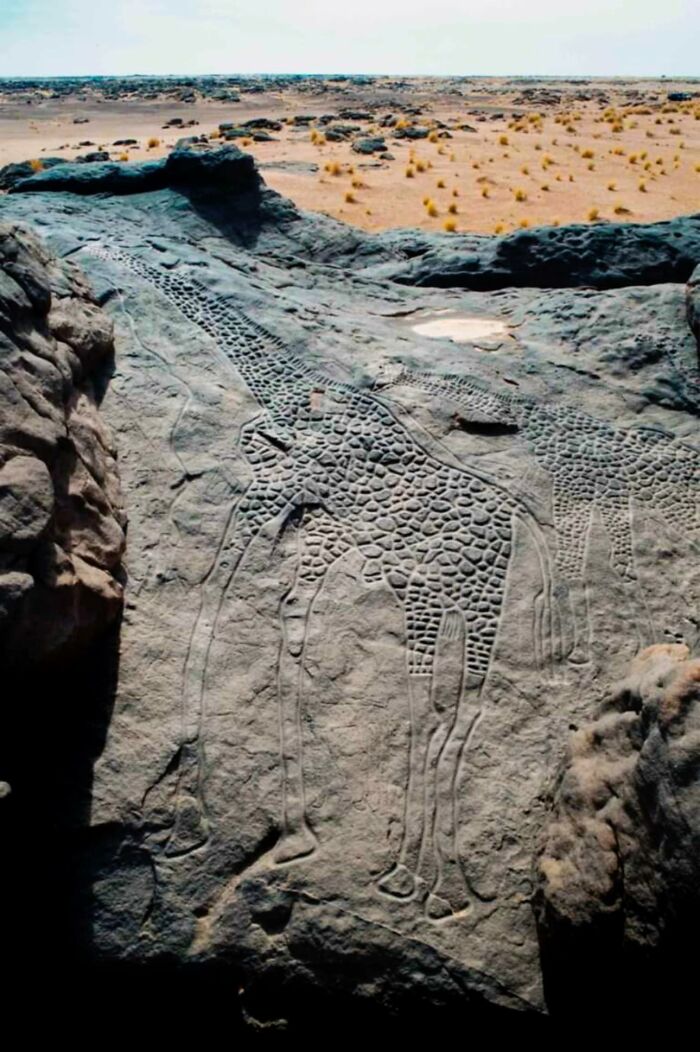
Over 9,000 Years Ago, When The Sahara Was A Thriving Savanna, Ancient Artists Carved A Remarkable Scene Into The Rocks Of What Is Now Niger’s Desert
Hidden in the Aïr Mountains, the Dabous giraffe carvings stand as a testament to a time when this vast desert was full of life.
These carvings depict two life-sized giraffes, with one led by a human figure, capturing a moment of interaction between man and nature. Each giraffe, stretching over 18 feet in length, was etched with care, reflecting the importance of these animals to the people of that era.
Today, the Dabous carvings are considered some of the most significant prehistoric rock art in Africa, offering a rare glimpse into a world long lost to the desert sands. They remind us that the Sahara, now barren, was once a green and vibrant landscape, alive with both humans and wildlife
I sort of knew the Sahara region was not a completely barren desert back then. But I did not expect it was this recent. Recent enough for modern humans to exist and thrive there.
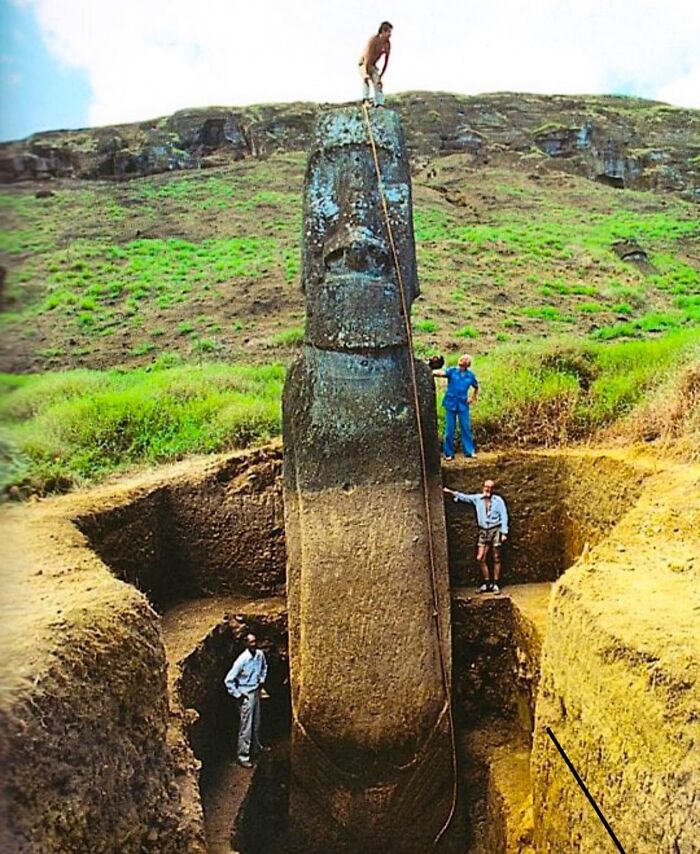
A Fully Unearthed Moai Statue On Easter Island
The Easter Island statues are iconic monolithic human figures carved by the Rapa Nui people on Easter Island in eastern Polynesia between the years 1250AD and 1500AD. They are believed to represent ancestors and were placed on ceremonial platforms called Ahu. The construction and transportation of these massive statues, some weighing up to 80 tons, remain a subject of fascination and study due to the island's remote location and the engineering feats involved.
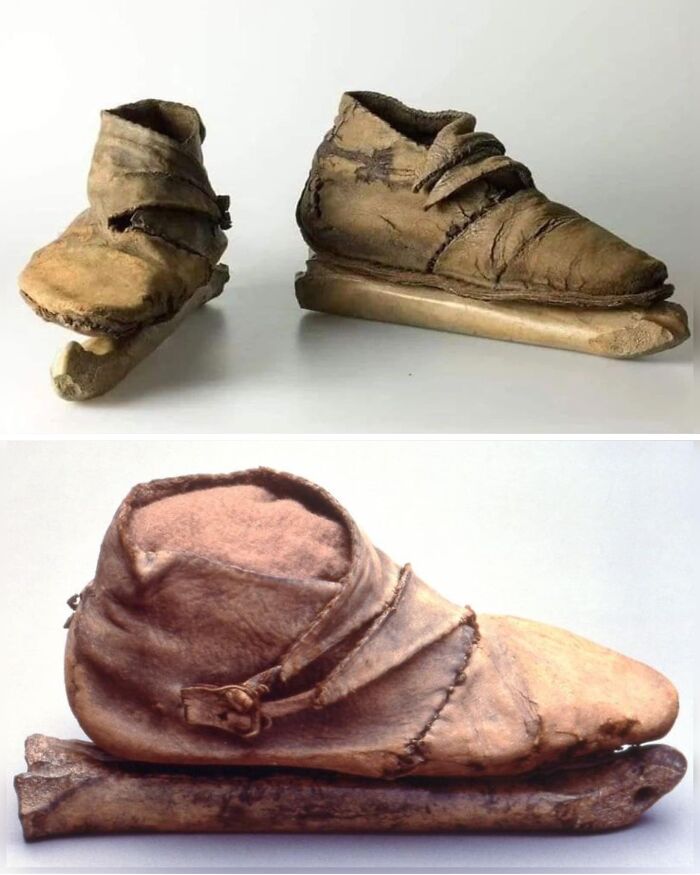
Viking Ice Skates Dating Back To The 10th Century Ad; Made Of Leather And Horse Bone
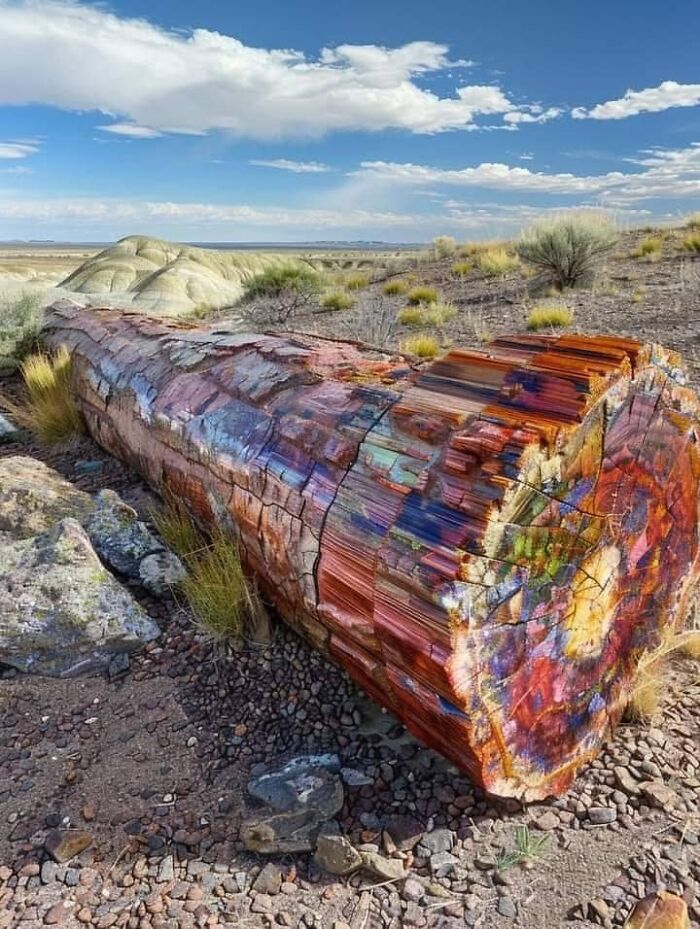
Petrified Forest National Park, Located In Northeastern Arizona, Is A Stunning Landscape Filled With Ancient Fossilized Trees, Colorful Desert Vistas, And Unique Geological Formations
The park covers about 346 square miles and preserves one of the world’s largest concentrations of petrified wood, some dating back over 225 million years to the Late Triassic period.
The petrified wood found here once belonged to massive conifer trees that grew in lush river ecosystems. Over time, volcanic ash buried the fallen trees, and minerals like quartz slowly replaced the organic material, turning them into stone. These colorful logs shimmer in hues of red, orange, and purple, scattered throughout the park
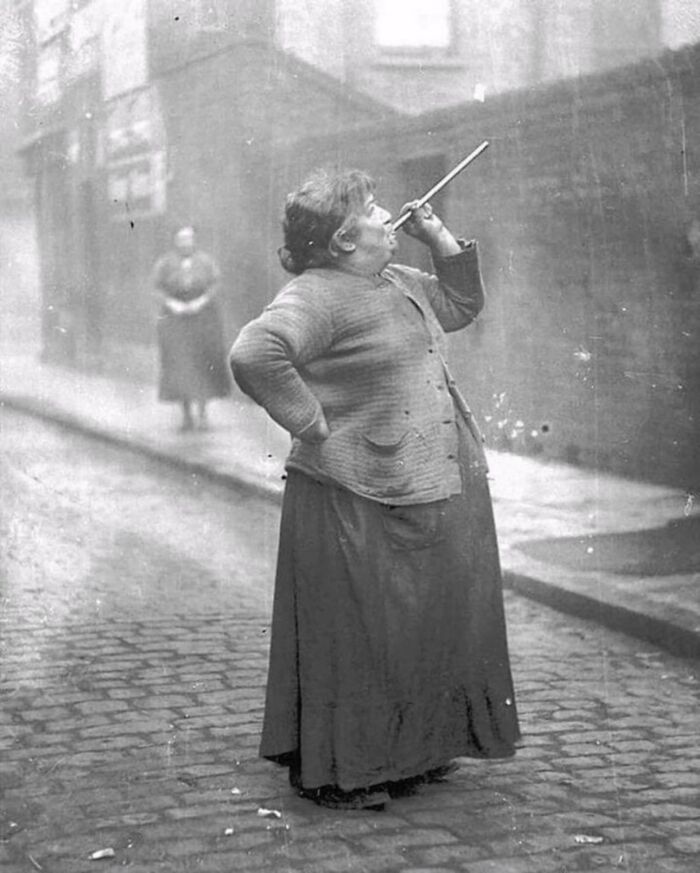
Mary Smith, A Famous London Knocker-Upper Who Earned Six Pence A Week Per Client By Waking Them With A Pea Shooter That Tapped On Their Windows
This unique service was essential in the early 20th century, before alarm clocks became widely available.
Who woke up the knocker-upper? How did they get up on time? Does anyone know?
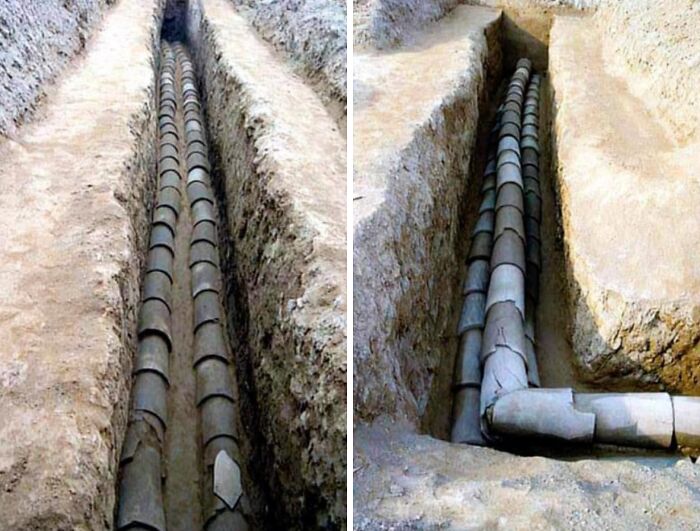
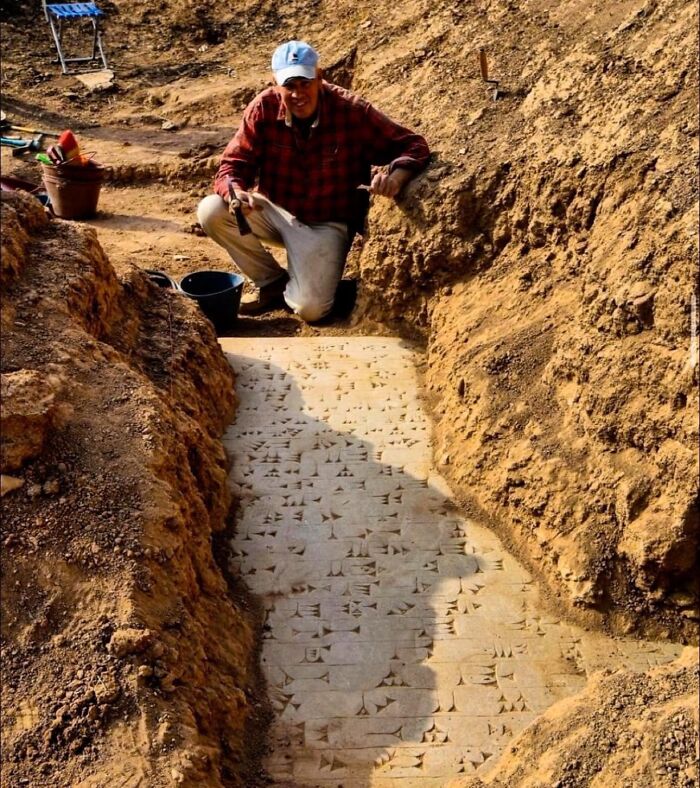
4,000 Year Old Chinese Ceramic Water Pipes Discovered At The Pingliangtai Archaeological Site In The Central Plains Of China
Utilizing advanced engineering and urban planning, these Neolithic people effectively managed water flow and prevented flooding in the ancient settlement.
