
Google Finds A Way To Transform Low-Quality Photos Into High-Resolution Images And The Results Are Impressive
Some people are afraid that AI will become so intelligent that it will outsmart humans and that in the future, computers will rule the world. Others don’t think about that at all and are trying to even further improve the technology we have.
You shouldn’t fear those improvements as they don’t look anything like in those apocalyptic movies about robots. Actually, one of the most recent breakthroughs that has been achieved by Google is in image enhancement technology. The way low-resolution photos are upscaled will never be the same and it’s much much better.
More info: Google AI Blog
Google announced that they had a breakthrough in image enhancement and that their new methods are better than any previous ones
Image credits: Google AI
Google has a separate branch that is dedicated to artificial intelligence and is called Google AI. This branch researches and develops AI tools and they write a blog to announce their accomplishments.
They have made a post titled “High Fidelity Image Generation Using Diffusion Models” in which they let us know that they majorly improved the photo enhancement game. And they say that this new technology will be useful in lots of different fields, ranging from simple ones such as just making old grainy family photos look better to improving medical imaging systems.
Image credits: Google AI
You know when in movies or TV series, they are able to improve the quality of a pixelated face that was reflected in a window caught by a security camera? That may be possible with the new super-resolution diffusion models.
Diffusion models are seen as superior to those deep generative models such as GANs, VAEs, and autoregressive models because they have several downsides. However, it is explained that diffusion models “work by corrupting the training data by progressively adding Gaussian noise, slowly wiping out details in the data until it becomes pure noise, and then training a neural network to reverse this corruption process. Running this reversed corruption process synthesizes data from pure noise by gradually denoising it until a clean sample is produced.”
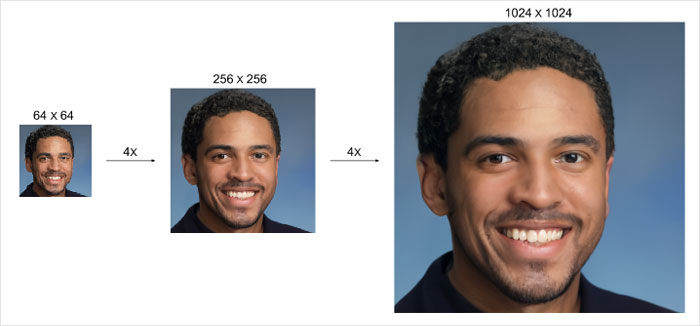
One of them is SR3, which improves a low-resolution image by rebuilding it from pure noise
Image credits: Google AI
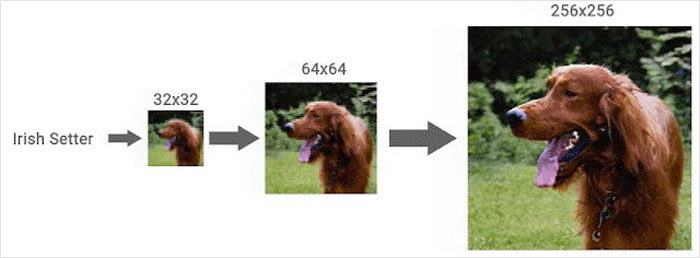
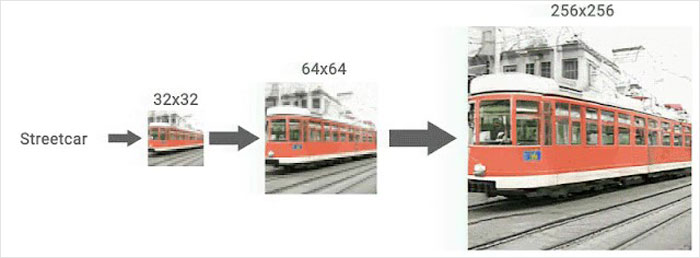
One of the models that is presented is called SR3, or Super-Resolution via Repeated Refinement. In the blog it is explained as a “model that takes as input a low-resolution image, and builds a corresponding high resolution image from pure noise.”
This model puts more and more noise on the image until it is just pure noise. Then it reverses the process. It starts to remove the noise which was preventing the photo from looking good and a low-resolution photo seems like it was taken as a high-resolution image.
Image credits: Google AI
The other one is CDM and it uses SR3 in class-conditional image generation
Image credits: Google AI
The technology is so good that people are tricked into thinking that the enhanced photos are the original ones. There was an experiment conducted in which the subjects were asked to guess which one of two images was taken with a camera, i.e. which one looked better quality and more natural, realistic.
Turns out, people had a hard time distinguishing them. The confusion rate was nearly 50 percent while experiments with previous image enhancement technology showed a confusion rating just below 34 percent.
Image credits: Google AI
Once the success of the SR3 model was seen, scientists thought they could implement it in class-conditional image generation. Conditional image generation is the task of generating new images from a dataset conditional on their class. (https://paperswithcode.com/task/conditional-image-generation)
They called it CDM: Class-Conditional ImageNet Generation. They “built CDM as a cascade of multiple diffusion models. This cascade approach involves chaining together multiple generative models over several spatial resolutions: one diffusion model that generates data at a low resolution, followed by a sequence of SR3 super-resolution diffusion models that gradually increase the resolution of the generated image to the highest resolution.”
Experiments show that subjects are often confused over which images had been enhanced with the tool and which ones were taken by a camera
Image credits: Google AI
Image credits: Google AI
The comparisons do look quite amazing and no image augmentation tools have done so well previously. It is unbelievable how a pixelated image that even a human eye can hardly recognize as a face is transformed into a normal picture as if it was taken as a high-resolution photo.
Have you heard about this Google achievement? What do you think about it and do you see a use for it? Maybe you think that they should put their resources in other places? Let us know your reactions in the comments!
These are some of the reactions people had to the news
As most of these comments said, the first thing that went through my head when I was reading this, is that the "Zoom and enhance" movie cliché won't be a cliché anymore but a reality!!!
As most of these comments said, the first thing that went through my head when I was reading this, is that the "Zoom and enhance" movie cliché won't be a cliché anymore but a reality!!!

 Dark Mode
Dark Mode 

 No fees, cancel anytime
No fees, cancel anytime 








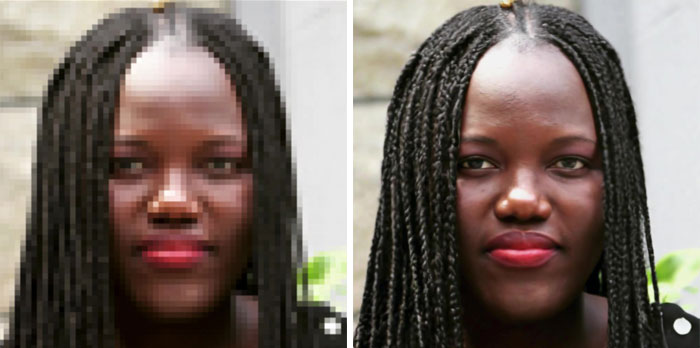
















































100
41