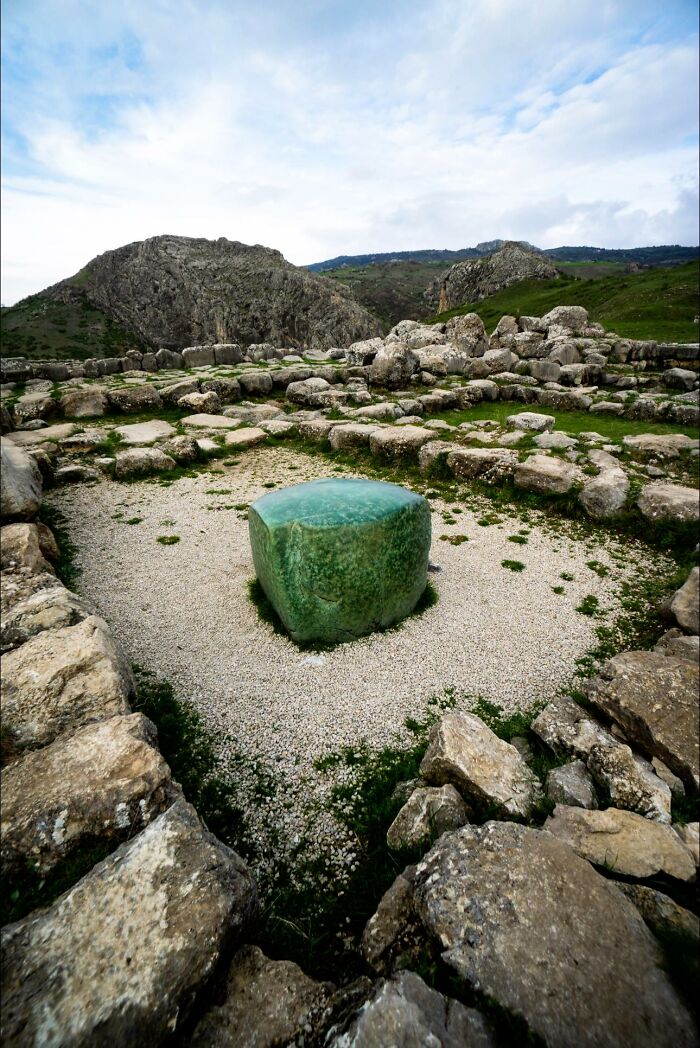
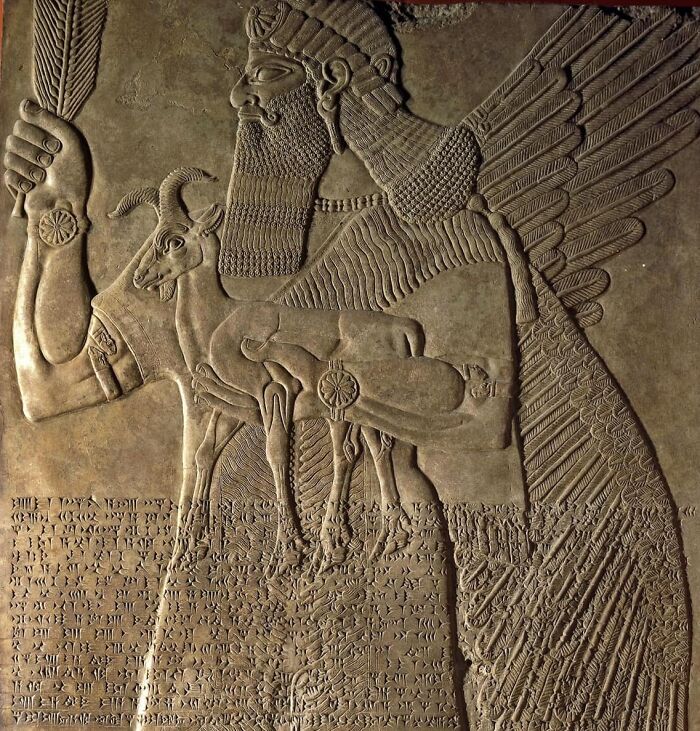
In The Heart Of Hattusa, The Former Capital Of The Hittite Empire In Modern-Day Turkey, Lies A Mysterious Green Stone, Believed To Be Made Of Serpentinite
This stone, housed in the temple complex, likely played a crucial role in Hittite religious practices before the city's destruction around 1200 BC. Its exact purpose remains unknown, adding to the intrigue that surrounds this ancient relic.
And for the ancient Greeks this may have turned into Gaia's navel stone (which some mythologists locate at Delphi anyway)...🪨
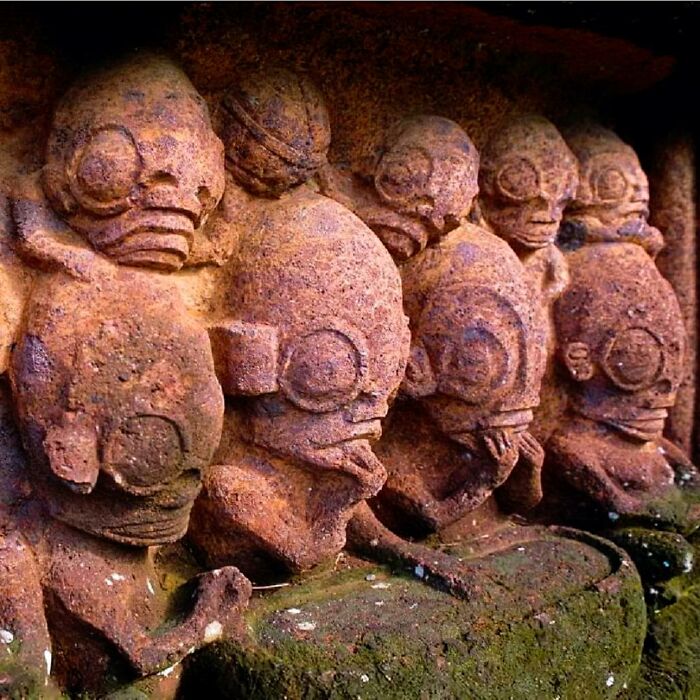
The Bison Sculptures Found In The Le Tuc D’audoubert Cave In Ariège, France
Extraordinary examples of prehistoric art, estimated to be around 14,000 years old. Dating back to the Upper Paleolithic period, specifically the Magdalenian culture, these sculptures depict two bison and are remarkable for their detail and realism.
Discovered in 1912 by the three teenage sons of the French count Henri Begouën, the sculptures have been well-preserved due to the cave’s stable environment. Crafted in high relief from clay, the bison showcase the skill and artistic ability of prehistoric humans. The artists used their hands, fingernails, and simple tools to shape the clay, creating lifelike textures and details such as fur and muscle structure.
This is probably a dumb question but I genuinely don’t know. How do we know this was prehistoric and not someone in the 1500s? (It would still be old and is still pretty amazing, but how do they date rock as to when it was carved?)
They can carbon date anything with charcoal, which is how they date many drawings, but engraved or sculpted stone or red paintings can be estimated by the build up of certain materials on the surface of the work. For example: a rock would have mineral deposits on it, which would be destroyed when it was carved. Then new deposits would form. They know how long it takes for those deposits to form. Not a stupid question. I have a background in archeology and didn't know this. I had the read the scientific article on dating to find out.
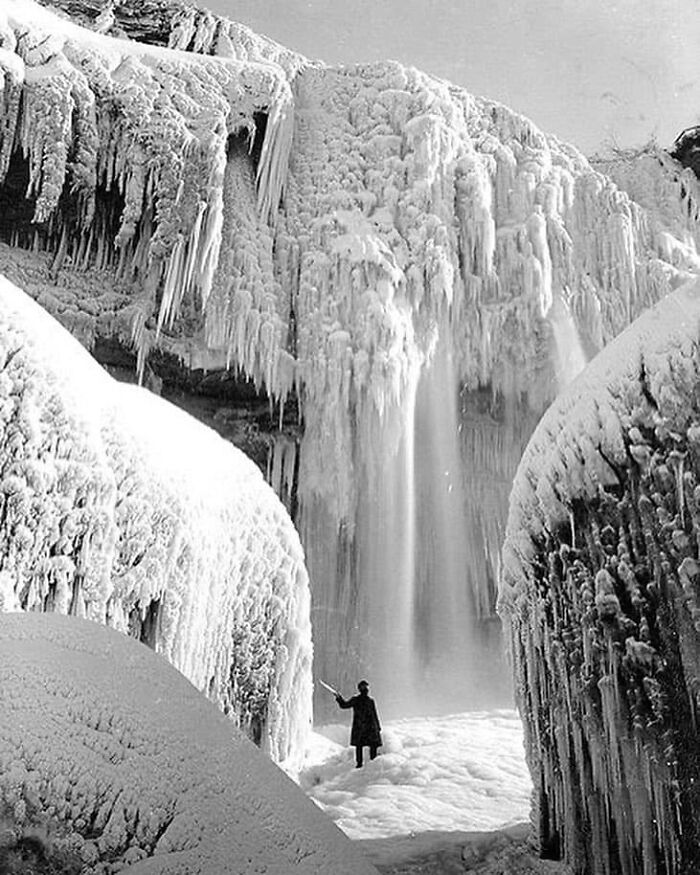
Load More Replies...Niagara Falls As A Breathtaking Spectacle Of Ice In The Early 1900s, Showcasing One Of The Rare Times It Has Frozen Over
I do have a postcard showing Niagara Falls completely frozen over. And it is much more recent than this. I'd say in the 1980's - to 1990's.
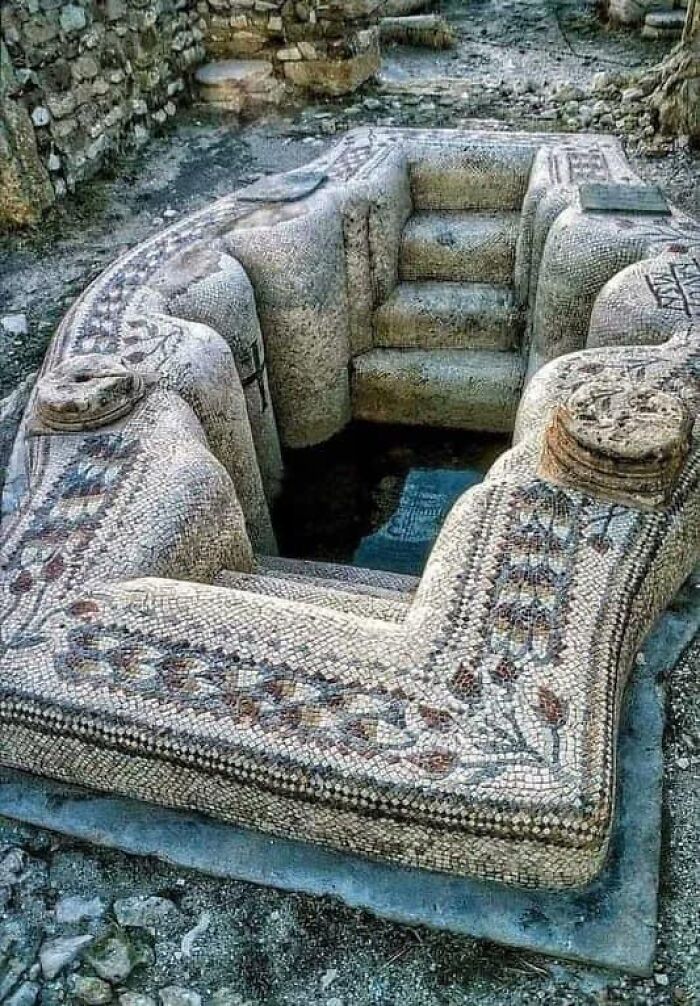
In 2021, Archaeologists In Sbeitla, Tunisia, The Ancient City Of Sofitola, Uncovered A 1,500-Year-Old Byzantine Bathtub
Made from stone, this tub exemplifies the region’s advanced craftsmanship and the luxurious lifestyle during the Byzantine period. The discovery provides insight into the wealth and sophistication of the city, revealing how even provincial towns like Sbeitla embraced high standards of architecture and infrastructure.
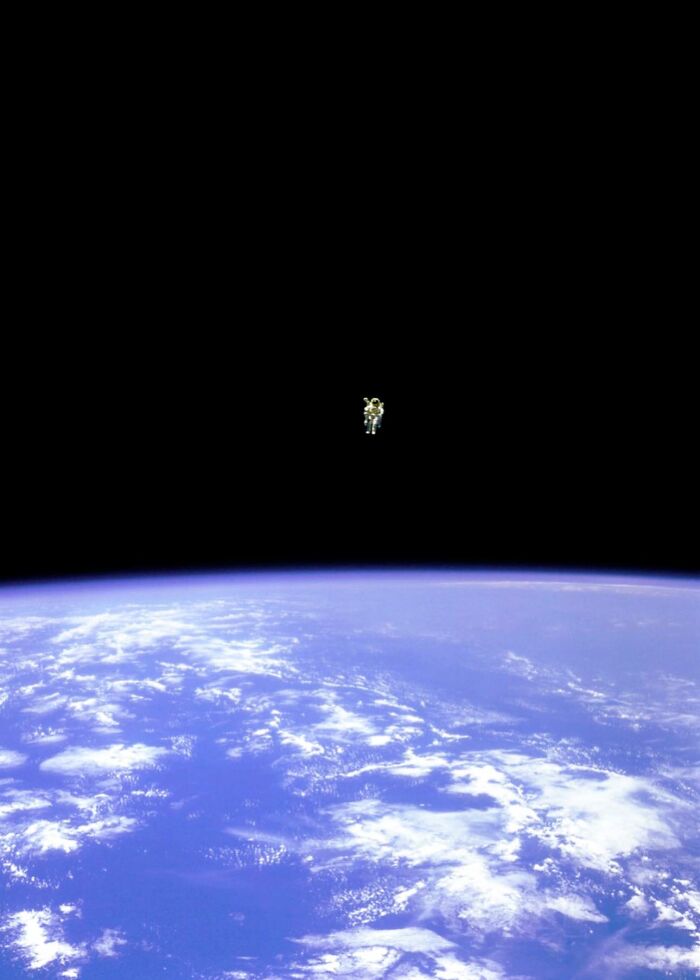
Bruce Mccandless Made History As The First Human To Float Freely In Space Without Any Tether To A Spacecraft
On February 7, 1984, during the STS-41-B mission, he ventured into the vast expanse equipped only with his Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), a jetpack-like device that allowed him to navigate in zero gravity. Drifting away from the safety of the space shuttle Challenger, McCandless became a solitary figure against the backdrop of the cosmos, relying solely on the MMU's thrusters to control his movements.
This daring maneuver was more than a technical achievement; it symbolized the human drive to explore the unknown and push the boundaries of space travel. McCandless’s untethered spacewalk remains an iconic moment, showcasing both the bravery of astronauts and the remarkable advancements in space technology that made such feats possible.
While it is an amazing achievement and photo... I have to say... Aw hell naw...
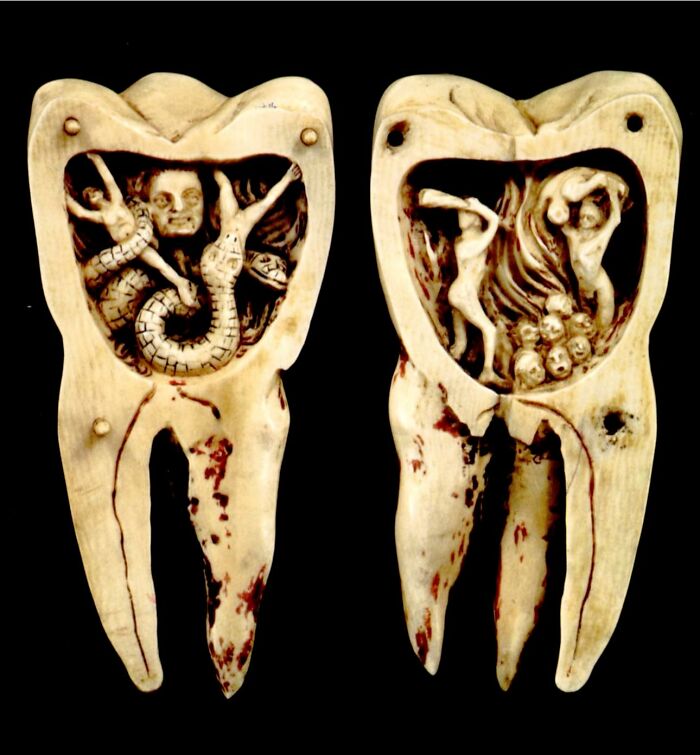
This Illustration Is An 18th-Century Depiction Of A Once-Common Belief That Toothaches Were Caused By Small, Demonic Creatures Known As "Tooth Worms"
In this folklore, the tooth worm was imagined as a malevolent entity burrowing into teeth, causing decay and pain. Before modern dentistry, people believed that the writhing of these worms within the tooth was the source of excruciating discomfort.
The concept dates back to ancient civilizations, but it endured well into the 18th century. Artists often portrayed the tooth worm as a demon from hell, adding to the fear and mystery surrounding dental ailments in a time when treatment was rudimentary and pain was inescapable.
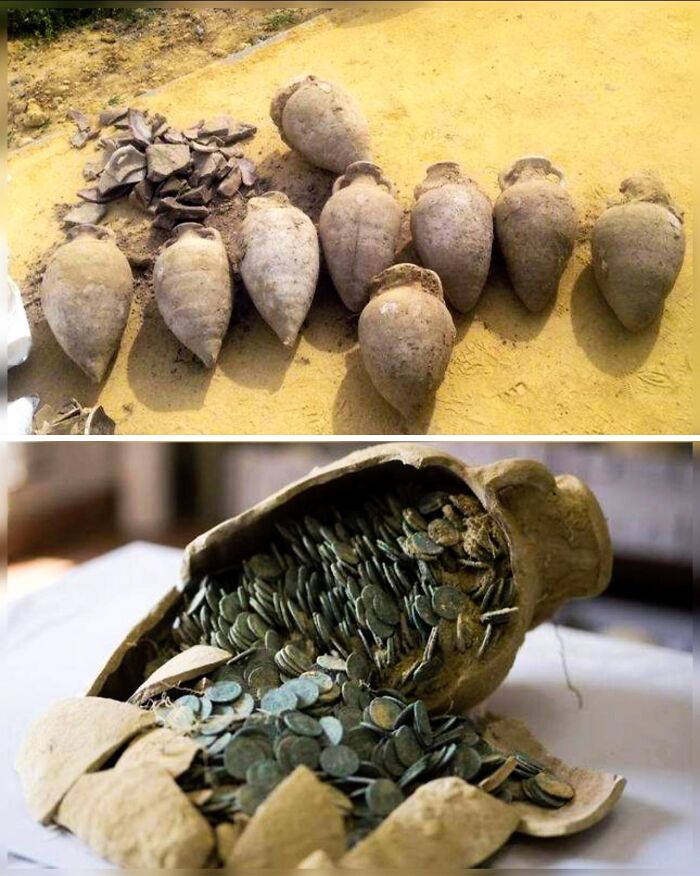
In April 2016, Construction Workers In Tomares, A Suburb Of Seville, Spain, Made A Serendipitous Discovery While Installing Electricity In El Zaudín Public Park
Using a mechanical digger, they unearthed a remarkable trove of Roman coins hidden in 19 large ceramic amphorae, buried about a meter underground. While the digger damaged 10 of the amphorae, nine remained intact and sealed. This hoard, weighing over 1,300 pounds and containing more than 50,000 bronze coins from the late third and early fourth centuries AD, was concealed with bricks and ceramic filler.
The workers halted their project and alerted authorities, prompting an excavation by archaeologists. By November 2022, experts from the University of Seville had completed their analysis, confirming the find as the largest Roman coin hoard ever discovered in Spain. This extraordinary cache provides invaluable insights into Roman economic history and highlights the strategic measures taken to safeguard wealth during that era.
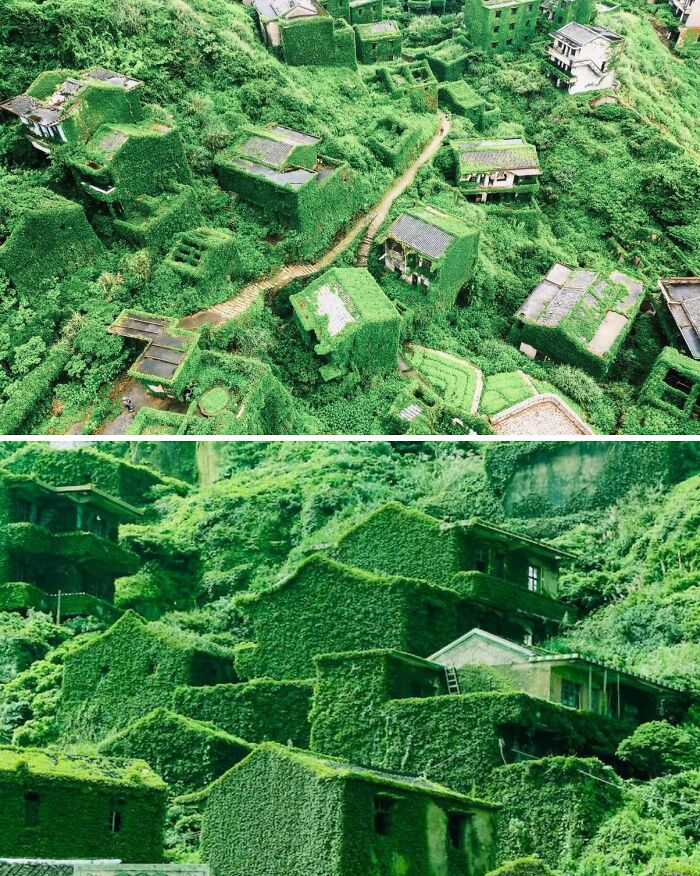
Houtouwan, Once A Thriving Fishing Village On Shengshan Island Off The Coast Of China, Is Now A Remarkable Example Of Nature Reclaiming Human Spaces
Abandoned in the 1990s due to its remote location and difficulty in accessing resources, the village’s stone houses are now completely overrun with thick green vegetation. Ivy and creeping plants have consumed the walls and roofs, creating a hauntingly beautiful landscape where the remnants of human life are barely discernible beneath layers of greenery.
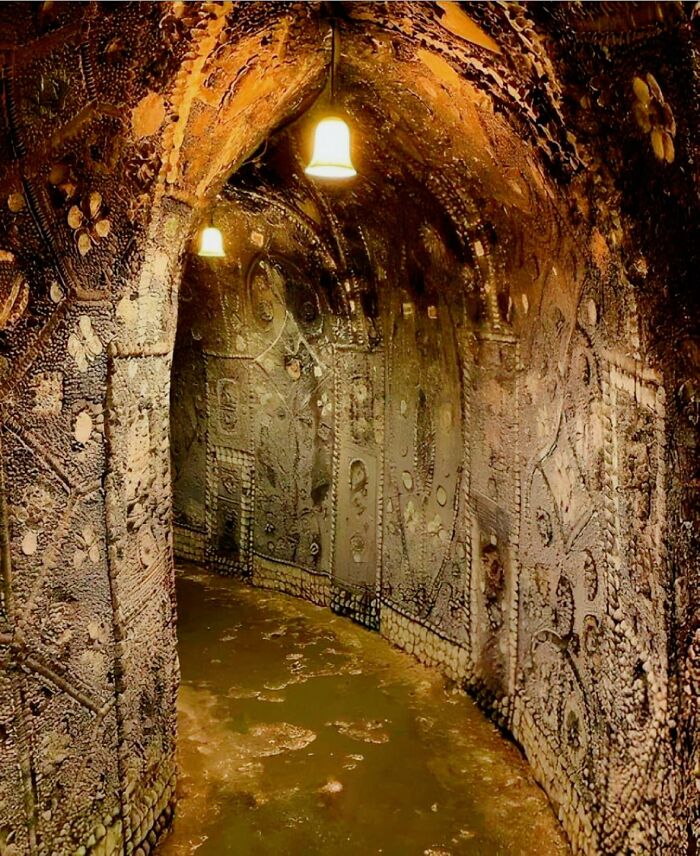
Underground Caves Lined With Millions Of Shells, And No One Knows Who Built Them
The Shell Grotto in Margate, Kent, England, stands as one of history’s most baffling mysteries. Discovered in 1835, this hidden passageway is adorned with over 4.6 million meticulously arranged shells, forming elaborate mosaics that cover every inch of its walls and ceilings. The designs are precise and intricate, depicting symbols, patterns, and figures whose meanings remain shrouded in mystery.
What makes the grotto so compelling is that no one knows who created it, when, or why. Some speculate it dates back to ancient times, possibly as far as the Roman or Phoenician period, while others believe it was constructed in the medieval era or even the 18th or 19th century by an eccentric individual. Was it a secret temple, a meeting place for a hidden society, or a mysterious art project? Theories are abundant, but definitive answers are nonexistent. The Shell Grotto is more than just a stunning piece of craftsmanship; it’s a riddle that continues to confound experts and captivate visitors from around the world.
Probably was some bored retiree that had boxes of seashells from holiday and an old passageway in need of sprucing up.
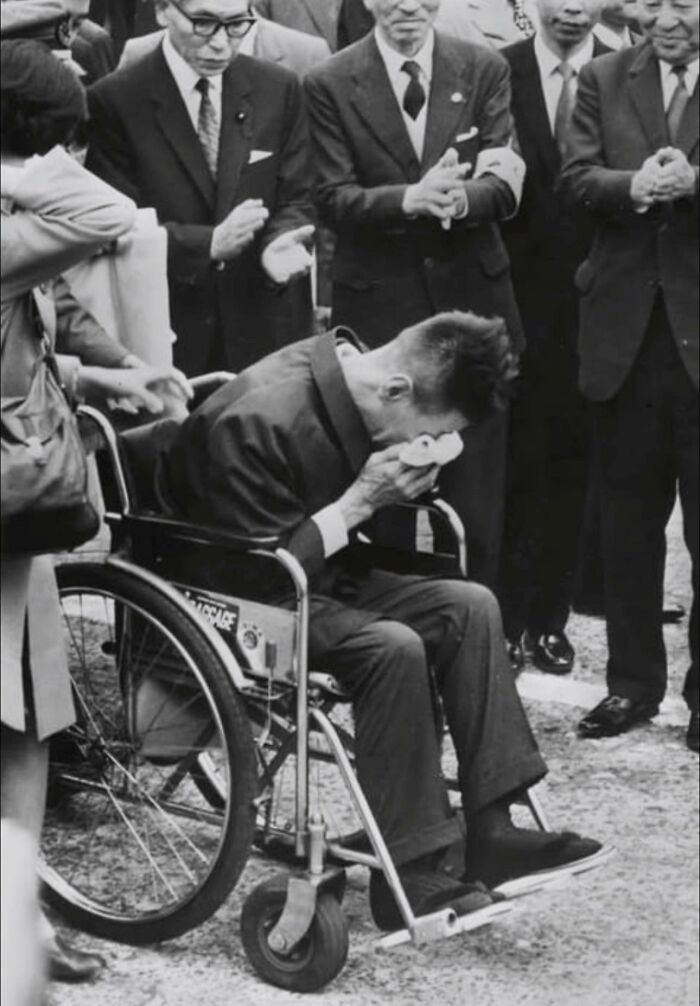
Shoichi Yokoi Was A Japanese Soldier Who Hid In The Jungles Of Guam For 27 Years After World War II Ended, Unaware That The War Was Over
He avoided capture out of fear and loyalty to the Imperial Japanese Army’s orders to never surrender.
Yokoi was discovered in January 1972 and returned to Japan in February of that year. Upon his return, he was overcome with emotion and wept, as it was his first time back in Japan since the war.
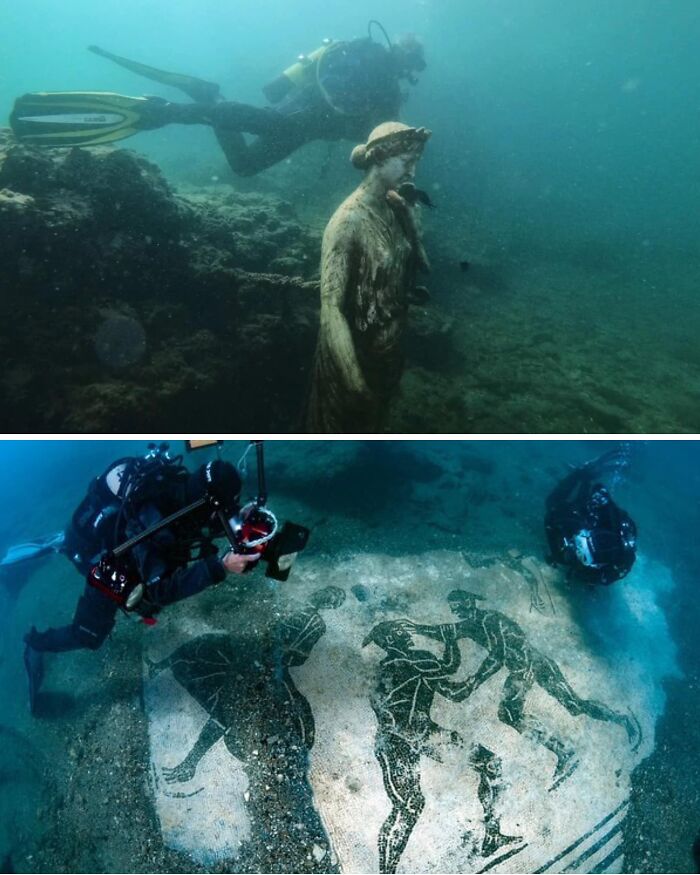
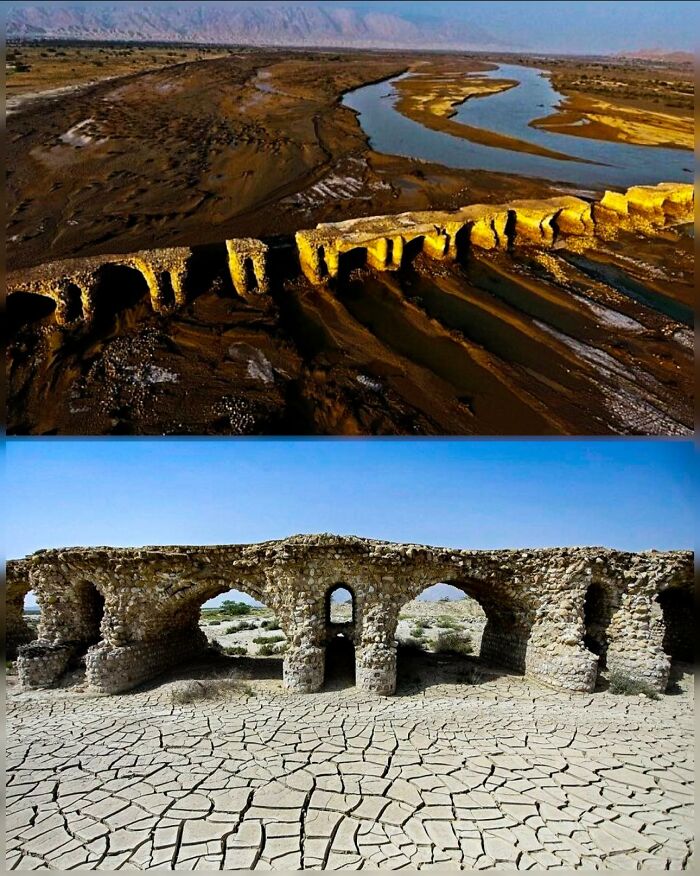
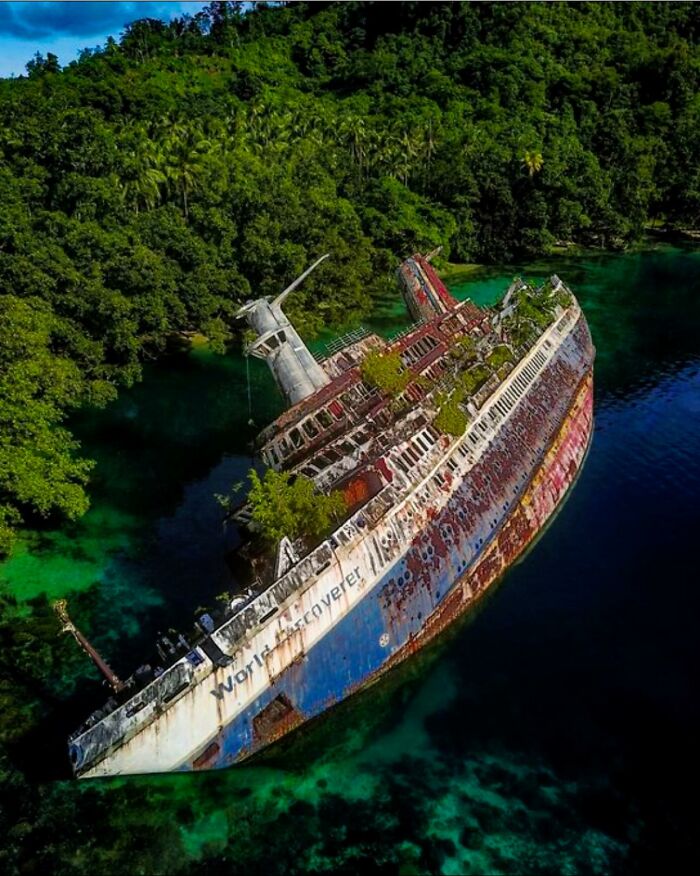
Once A Lavish Roman Resort Located On The Northwest Shore Of The Gulf Of Naples, Baiae Was The Playground Of Emperors Like Nero And Julius Caesar, Famed For Its Opulent Villas, Hot Springs, And Scandalous Reputation
Known for corruption and excess, it was a place where Rome’s elite indulged in debauchery and political schemes.
However, the same volcanic activity that powered its famous hot springs ultimately sealed its fate. Due to a process called bradyseism, the land slowly sank from volcanic activity beneath the surface, causing much of the city to gradually submerge, taking its grandeur with it beneath the waves.
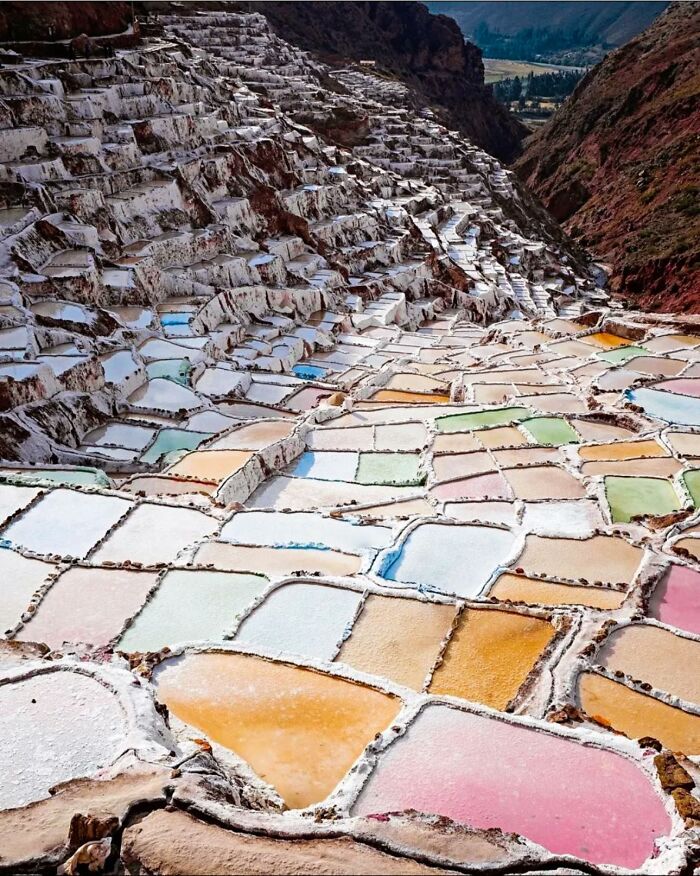
The Maras Salt Mines, Located In Peru's Sacred Valley, Are An Ancient Site Where Salt Has Been Harvested For Over 2,000 Years
These mines consist of over 5,000 small, terraced salt pans that stretch across a mountainside. The salt is collected from a natural underground stream that fills the pans with mineral-rich water. As the water evaporates in the sun, it leaves behind salt crystals.
The history of the Maras salt mines dates back to before the Inca Empire, making them one of the oldest known salt production sites in the world. The Incas took control of the mines and used the salt as a key resource for trade and preservation. Remarkably, the traditional methods of salt harvesting at Maras have been preserved and are still used today by local families.
These salt mines are not only a significant historical site but also a living part of the local culture, where ancient practices continue in the modern world. The Maras salt mines offer a unique glimpse into the past, showing how ancient civilizations utilized natural resources in ways that remain relevant today.
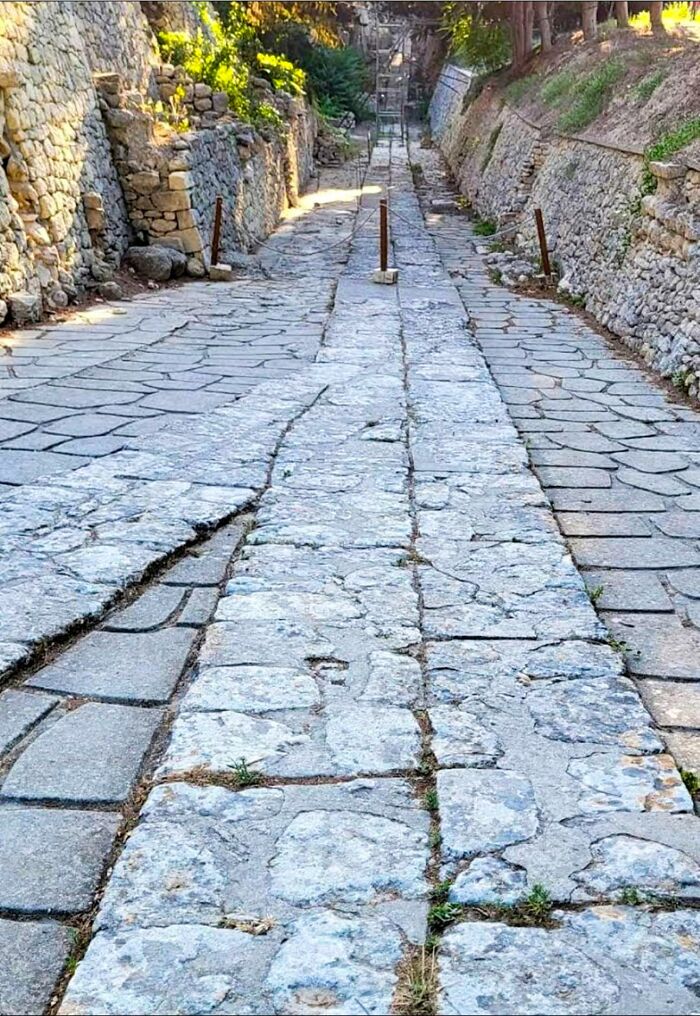
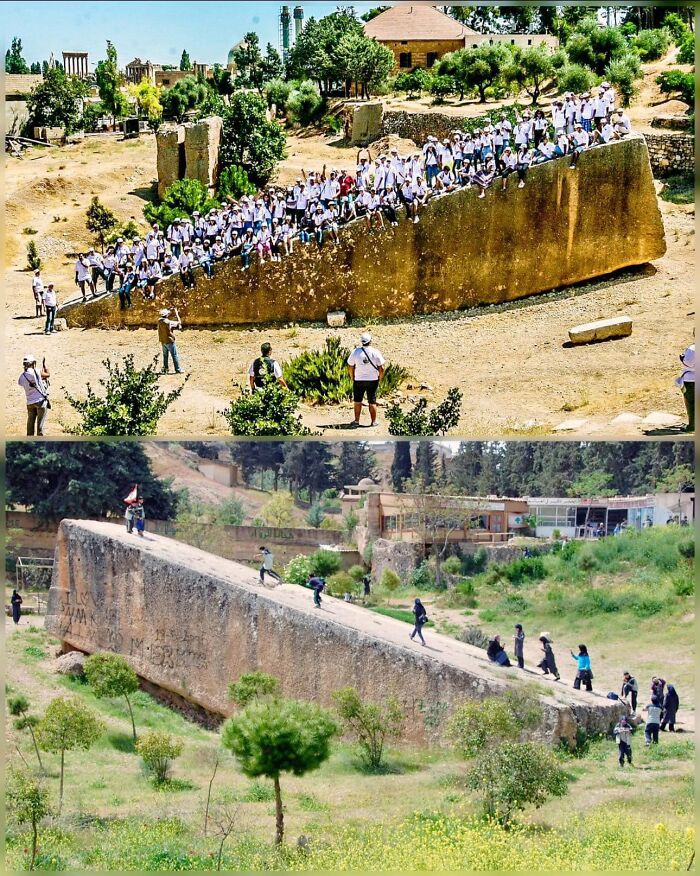
Europe’s Oldest Known Road Lies On The Island Of Crete, A Remarkable Engineering Feat Over 3,500 Years Old
This Minoan road spans roughly 50 kilometers, connecting the ancient city of Knossos with Gortyn and Lebena.
What makes this road so extraordinary is its advanced construction. It features side drains to manage water runoff, which helped preserve the road over millennia. The roadbed is composed of a 20-centimeter-thick pavement of sandstone blocks, tightly fitted and bound with a durable clay-gypsum mortar.
On top of this foundation, a layer of basaltic flagstones was laid to provide a smooth, hard-wearing surface. The inclusion of separate shoulders, which were uncommon for the time, demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of road design, ensuring safe and efficient travel.
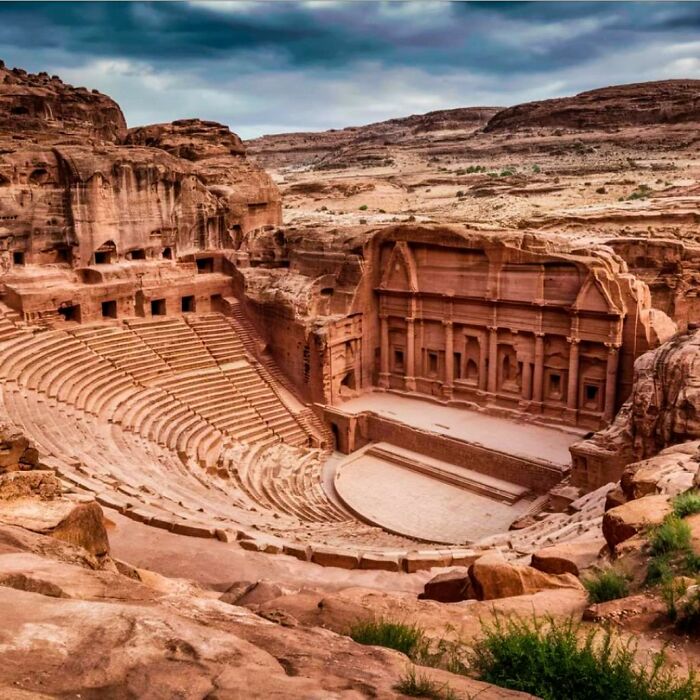
Petra Theater, Constructed During The 1st Century Ad In Petra, Jordan, Exemplifies The Advanced Engineering And Architectural Prowess Of The Nabataeans
This impressive structure features a semi-circular auditorium meticulously carved out of the local sandstone, with the seating area divided into three horizontal tiers, separated by broad passageways and accessible via seven stairways.
The theater's stage and external walls, built from dressed stone, complement the rock-carved auditorium. With a capacity of up to 3,000 spectators, Petra Theater was a central venue for public performances and gatherings, reflecting the cultural and social significance of the Nabataean civilization.
The theater's integration of rock-cut and constructed elements highlights the innovative blend of natural and man-made materials, showcasing the Nabataeans' exceptional architectural skill.
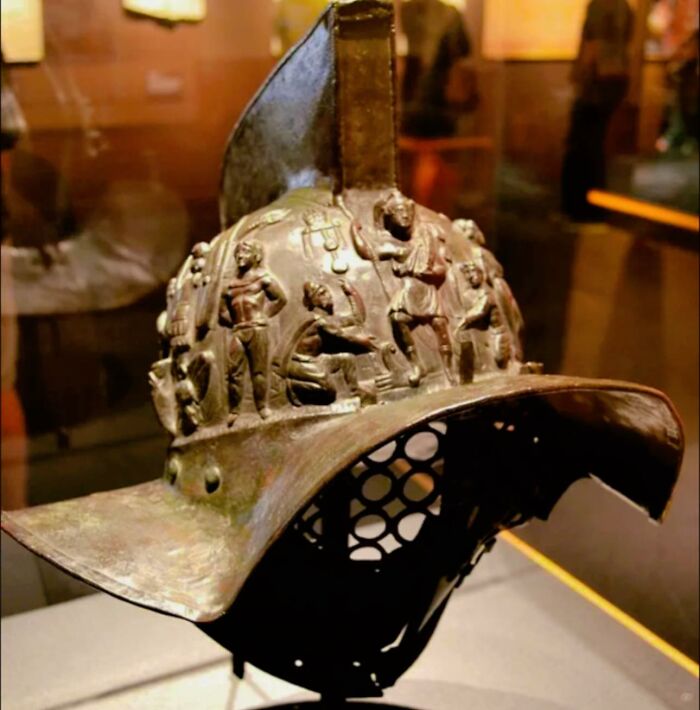
In 2009, Archaeologists Unearthed A Striking Gladiator Helmet From Pompeii’s “Gladiators’ Barracks” (Regio V), Offering A Captivating Glimpse Into Ancient Roman Combat
This helmet, crafted from bronze and featuring intricate engravings, belonged to a murmillo—a type of gladiator known for his distinctive fish-shaped helmet. The murmillo’s high crest and broad rim were designed to resemble a fish, and the term “murmillo” itself is derived from the Greek word for a type of saltwater fish.
The murmillo’s gear also included a loincloth, a belt, short greaves protecting his lower legs, a linen arm guard for his right arm, and a curved rectangular shield. He wielded a gladius, the short, straight sword from which gladiators took their name. The helmet’s detailed craftsmanship and its connection to the murmillo’s unique fighting style highlight the fierce and dramatic nature of gladiatorial contests in ancient Rome.
This find not only enriches our understanding of Roman gladiatorial equipment but also vividly illustrates the cultural and social dynamics of Pompeii, preserved under volcanic ash since the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD.
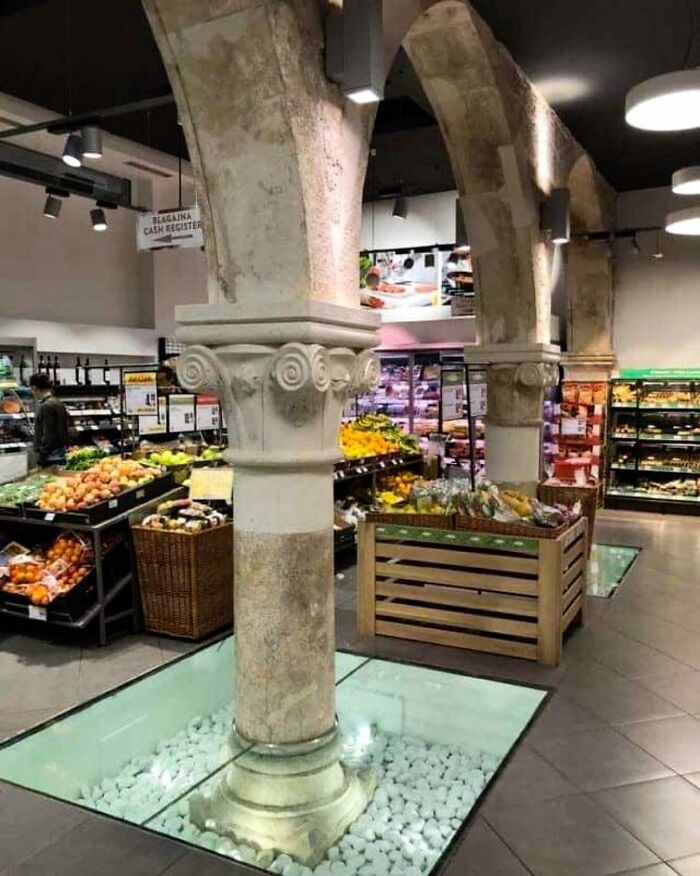
In The Center Of Split, Croatia, There’s A Grocery Store With A Truly Unique Location—set Within The Ancient Walls Of Diocletian’s Palace, A Unesco World Heritage Site Built In The Fourth Century Ad
This impressive palace was constructed by the Roman Emperor Diocletian as a retirement residence. The grocery store itself occupies the ground floor of Mala Papalićeva Palača, a noble residence added to the complex in the 13th century, merging modern life with a rich tapestry of history.
Though Diocletian’s Palace received UNESCO recognition in 1979, parts of the complex remained privately owned. This allowed the grocery store to open in 2014, much to the surprise of locals. Because of the private ownership, authorities were unable to prevent it.
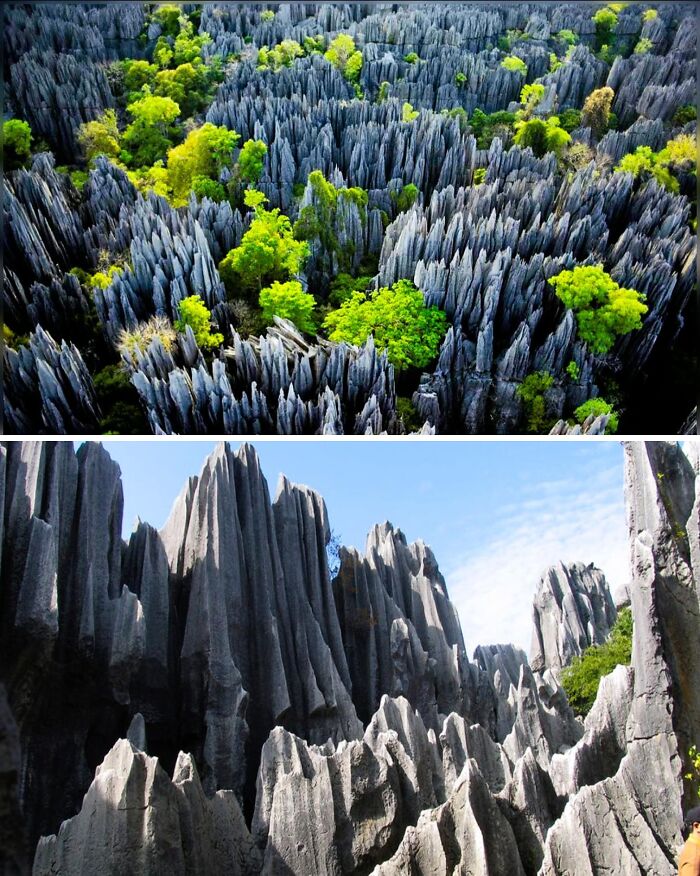
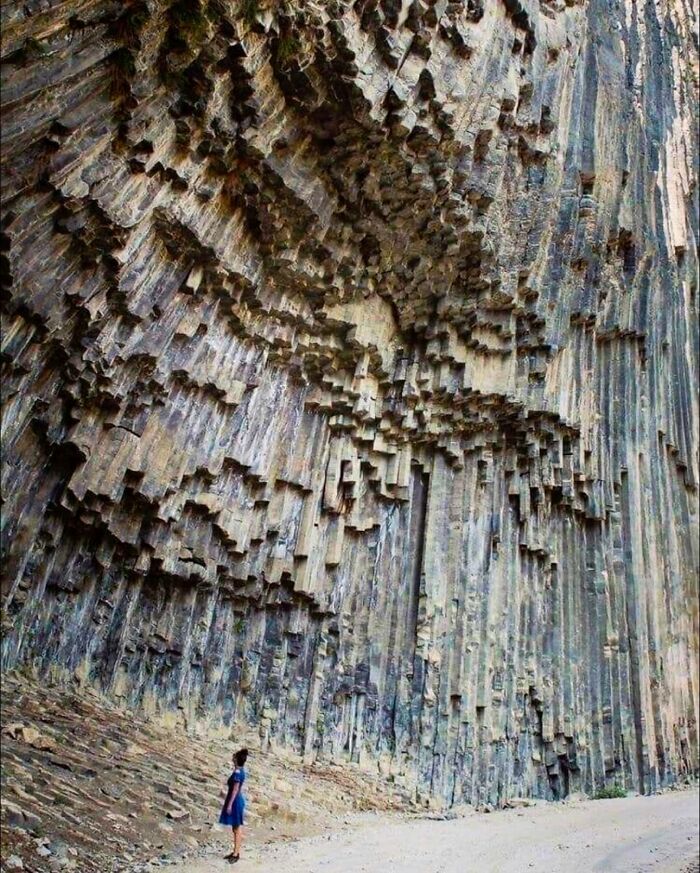
The Shilin Stone Forest In China’s Yunnan Province Is A Breathtaking Labyrinth Of Towering Limestone Pillars, Spread Over 180 Square Miles
Known as the “first natural wonder of the world,” this remarkable site is the result of 270 million years of natural forces—rain, wind, and seismic activity—that carved the landscape into its current form. The forest is part of the South China Karst, a vast region that emerged after the sea receded during the Permian period.
Walking through this otherworldly terrain feels like stepping into a fairy tale. The stone formations, resembling animals, people, and plants, evoke a sense of magical realism. In the Greater Stone Forest, you might encounter rock shapes that look like mythical creatures, while the Lesser Stone Forest offers tranquil meadows and bamboo groves.
The area is steeped in local legends. One of the most captivating tales is that of Ashima, a beautiful girl who was turned to stone after a tragic love story. According to local lore, Ashima’s rejection of a suitor led to her being kidnapped and later drowned in a flood. Today, a stone named after her is said to echo her name when called out, adding a haunting layer to this already mystical place.
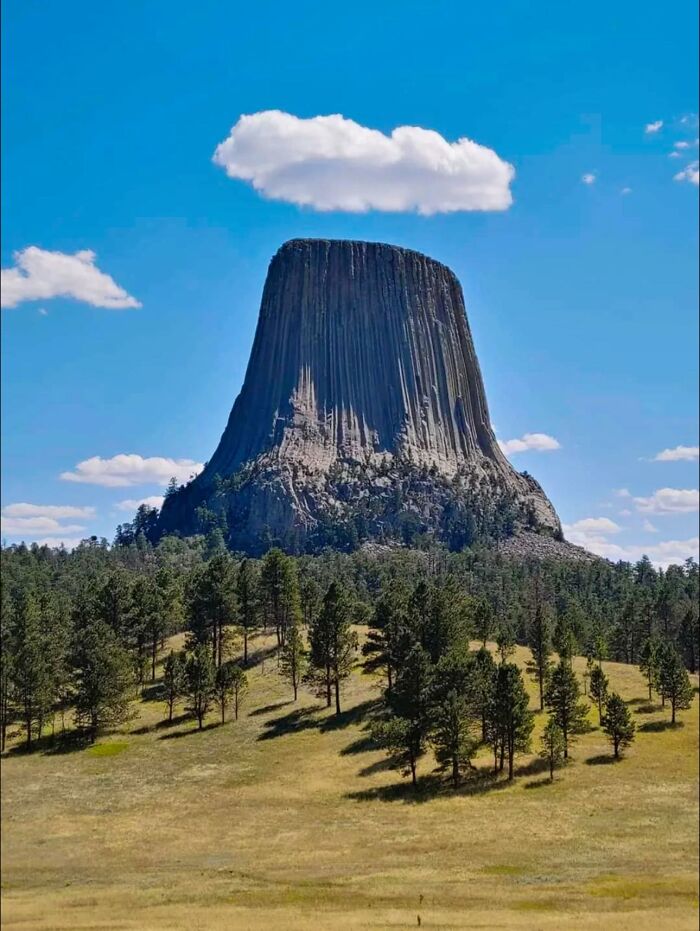
Devils Tower, Located In Northeastern Wyoming, Is A Dramatic Geological Formation That Rises Nearly 1,267 Feet Above The Surrounding Landscape
This massive monolithic butte, composed of igneous rock, features striking vertical grooves and a towering pillar-like appearance. Formed about 50 million years ago, Devils Tower is thought to be the eroded remnant of a volcanic intrusion, with its distinctive columns.
Beyond its geological intrigue, Devils Tower holds significant cultural importance. Native American legends from multiple tribes describe the tower as the result of a dramatic escape from giant bears. According to these stories, the ground rose to save a group of girls from the bears, leaving deep claw marks on the rock.
Today, the tower is regarded as a sacred site, where rituals and offerings are made by local tribes. While a popular climbing destination, a voluntary climbing ban in June respects these cultural traditions. Devils Tower continues to captivate with its blend of natural beauty and cultural richness, standing as a powerful symbol of both geological and spiritual significance
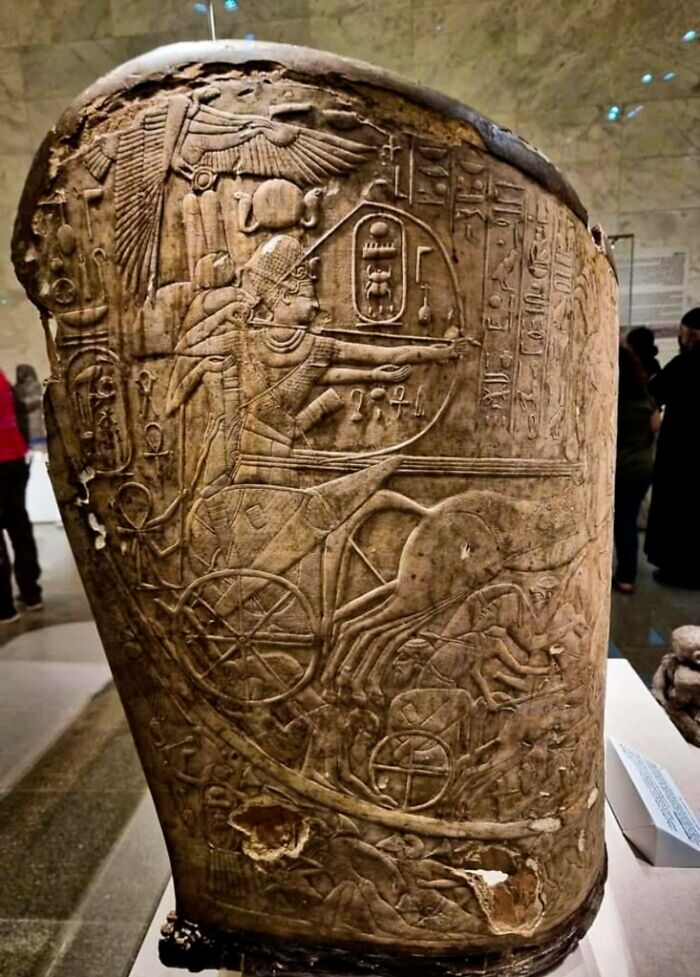
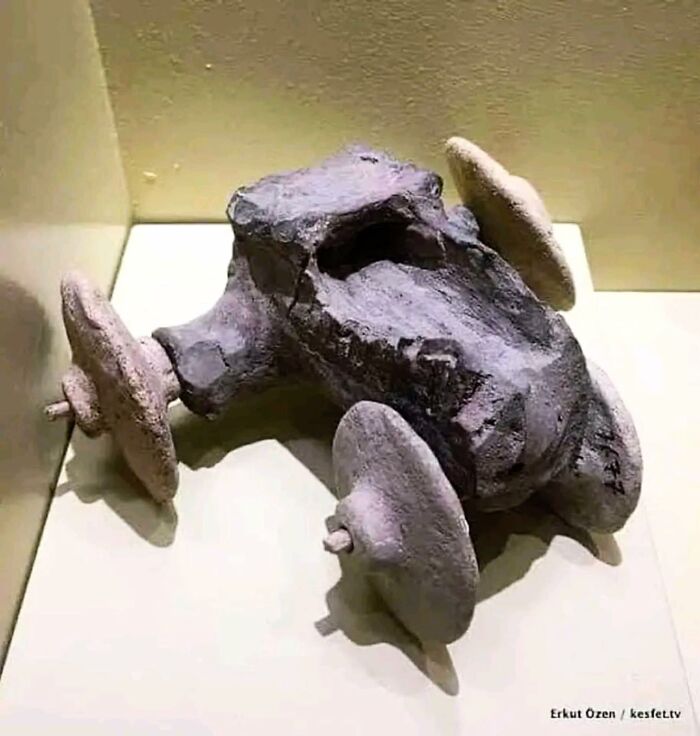
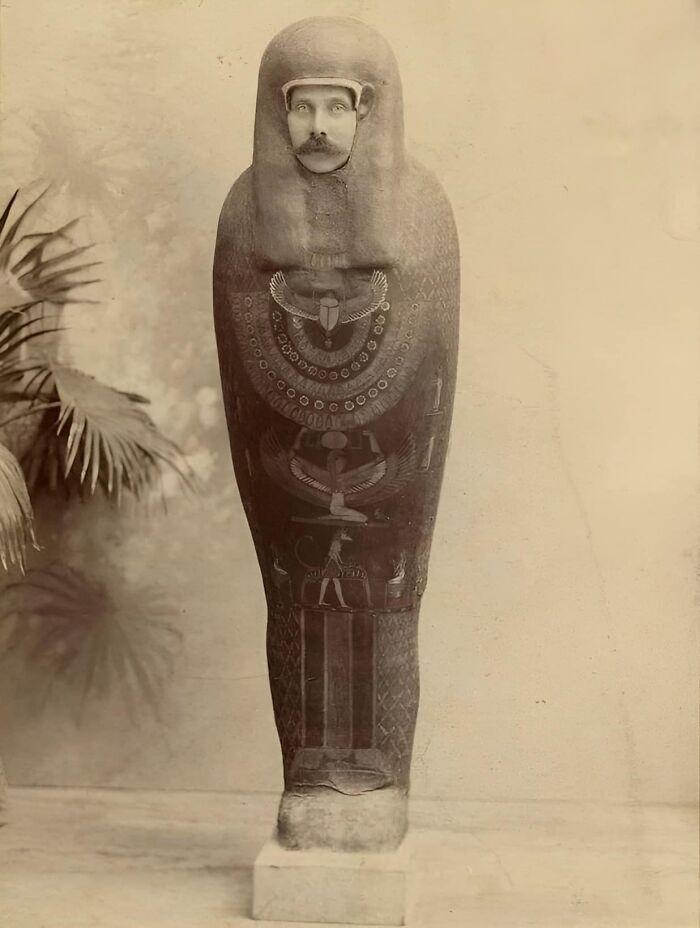
Nearly 3,400-Year-Old Chariot Body Of Thutmose IV
Found in his tomb, KV 43, this chariot is one of the few Egyptian examples to survive into the modern day. It was part of the king’s burial items, meant to serve him in the afterlife, and offers a rare glimpse into the past.
Made from lightweight wood, the chariot was designed for speed and maneuverability, essential for both battle and ceremony. It wasn’t just practical; it was also beautifully decorated, likely with gold leaf, leather, and intricate designs. These details highlighted the king’s power and status, fitting for a ruler who was both a warrior and a god-like figure.
The discovery of Thutmose IV's chariot gives us a valuable look at the engineering and artistry of the 18th Dynasty. Despite being buried for millennia, its preservation helps us understand the significance of chariots in ancient Egypt and showcases the skill of its craftsmen.
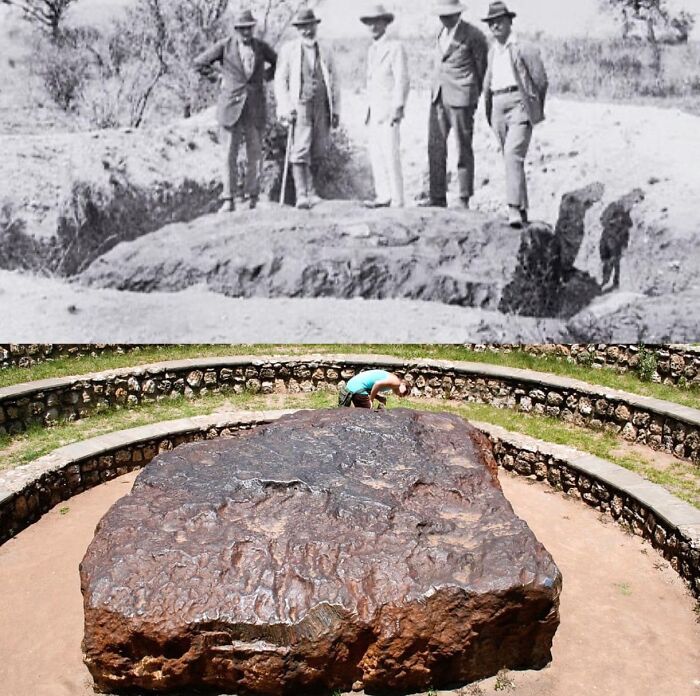
Discovered Accidentally By A Farmer In Namibia Africa, The Hoba Meteorite Remains A Mysterious Marvel
This mammoth slab of iron, weighing a staggering 60 tons, is Earth's largest natural chunk of iron. It's estimated to have impacted our planet some 80,000 years ago, and one of the most fascinating aspects of the meteorite is that it left no impact crater, despite its immense size.
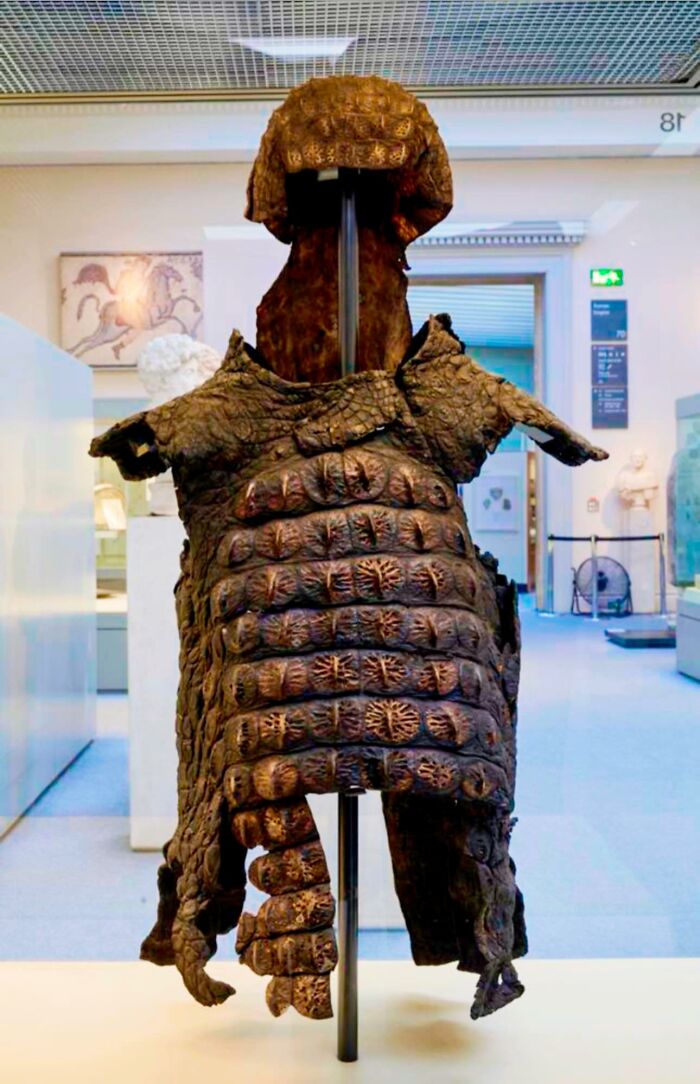
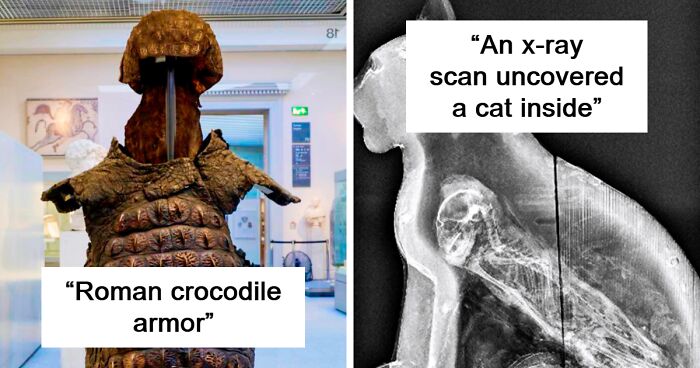
Roman Crocodile Armor, Dating Back To The 3 Century Ad, Was A Form Of Protective Gear Crafted From The Tough Hide Of Nile Crocodiles
The Romans likely adopted this type of armor during their conquests in Egypt and other regions where crocodiles were prevalent.
Crocodile armor was not as widely used as other types of Roman armor, and scholars believe that it might have been worn during processions or ceremonies, rather than in combat. As a result, crocodile armor was more of a rare and exotic choice rather than a standard issue for Roman soldiers.
I was really, really hoping that this was armour FOR crocodiles! 🙄
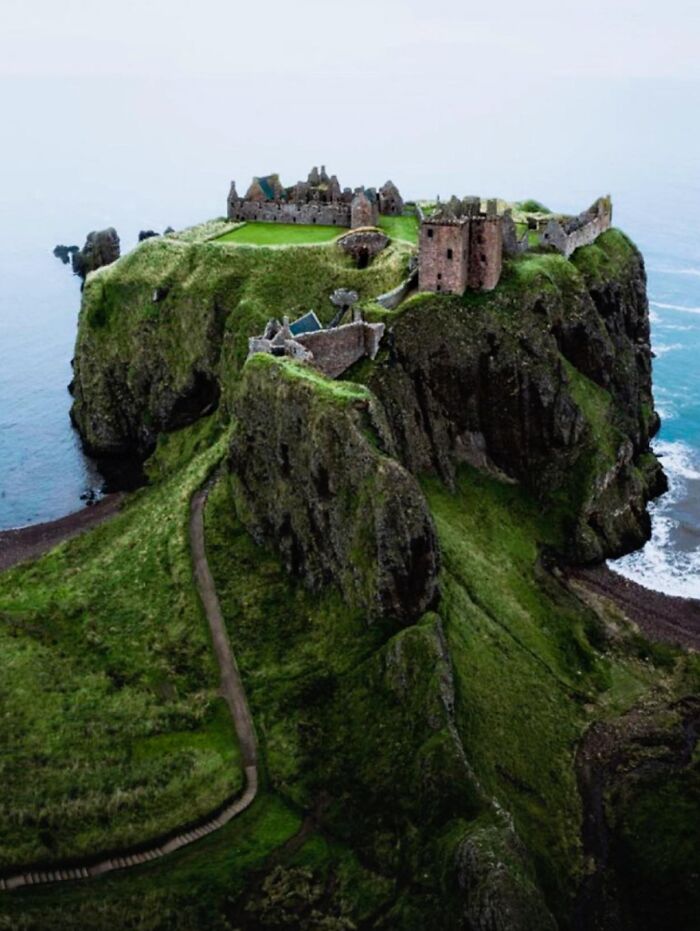
Dunnottar Castle, Located On A Rugged Headland On Scotland's Northeast Coast, Holds A Fascinating And Complex History
Although the castle as it stands today primarily dates from the 15th and 16th centuries, its story stretches back much further. Archaeological evidence suggests that the site has been fortified since at least the 7th century, but specific details about these early fortifications remain unknown.
Throughout the medieval period, Dunnottar Castle was a pivotal stronghold. It played a crucial role during the Wars of Scottish Independence, notably enduring a prolonged siege by English forces in 1296. Despite the overwhelming odds, the defenders managed to hold the castle for months, a testament to its formidable defenses.
One of the most intriguing chapters in Dunnottar Castle's history involves the Scottish Crown Jewels. In 1651, amidst the chaos of the English Civil War, the jewels were hidden in a secret vault within the castle to protect them from Oliver Cromwell’s forces. They remained concealed there until 1660, when they were recovered and later displayed in Edinburgh
The story above about the Scottish crown jewels ("The Honor's of Scotland") is incorrect. The real story is more interesting. When it became clear that the castle would fall to Cromwell's forces the Scots managed to sneak the items to a church, where they lay safe. Worth a read: https://www.historic-uk.com/HistoryUK/HistoryofScotland/The-Honours-of-Scotland/
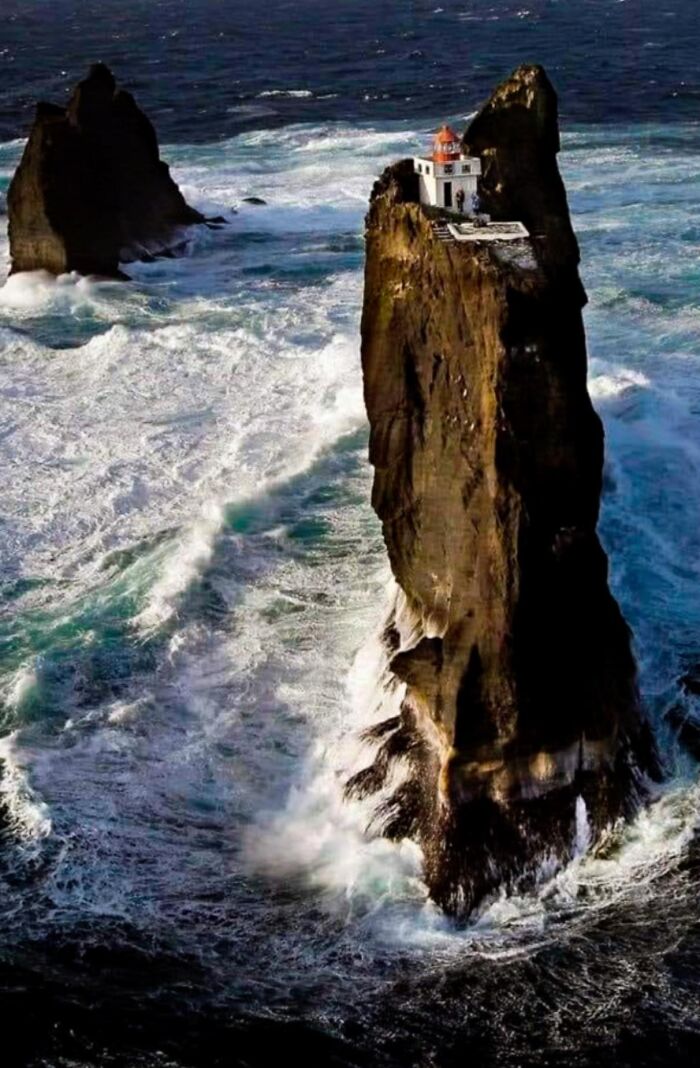
Þrídrangar Lighthouse, Built In 1939, Is One Of The Most Isolated And Remarkable Lighthouses In The World
Perched atop a jagged sea stack off Iceland’s coast, it’s surrounded by the relentless North Atlantic Ocean, making it accessible only by helicopter or a perilous climb. The name “Þrídrangar,” meaning “Three Rock Pillars,” reflects the lighthouse’s precarious position on the highest of these rugged formations.
Constructing the lighthouse was an extraordinary feat of human determination. Workers scaled the steep rock faces, facing great personal risk, to establish this vital beacon in one of the most remote and inhospitable locations imaginable. Despite its isolation, Þrídrangar has served as a crucial navigational aid, guiding seafarers through some of the most dangerous waters on the planet.
Its lonely position, far from any human settlement, adds to its mystique. Þrídrangar stands not just as a lighthouse but as a symbol of human resilience, defying nature’s extremes and enduring the test of time.
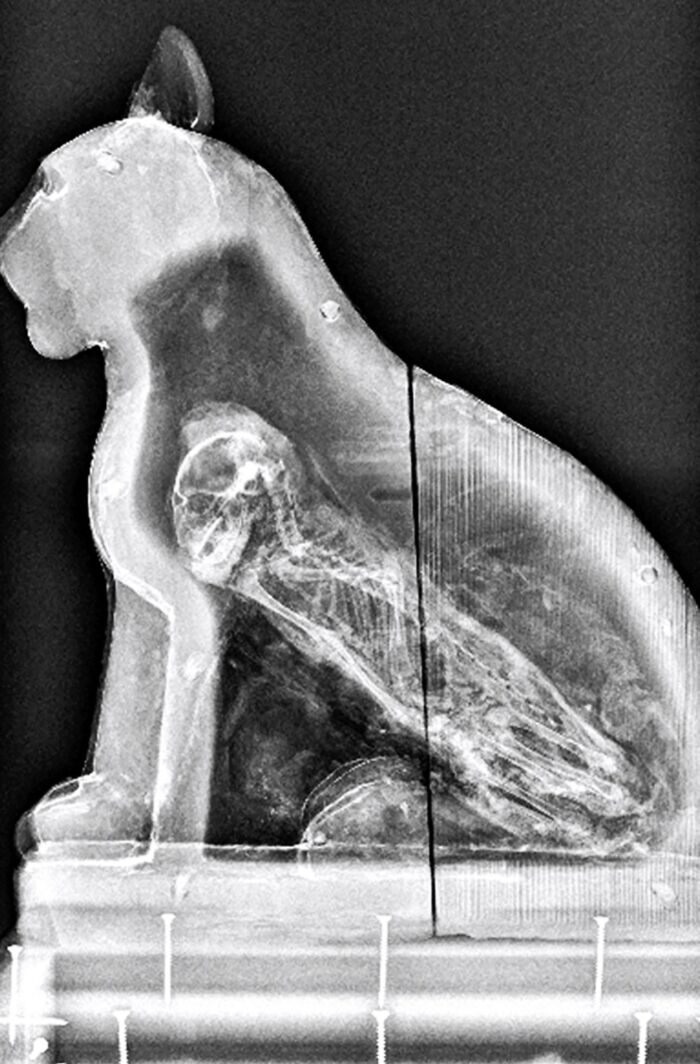
An X-Ray Scan Of A Sarcophagus From Saqqara, An Ancient Burial Ground South Of Modern-Day Cairo, Uncovered The Presence Of A Cat Inside
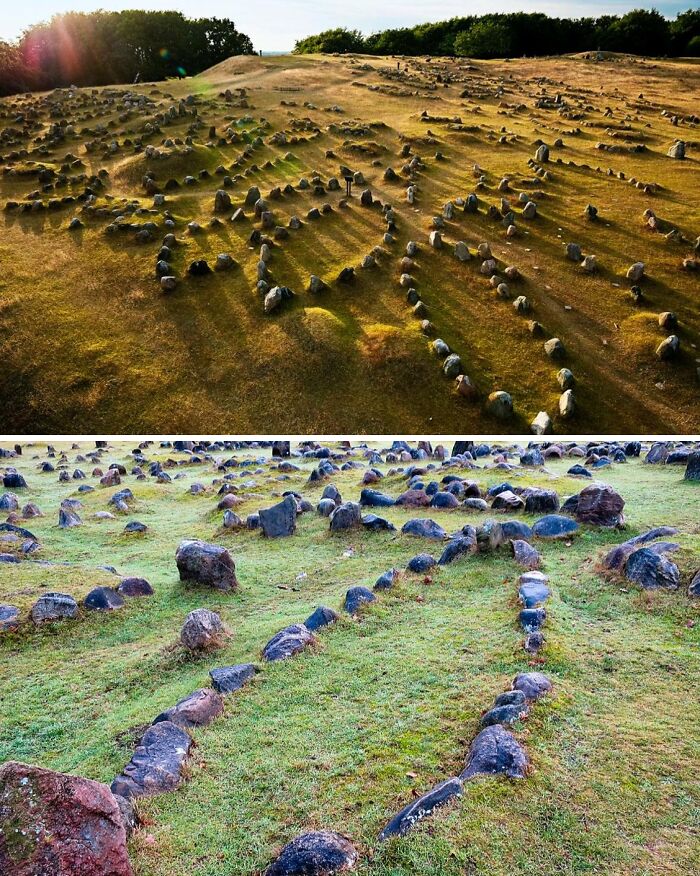
Lindholm Høje, Located Near Aalborg In Denmark, Is One Of Scandinavia’s Largest And Most Important Viking Burial Sites
This ancient site, used from the Germanic Iron Age through the Viking Age, contains over 700 graves and approximately 150 stone ship settings—stones arranged to outline the shape of ships, a symbolic gesture meant to honor the deceased and guide them to the afterlife. The site reveals a complex picture of Viking burial customs, featuring both cremation and inhumation practices that evolved over time. What makes Lindholm Høje particularly striking is its remarkable preservation; for centuries, it was buried under layers of drifting sand, protecting it from the ravages of time until modern excavations in the 20th century brought it to light. Among the graves, archaeologists have found a wealth of artifacts, including weapons, jewelry, and tools, offering valuable insights into Viking daily life, social structures, and beliefs. Lindholm Høje stands out not just for its scale but for the stories it tells about the Vikings—a society that was not only fearsome warriors but also skilled craftsmen, traders, and farmers. As you explore this site, the stone ship settings and burial mounds serve as a powerful reminder of the Viking era’s reach and its deep connection to both land and sea.
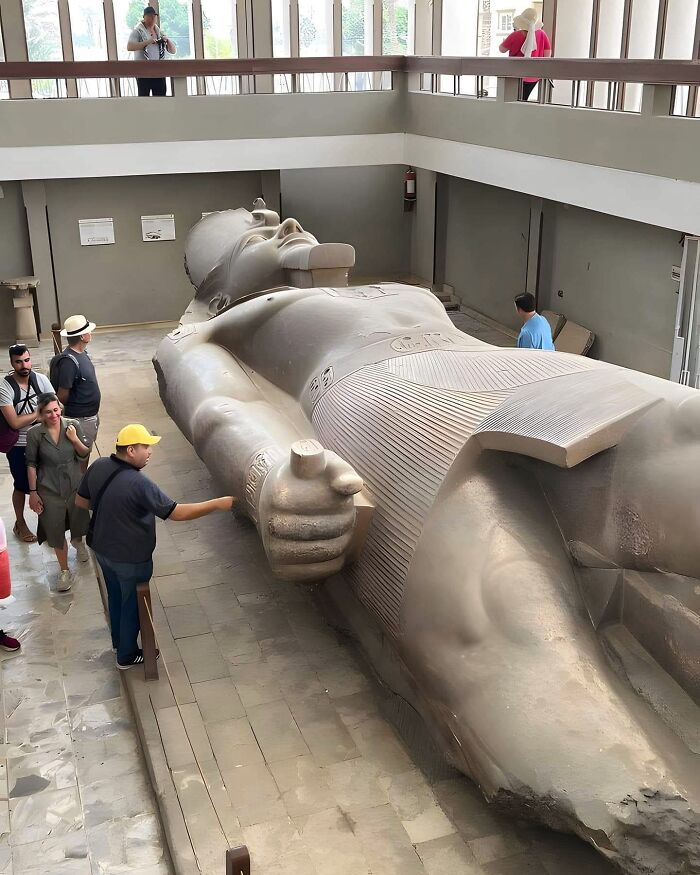
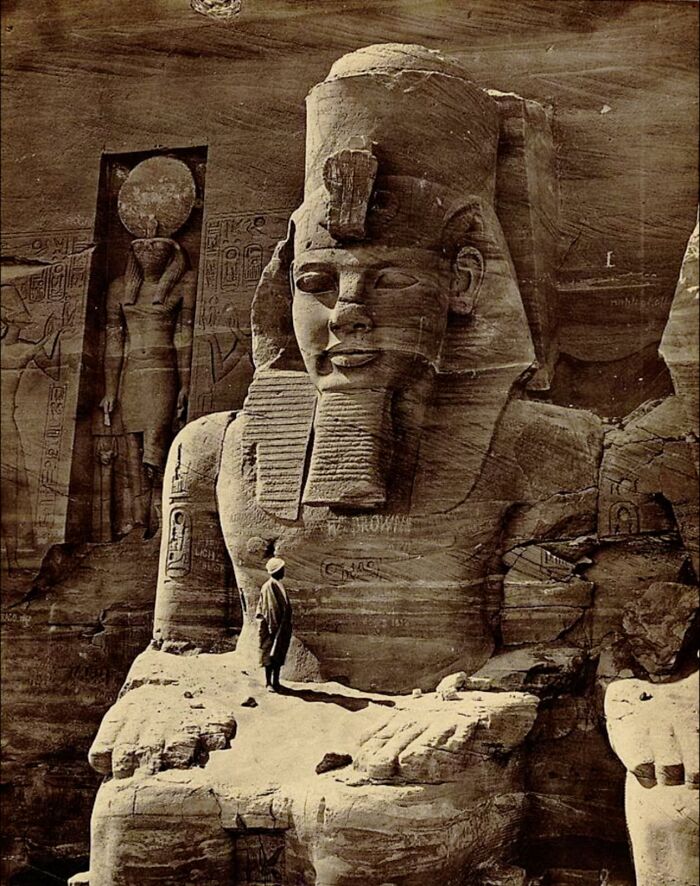
The Colossal Statue Of Ramesses II In Memphis, Egypt, Stands As An Impressive Relic Of Ancient Times
Originally carved from limestone, it once reached a towering height of over 10 meters, depicting the mighty pharaoh in a powerful stance.
Unearthed in 1820 near the ruins of the former capital, the statue reflects the grandeur of Ramesses II’s rule, a period marked by his prominence during the New Kingdom. Interestingly, during the 19th century, there were plans to transport the statue to London, but its sheer size made the task impossible, leaving it to remain in Egypt.
Though now lying horizontally due to centuries of damage, the statue’s detailed craftsmanship, from the pharaoh’s facial features to the hieroglyphic inscriptions, continues to captivate visitors, offering a window into the majesty of Egypt’s past.
Visitors trying to touch it? ... (soft) limestone ... subsequent wear. Those barriers aren't high enough or far enough away to stop peeps like the bloke in the yellow cap.
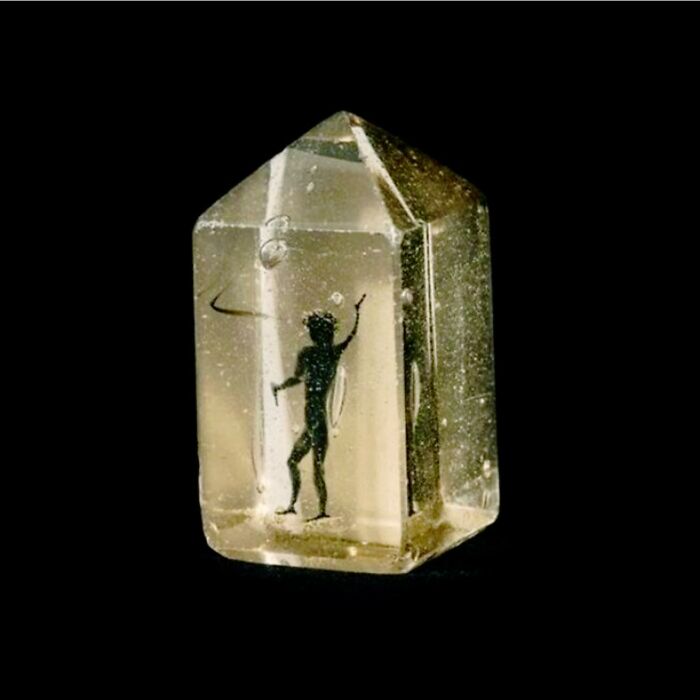
In The 18th Century, The Imperial Treasury Of Vienna Housed A Bizarre And Unsettling Artifact—a Tiny Figure Encased In A Prism Of Glass, Believed To Be A Demon
According to accounts, this "devil" had been trapped during an exorcism in Germany a century earlier. The figure, now part of the Kunsthistorisches Museum Collection in Vienna, was considered by some to be proof of supernatural forces at play.
At the time, religious beliefs and the fear of the occult were intertwined, and objects like this one became symbols of the battle between good and evil. Though now such claims are viewed with skepticism, this artifact remains a strange reminder of a time when people believed that demons could be physically captured and confined. The figure’s eerie preservation in glass adds an otherworldly quality to its mysterious past.
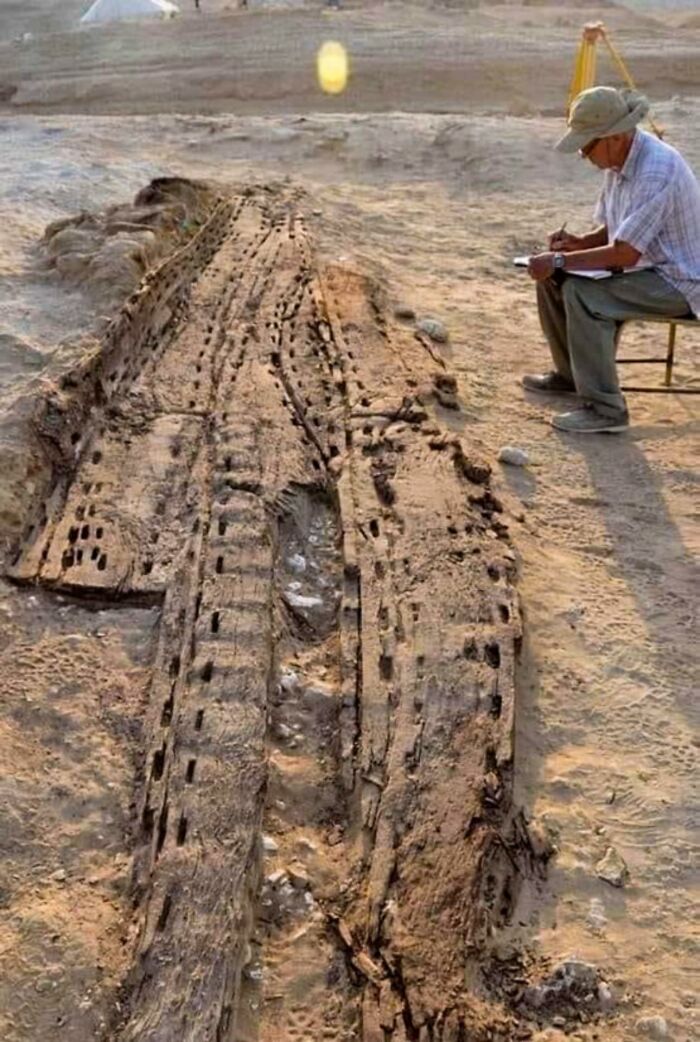
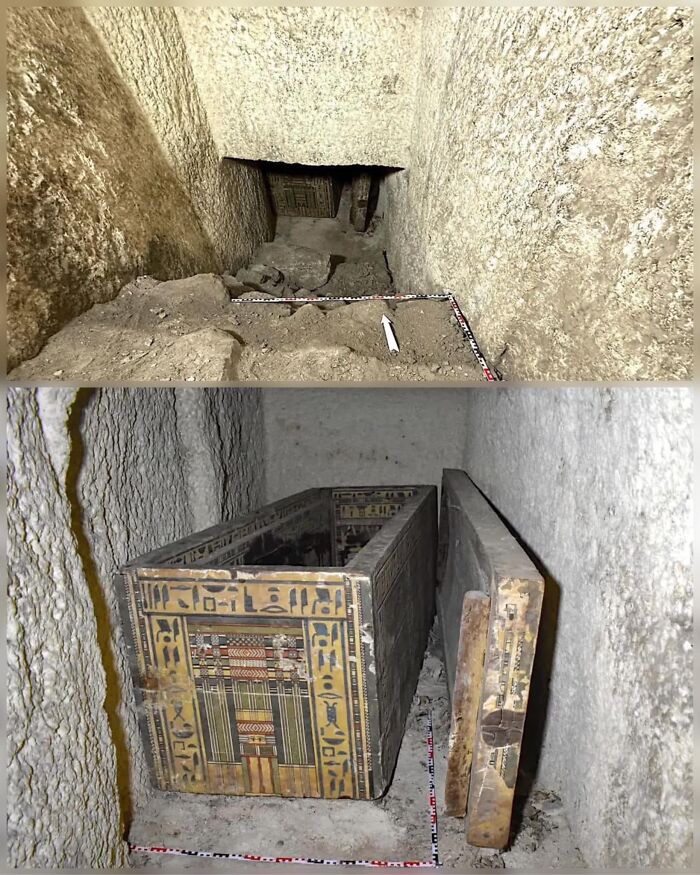
A 5,000-Year-Old Wooden Boat, Believed To Have Been Used By The Pharaohs Of Ancient Egypt, Was Unearthed Near The Saqqara Necropolis
This remarkable discovery sheds new light on the maritime traditions of Egypt’s early dynastic period. The vessel, remarkably well-preserved despite its age, is thought to have played a key role in the funerary practices of the time, potentially serving as a symbolic vehicle for the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife.
Crafted from local wood, the boat’s exceptional state allows archaeologists to closely examine the boat-building techniques of ancient Egyptians, revealing how these vessels were constructed and their cultural importance. This find not only enriches our understanding of early Egyptian history but also offers a rare glimpse into their spiritual beliefs and the significant role that boats played in pharaonic rituals.
This discovery stands as a testament to the ingenuity of ancient Egyptian craftsmanship and deepens our appreciation of their complex spiritual and cultural traditions.
The owner *swears* he's gonna get the hull patched next time he has a free weekend!
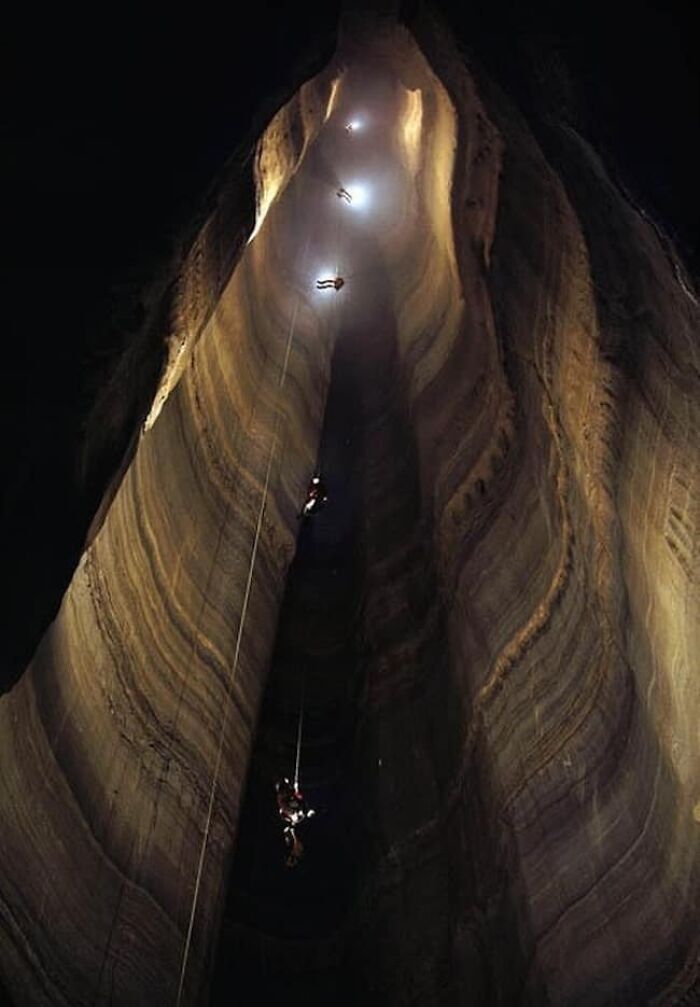
Voronya Cave, Also Known As Krubera Cave, Holds The Distinction Of Being The Deepest Known Cave On Earth
It is situated in the Arabika Massif of the Western Caucasus in Abkhazia, Georgia. The cave reaches an astounding depth of 2,197 meters (7,208 feet), making it a significant point of interest for speleologists and geologists.
The cave was first discovered in 1960, but its depth wasn't fully explored until the early 2000s, primarily through the efforts of Ukrainian cavers. These explorers were the first to reach the cave's maximum depth, which required navigating a complex network of narrow passages, vertical shafts, and underground chambers. The exploration of Voronya Cave demands not only advanced technical skills but also specialized equipment due to the extreme conditions within the cave.
The cave environment is particularly harsh, characterized by low temperatures, high humidity, and total darkness. These conditions make exploration difficult and limit the extent to which the cave has been mapped. Despite numerous expeditions, much of the cave's lower reaches remain unexplored.
Voronya Cave's significance lies not only in its record-breaking depth but also in the ongoing exploration challenges it presents. It continues to be a focal point for those studying the geological processes that shape the Earth's underground structures. The cave remains a symbol of the complexities and dangers inherent in exploring the world's most remote and inaccessible places.
As should be expected because this is BP, the photo is from Fantastic Pit in Ellison's Cave, in northwestern Georgia. The US state, not the country.
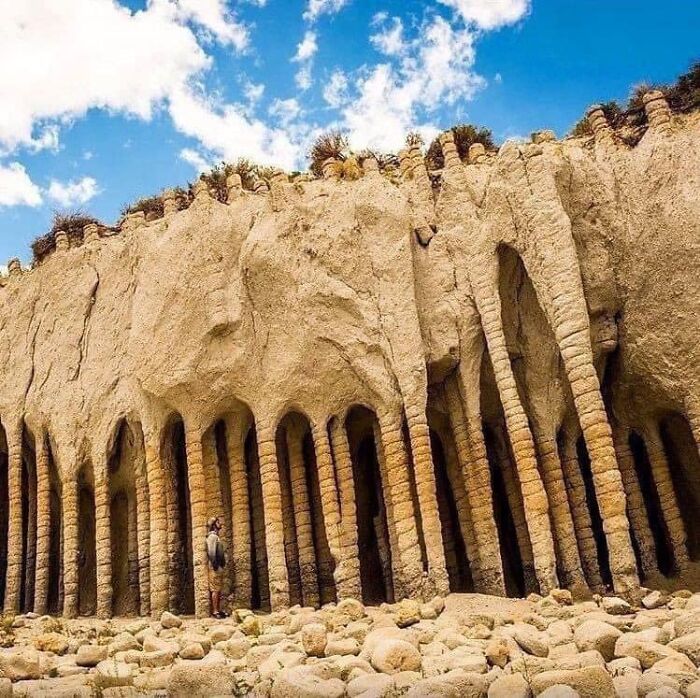
The Crowley Lake Columns
It's located in California’s Eastern Sierra region, are a stunning geological formation resulting from ancient volcanic activity.
These unique columns, which can tower up to 20 feet high, are primarily composed of ash and pumice from the Long Valley Caldera eruption approximately 760,000 years ago.
The columns are thought to have formed through a combination of rapid cooling and subsequent erosion, rather than solely from molten lava cooling and contracting. They offer a captivating glimpse into Earth’s geological history and the powerful natural forces at work
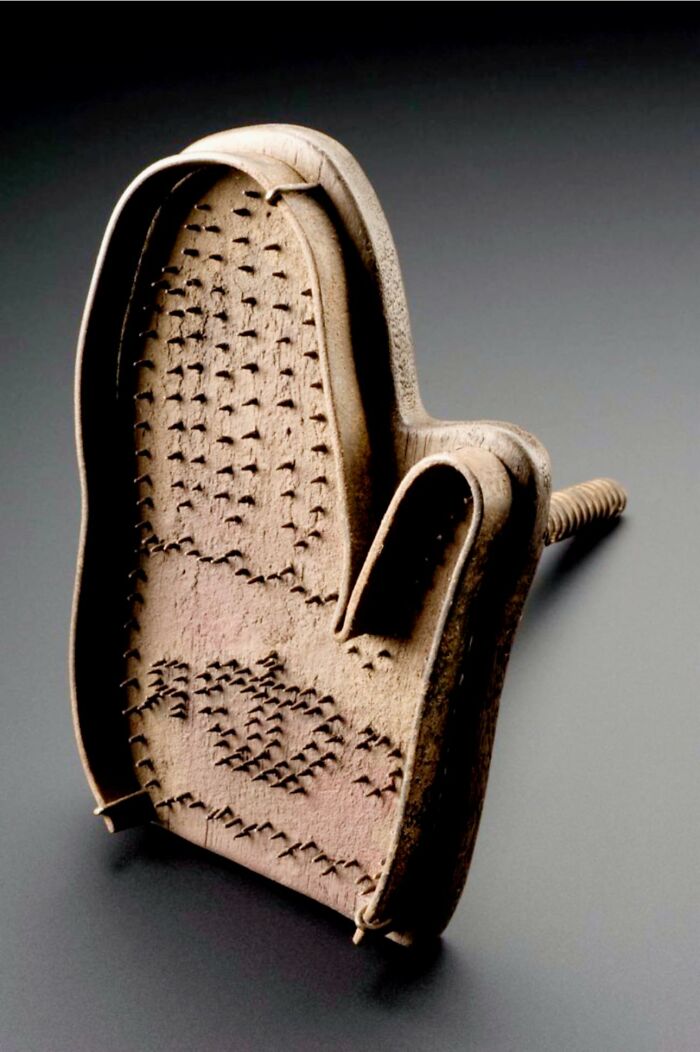
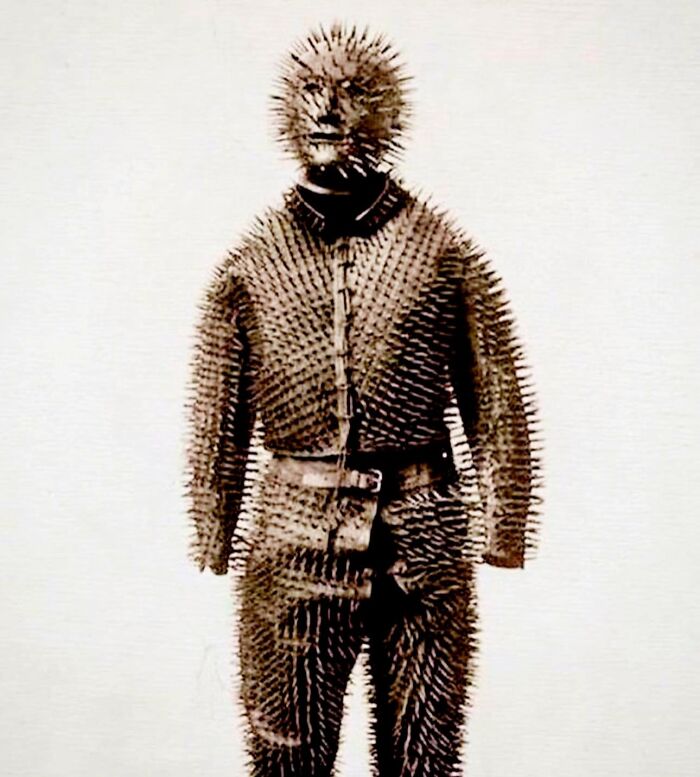
The Hand Brand, Used By The British Army During The English Civil War (1641-1651), Served To Mark Deserters And Criminals
I love these posts, all the pictures were fascinating in their own way.
I love these posts, all the pictures were fascinating in their own way.

 Dark Mode
Dark Mode 

 No fees, cancel anytime
No fees, cancel anytime